Abstract
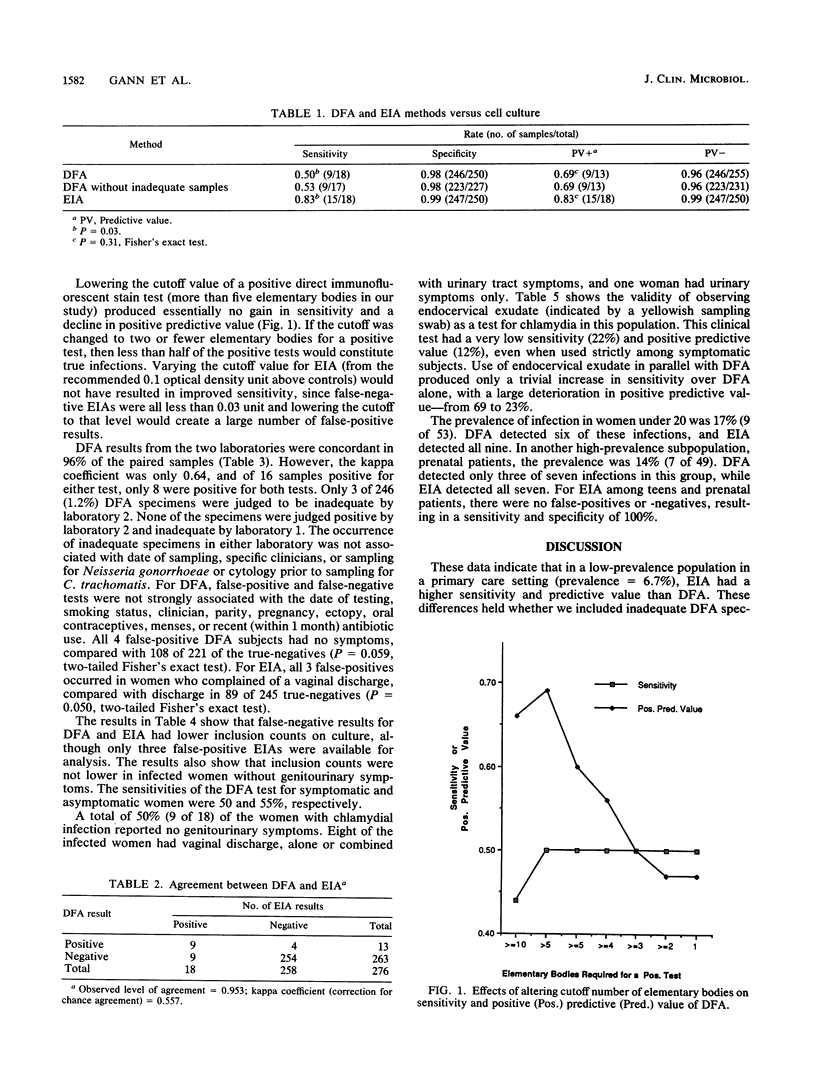
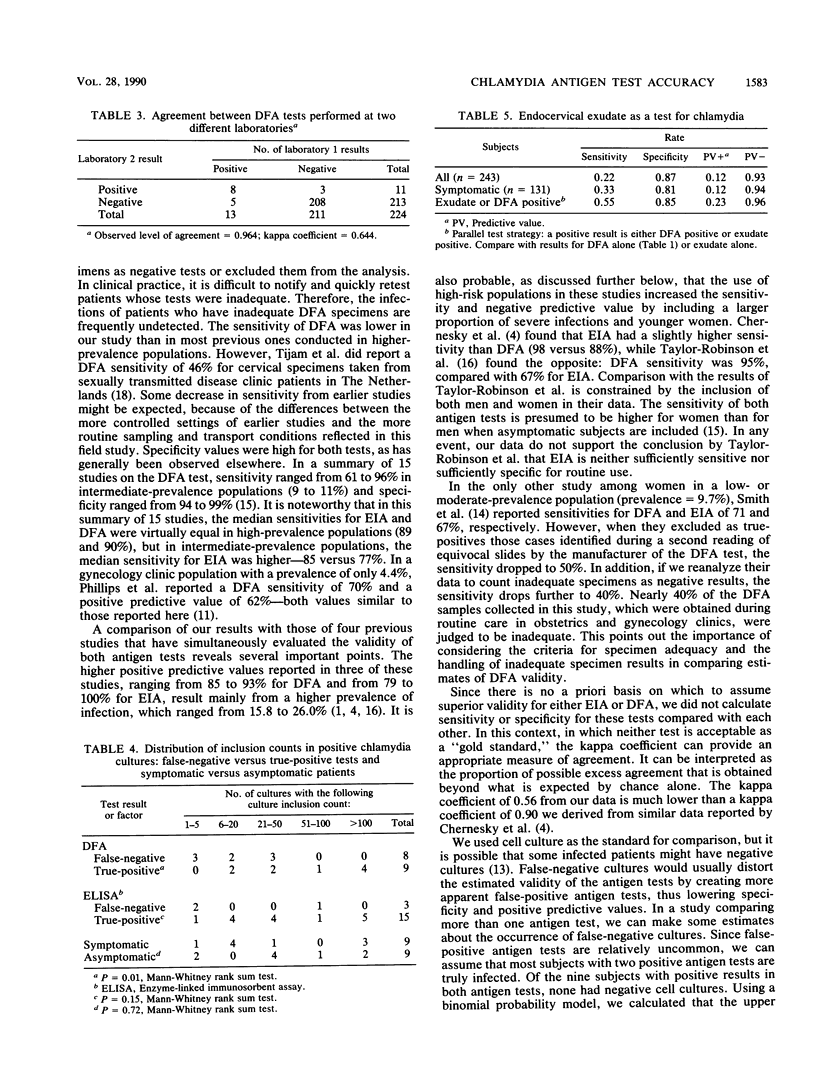
We compared a direct fluorescent-antibody stain (DFA) and an enzyme immunoassay (EIA) with a standard cell culture technique for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis infection in women in an urban family practice setting. We also evaluated a DFA sample in a commercial laboratory to determine the interlaboratory reliability of this test. There were 268 women in the study; the EIA provided a higher sensitivity (83 versus 50%) and a higher positive predictive value (83 versus 69%) than the DFA test and comparably high specificity (99 versus 98%). Concordance between the two laboratories on the DFA test was not high when data were adjusted for chance agreement (kappa coefficient = 0.64). DFA validity was optimal with an elementary body cutoff of greater than 5, while EIA validity was optimal at the recommended cutoff of 0.1 optical density unit. None of 11 women with negative cultures after treatment had false-positive antigen tests. False-negative results with both tests were associated with low culture inclusion counts but were not strongly associated with the presence or absence of symptoms, menses, pregnancy, or recent antibiotic use. False-positive results with EIA were seen only for three women who had a chief complaint of vaginal discharge. Although the positive predictive value of DFA could be increased in high-prevalence subpopulations, EIA was still more valid in two such groups: teenagers and prenatal patients. These results indicate that EIA might be preferable for low- or moderate-prevalence populations in primary care settings and that a falloff in DFA sensitivity could be explained by lower infection burdens in low-prevalence groups.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baselski V. S., McNeeley S. G., Ryan G., Robison M. A comparison of nonculture-dependent methods for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis infections in pregnant women. Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Jul;70(1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Paavonen J., Stevens C. E., Kiviat N., Kuo C. C., Critchlow C. W., Holmes K. K. Mucopurulent cervicitis--the ignored counterpart in women of urethritis in men. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 5;311(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407053110101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernesky M. A., Mahony J. B., Castriciano S., Mores M., Stewart I. O., Landis S. J., Seidelman W., Sargeant E. J., Leman C. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis antigens by enzyme immunoassay and immunofluorescence in genital specimens from symptomatic and asymptomatic men and women. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):141–148. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsfield H. H., Jasman L. L., Roberts P. L., Hanson V. W., Kothenbeutel R. L., Stamm W. E. Criteria for selective screening for Chlamydia trachomatis infection in women attending family planning clinics. JAMA. 1986 Apr 4;255(13):1730–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson D., Karayiannis P., Byng R. E., Rees E., Tait I. A., Davies J. A. Quantitative aspects of chlamydial infection of the cervix. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Jun;56(3):156–162. