Abstract
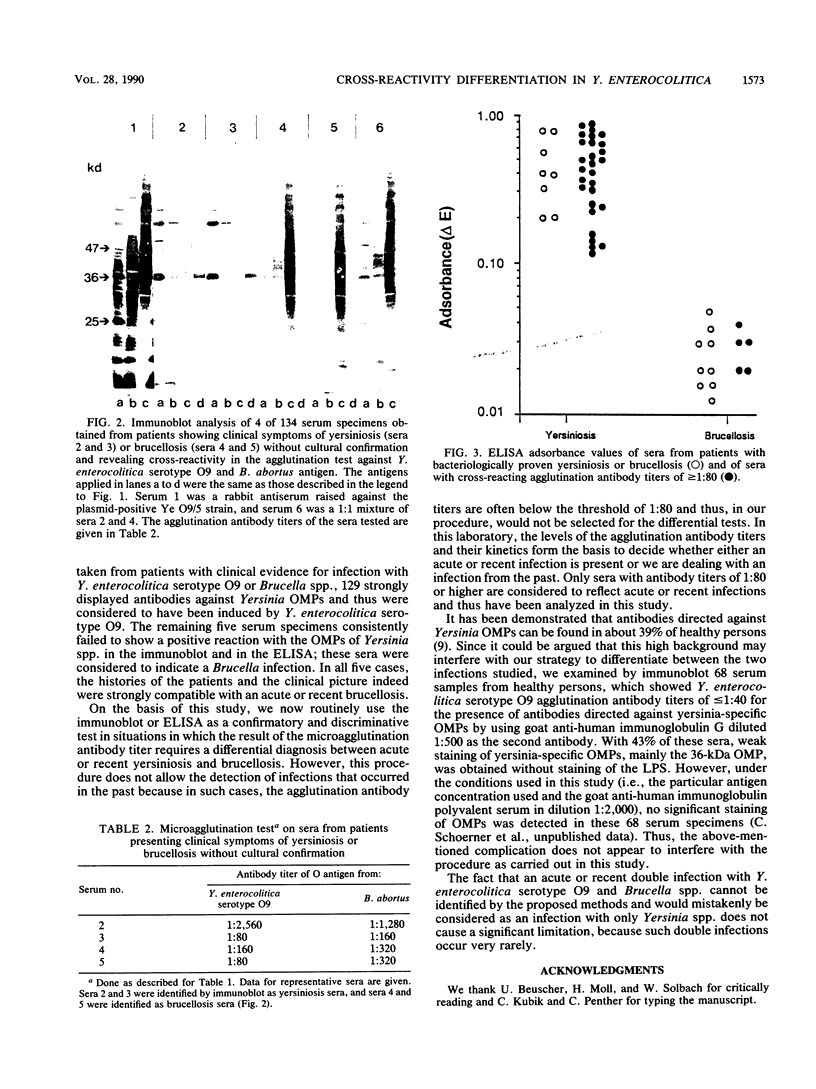
Serum samples from 134 patients showing by the microagglutination test serological cross-reactivity between Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O9 and Brucella spp. were analyzed by immunoblot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques for the presence of antibodies directed against plasmid-encoded, yersinia-associated outer membrane proteins (OMPs). Since these OMPs are exclusively expressed in pathogenic strains of Yersinia spp., this characteristic was chosen for serological differentiation of infections caused by these bacteria. The presence of antibodies against plasmid-encoded OMPs of pathogenic Yersinia spp. in patient sera appeared to be a suitable means to identify acute or recent infection with Y. enterocolitica serotype O9, whereas the failure to detect such antibodies indicated an acute or recent infection with Brucella spp.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahvonen P., Jansson E., Aho K. Marked cross-agglutination between Brucellae and a subtype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(2):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Gidney M. A., Perry M. B., Duncan J. R., Cherwonogrodzky J. W. Serological confirmation of Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 O-antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):389–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.389-393.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B. Structure of the O-chain of the phenol-phase soluble cellular lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 15;139(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J., Stuart F. A., Brewer R. A. Observations on serological cross-reactions between smooth Brucella species and organisms of other genera. Dev Biol Stand. 1984;56:341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M. K., Toivanen A. Measurement of immunoglobulin M, immunoglobulin G, and immunoglobulin A antibodies against Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: comparison of lipopolysaccharide and whole bacterium as antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.6-14.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Eggers C., Schröder J. Serological diagnosis of yersiniosis by immunoblot technique using virulence-associated antigen of enteropathogenic Yersiniae. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:285–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Gross U., Schmidt N., Laufs R. Immunochemical analysis of plasmid-encoded proteins released by enteropathogenic Yersinia sp. grown in calcium-deficient media. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):561–567. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.561-567.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Keller C., Morawa R., Schmidt N., Siemens H. J., Laufs R. Plasmids of human strains of Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular relatedness and possible importance for pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):107–115. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Ahvonen P., Thal E. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Agglutination and complement fixation. Acta Vet Scand. 1971;12(1):86–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A., Carlsson H. E. Differentiation of antibodies against Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Acta Vet Scand. 1972;13(4):472–483. doi: 10.1186/BF03547153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Sändulache R., Pop A., Cerbu A. Serological cross-reactions between Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica IX. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(4):429–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Ricciardi I. D., Tizard I. R. Indirect hemagglutination employing enterobacterial common antigen and Yersinia somatic antigen: a technique to differentiate brucellosis from infections involving cross-reacting Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):149–152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.149-152.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Martinez R. J. Role of a plasmid in the pathogenicity of Yersinia species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:29–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhlberg T. H., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Immunoblot analysis of human IgM, IgG and IgA responses to plasmid-encoded antigens of Yersinia enterocolitica serovar O3. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Sep;24(2):157–163. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-2-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weninger J., Schoerner C., Wartenberg K., Röllinghoff M. Detection of cross-reacting epitopes on plasmid-encoded outer membrane proteins of enteropathogenic Yersinia by monoclonal antibodies. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1989;178(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00202291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weninger J., Wartenberg K., Röllinghoff M. Immunological characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 and O:3 LPS antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;269(3):298–313. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]