Abstract
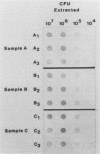
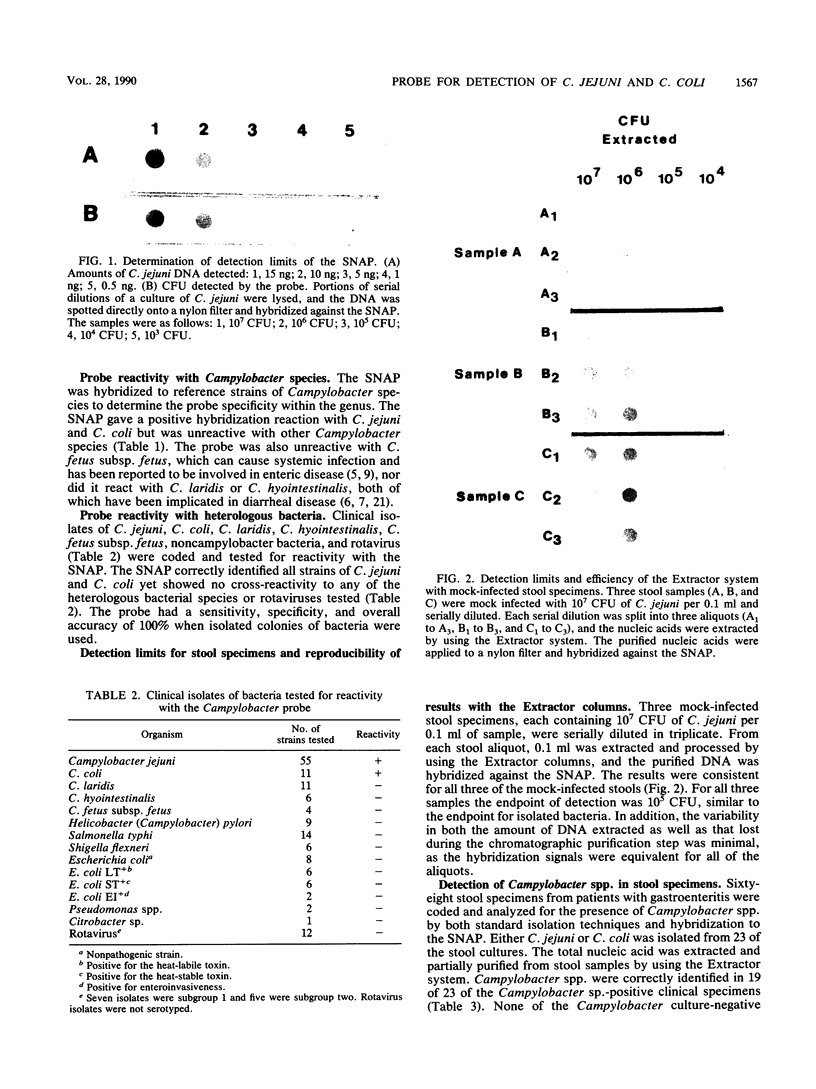
A commercially available synthetic nucleic acid probe (SNAP) conjugated to alkaline phosphatase was compared with standard culture techniques for detecting Campylobacter species. The SNAP was able to detect either 5 ng of C. jejuni DNA or 10(5) CFU of bacteria. The SNAP could also detect DNA extracted from 10(5) CFU in mock-infected stool samples. The SNAP detected C. jejuni and C. coli but showed no reactivity with C. laridis, C. fetus subsp. fetus, C. fetus subsp. venerealis, C. fennelliae, "C. upsaliensis," C. cinaedii, C. fecalis, C. hyointestinalis, C. mucosalis, or Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori. The SNAP also showed no cross-reactivity with other enteric pathogens. When applied to pure cultures, the SNAP detected 55 clinical isolates of C. jejuni and 11 clinical isolates of C. coli, with an accuracy of 100%. When applied directly to clinical specimens, the SNAP detected Campylobacter spp. in 19 of 23 culture-positive stool specimens (sensitivity, 82.6%; specificity, 100%). Pure cultures of the Campylobacter strains isolated from the four probe-negative, culture-positive stool specimens gave positive reactions with the SNAP. While the SNAP had excellent sensitivity and specificity for isolated bacterial colony isolates, the main limitation to the Campylobacter probe detection kit may be the sensitivity limit on direct detection of Campylobacter organisms in stools.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Campylobacter enteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1444–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boileau C. R., d'Hauteville H. M., Sansonetti P. J. DNA hybridization technique to detect Shigella species and enteroinvasive escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):959–961. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.959-961.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus P., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. The use of gene-specific DNA probes for the identification of enteric pathogens. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1983;7(3-4):139–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll P., Phillips K., Tenover F. C. Evaluation of a rapid method of extracting DNA from stool samples for use in hybridization assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2245–2248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2245-2248.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin H. R., McIntyre L. Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus in homosexual males. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):999–1000. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.999-1000.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Patton C. M., Griffin P. M., Barrett T. J., Schmid G. P., Baker C. N., Lambert M. A., Brenner D. J. Campylobacter hyointestinalis associated with human gastrointestinal disease in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):685–691. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.685-691.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennell C. L., Rompalo A. M., Totten P. A., Bruch K. L., Flores B. M., Stamm W. E. Isolation of "Campylobacter hyointestinalis" from a human. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):146–148. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.146-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitts R., Diamond M., Hamilton C., Neri M. DNA-DNA hybridization assay for detection of Salmonella spp. in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1146-1151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. M., Greenwood J. R. Probable Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1278–1279. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1278-1279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Penner J. L., Fleming P. C., Williams A., Hennessy J. N. The serotype and biotype distribution of clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli over a three-year period. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):243–246. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M., Khalik D. A., Sethi S. K. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using alkaline phosphatase-labeled synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):167–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01963071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M., Sethi S. K. Detection of human rotavirus by using an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated synthetic DNA probe in comparison with enzyme-linked immunoassay and polyacrylamide gel analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):53–57. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.53-57.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis - the first five years. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):175–184. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]