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.3.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettleman M. D., Jones R. B. Cost-effectiveness of screening women at moderate risk for genital infections caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. JAMA. 1988 Jul 8;260(2):207–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. S., Aronson M. D., Taylor W. C., Safran C. Should tests for Chlamydia trachomatis cervical infection be done during routine gynecologic visits? An analysis of the costs of alternative strategies. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Aug;107(2):188–194. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. S., Hanff P. A., Kauffman R. S., Aronson M. D. Use of a direct fluorescent antibody test for detecting Chlamydia trachomatis cervical infection in women seeking routine gynecologic care. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):575–581. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Warfield P., Kappus E., Barbacci M., Spence M. Screening for Chlamydia trachomatis infection in an inner-city population: a comparison of diagnostic methods. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):419–423. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Rogers R. E., Katz B. P., Brickler J. F., Lineback P. L., Van der Pol B., Jones R. B. Diagnosis of chlamydial infection in women attending antenatal and gynecologic clinics. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):868–872. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.868-872.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E. Diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis genitourinary infections. Ann Intern Med. 1988 May;108(5):710–717. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-5-710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Thomas B. J., Osborn M. F. Evaluation of enzyme immunoassay (Chlamydiazyme) for detecting Chlamydia trachomatis in genital tract specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Feb;40(2):194–199. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. D., Walter S. D. A reappraisal of the kappa coefficient. J Clin Epidemiol. 1988;41(10):949–958. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(88)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjiam K. H., van Eijk R. V., van Heijst B. Y., Tideman G. J., van Joost T., Stolz E., Michel M. F. Evaluation of the direct fluorescent antibody test for diagnosis of chlamydial infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;4(6):548–552. doi: 10.1007/BF02013392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg A. I., Washington A. E., Halldorson S. A cost-based decision analysis for Chlamydia screening in California family planning clinics. Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Jan;71(1):101–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland T. L., Noller K. L., Smith T. F., Ory S. J. Comparison of Dacron-tipped applicator and cytobrush for detection of chlamydial infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2437–2438. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2437-2438.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder B. L., Stamm W. E., Koester C. M., Alexander E. R. Microtest procedure for isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1036-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



