Abstract
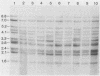
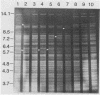
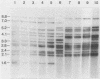
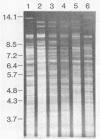
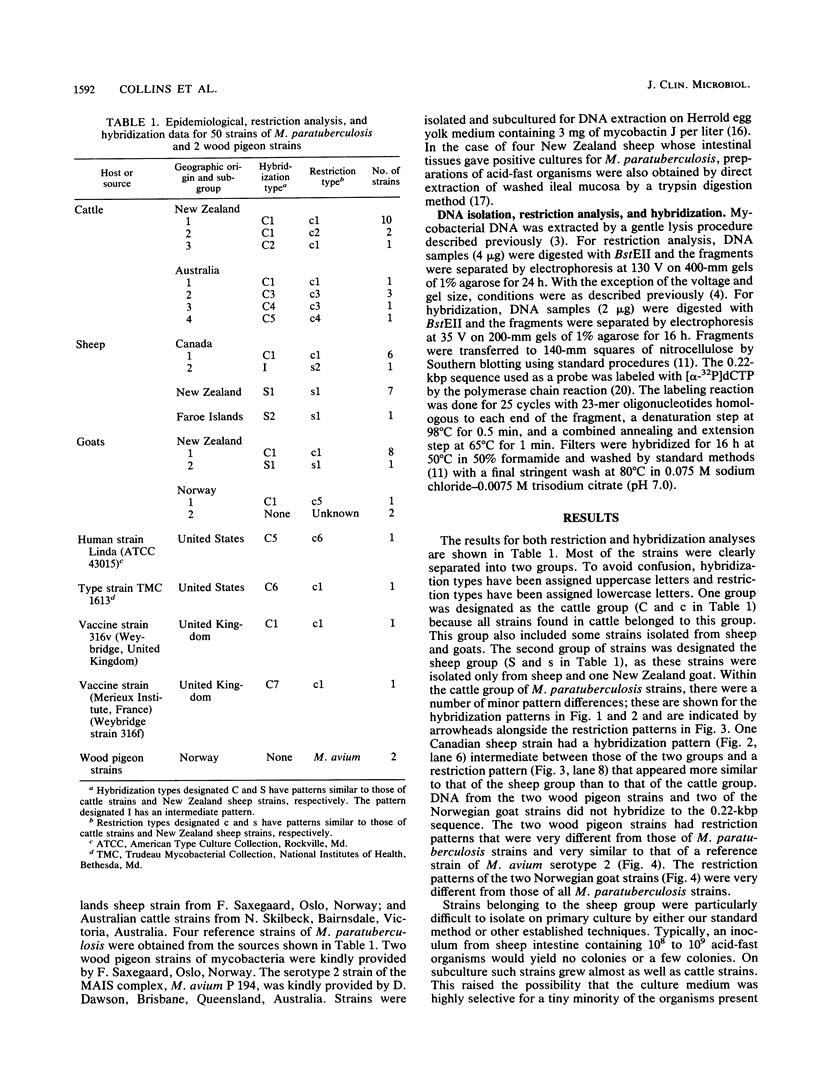
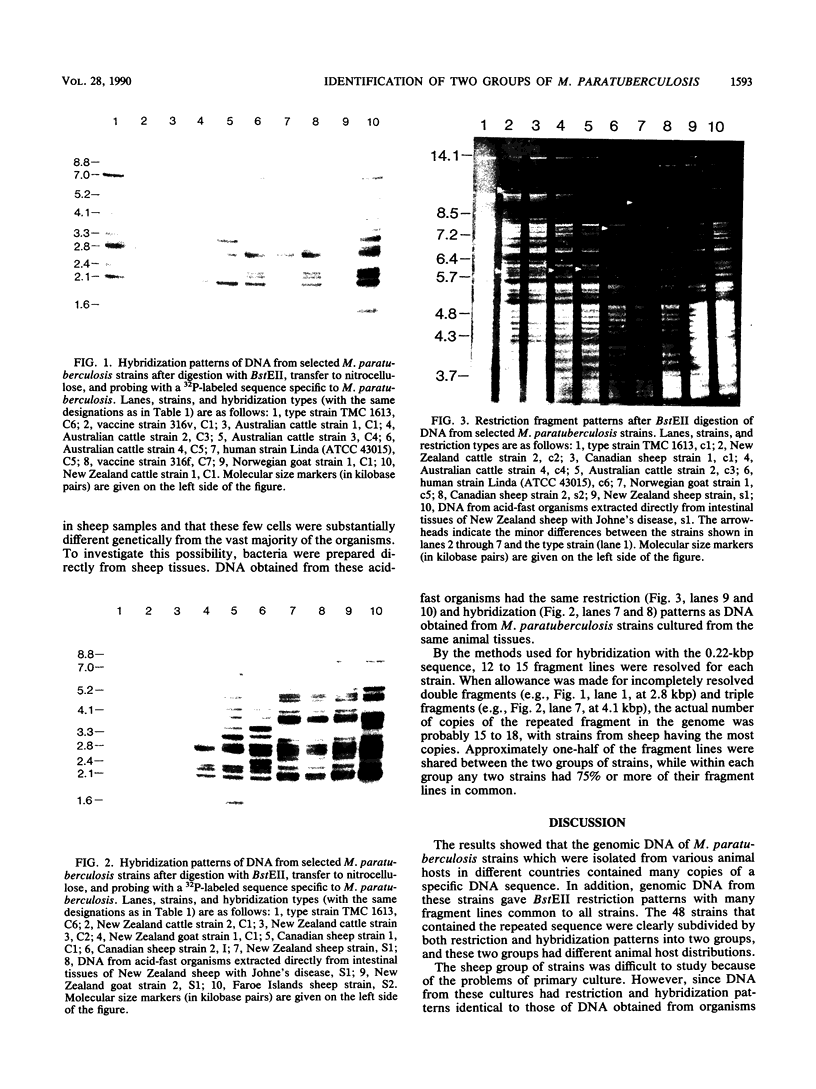
Genomic DNA was prepared from four reference strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and 46 isolates of this organism from New Zealand, Australia, Canada, and Norway and also from two mycobactin-dependent "wood pigeon" strains. The DNA was characterized by restriction endonuclease analysis, both with and without DNA hybridization, with a probe specific to a repetitive DNA sequence in M. paratuberculosis. Both techniques differentiated M. paratuberculosis strains into two groups, but DNA hybridization revealed more differences between strains within the larger group. All the strains from cattle and many strains from other animals belonged to this group. The second group of nine strains included the Faroe Islands strain, all New Zealand sheep strains, and one New Zealand goat strain. Primary isolation of strains belonging to this group was difficult to achieve. DNA from acid-fast organisms harvested directly from intestinal tissues of sheep with Johne's disease was shown to have restriction and hybridization patterns identical to those of DNA obtained from M. paratuberculosis isolates cultured from the same tissues. Two Norwegian goat strains and the wood pigeon strains did not hybridize to the M. paratuberculosis probe and had restriction patterns very different from those of other M. paratuberculosis strains. The wood pigeon strains had restriction patterns very similar to those of strains of Mycobacterium avium, indicating that they should be classified as that species. The presence of two distinct groups of M. paratuberculosis strains and their predominant distribution in different host animals may be significant in management of mixed-animal farming operations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. BCG identification by DNA restriction fragment patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1431–1434. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., De Lisle G. W. DNA restriction endonuclease analysis of Mycobacterium bovis and other members of the tuberculosis complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):562–564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.562-564.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Gabric D. M., De Lisle G. W. Identification of a repetitive DNA sequence specific to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90503-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., de Lisle G. W. Restriction endonuclease analysis of various strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis isolated from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Oct;47(10):2226–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P., McDiarmid A., Thomas L. H., Matthews P. R. Comparison of the pathogenicity of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and Mycobacterium spp isolated from the wood pigeon (Columba palumbus-L). J Comp Pathol. 1985 Oct;95(4):591–597. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(85)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson E., Fodstad F. H. Cultural and biochemical characteristics of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis isolated from goats in Norway. Acta Vet Scand. 1979;20(1):122–134. doi: 10.1186/BF03546635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERKAL R. S., KOPECKY K. E., LARSEN A. B., THURSTON J. R. IMPROVEMENTS IN THE TECHNIQUES FOR PRIMARY CULTIVATION OF MYCOBACTERIUM PARATUBERCULOSIS. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Jul;25:1290–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews P. R., McDiarmid A. The production in bovine calves of a disease resembling paratuberculosis with a Mycobacterium sp isolated from a woodpigeon (Columba palumbus L). Vet Rec. 1979 Mar 31;104(13):286–286. doi: 10.1136/vr.104.13.