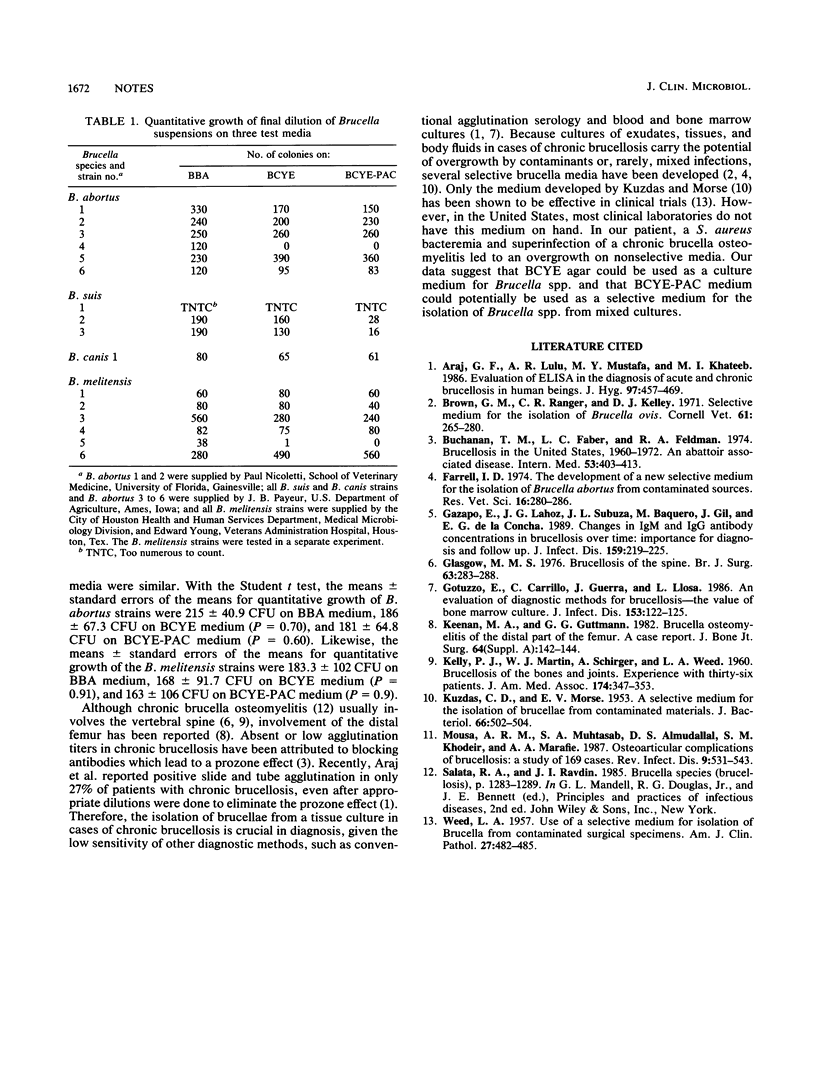
Abstract
A patient with chronic osteomyelitis caused by Brucella abortus had negative agglutination titers. Because of a superimposed staphylococcal infection that resulted in the overgrowth of this organism on nonselective media, brucellae were isolated only on a selective buffered charcoal-yeast extract (BCYE) agar. Sixteen strains of various Brucella species were inoculated on BCYE agar; selective BCYE agar with polymyxin, anisomycin, and cefamandole; and brucella blood agar. The growth and recovery rates on the three media tested were comparable for 14 strains. BCYE agar with polymyxin, anisomycin, and cefamandole may be useful as a selective medium for the isolation of brucellae.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araj G. F., Lulu A. R., Mustafa M. Y., Khateeb M. I. Evaluation of ELISA in the diagnosis of acute and chronic brucellosis in human beings. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Dec;97(3):457–469. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400063634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. M., Ranger C. R., Kelley D. J. Selective media for the isolation of Brucella ovis. Cornell Vet. 1971 Apr;61(2):265–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Faber L. C., Feldman R. A. Brucellosis in the United States, 1960-1972. An abattoir-associated disease. Part I. Clinical features and therapy. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Nov;53(6):403–413. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197411000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell I. D. The development of a new selective medium for the isolation of Brucella abortus from contaminated sources. Res Vet Sci. 1974 May;16(3):280–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazapo E., Gonzalez Lahoz J., Subiza J. L., Baquero M., Gil J., de la Concha E. G. Changes in IgM and IgG antibody concentrations in brucellosis over time: importance for diagnosis and follow-up. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):219–225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow M. M. Brucellosis of the spine. Br J Surg. 1976 Apr;63(4):283–288. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotuzzo E., Carrillo C., Guerra J., Llosa L. An evaluation of diagnostic methods for brucellosis--the value of bone marrow culture. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):122–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY P. J., MARTIN W. J., SCHIRGER A., WEED L. A. Brucellosis of the bones and joints. Experience with thirty-six patients. JAMA. 1960 Sep 24;174:347–353. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03030040001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUZDAS C. D., MORSE E. V. A selective medium for the isolation of brucellae from contaminated materials. J Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(4):502–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.4.502-504.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan M. A., Guttmann G. G. Brucella osteomyelitis of the distal part of the femur. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982 Jan;64(1):142–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousa A. R., Muhtaseb S. A., Almudallal D. S., Khodeir S. M., Marafie A. A. Osteoarticular complications of brucellosis: a study of 169 cases. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 May-Jun;9(3):531–543. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEED L. A. Use of a selective medium for isolation of Brucella from contaminated surgical specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Apr;27(4):482–485. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/27.4_ts.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