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. Crohn's disease-isolated mycobacteria are identical to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, as determined by DNA probes that distinguish between mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):796–801. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.796-801.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Thompson J., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. The use of DNA probes identifying restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms to examine the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre G., Stanford J. L. Immunodiffusion analysis shows that Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and other mycobactin-dependent mycobacteria are variants of Mycobacterium avium. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;61(4):295–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnamohan T. N., Spencer T. L. A technique for the purification of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis from the ileal mucosa of infected cattle. Aust Vet J. 1986 Jun;63(6):185–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1986.tb02970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxegaard F., Baess I., Jantzen E. Characterization of clinical isolates of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis by DNA-DNA hybridization and cellular fatty acid analysis. APMIS. 1988 Jun;96(6):497–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxegaard F., Baess I. Relationship between Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and "wood pigeon mycobacteria". Determinations by DNA-DNA hybridization. APMIS. 1988 Jan;96(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schowalter D. B., Sommer S. S. The generation of radiolabeled DNA and RNA probes with polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):90–94. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman J. T., Thompson D. R. Johne's disease in sheep. Aust Vet J. 1984 Jul;61(7):227–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1984.tb05995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. W. The experimental infection of cattle with varieties of Mycobacterium johnei isolated from sheep. J Comp Pathol. 1953 Oct;63(4):368–373. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(53)80038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorel M. F., Desmettre P. Etude comparative de souches de mycobactéries mycobactine-dépendantes, isolées de pigeon ramier, avec Mycobacterium avium et M. paratuberculosis: étude des caractères biologiques et antigéniques. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Sep-Oct;133(2):291–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorel M. F., Marly J., Trap D., Pardon P., Lechopier P. Paratuberculose expérimentale: diagnostic biologique chez des veaux inoculés avec des souches de mycobactéries mycobactine-dépendantes. Ann Rech Vet. 1985;16(1):7–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wards B. J., Collins D. M., de Lisle G. W. Restriction endonuclease analysis of members of the Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare-M. scrofulaceum serocomplex. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2309–2313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2309-2313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple D. L., Kapke P. A., Andrews R. E., Jr Analysis of restriction endonuclease fragment patterns of DNA from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Feb;19(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura H. H., Graham D. Y. Nucleic acid hybridization studies of mycobactin-dependent mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1309–1312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1309-1312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]