Abstract
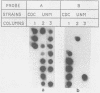
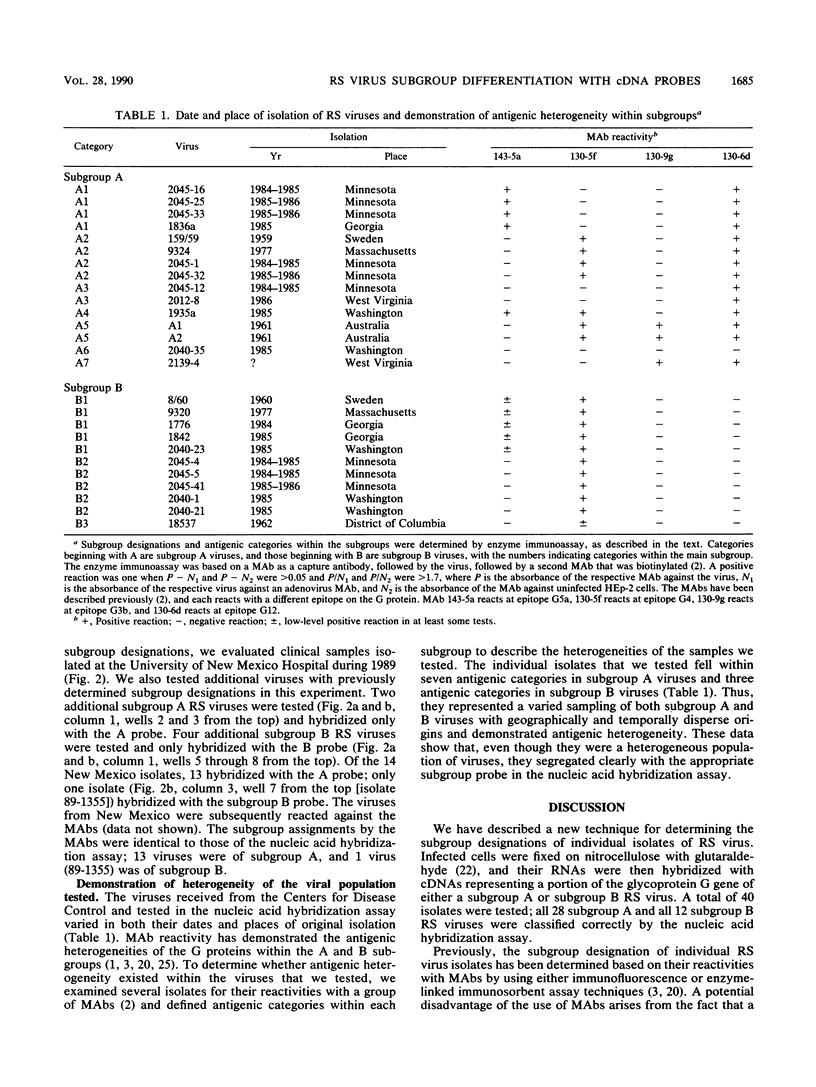
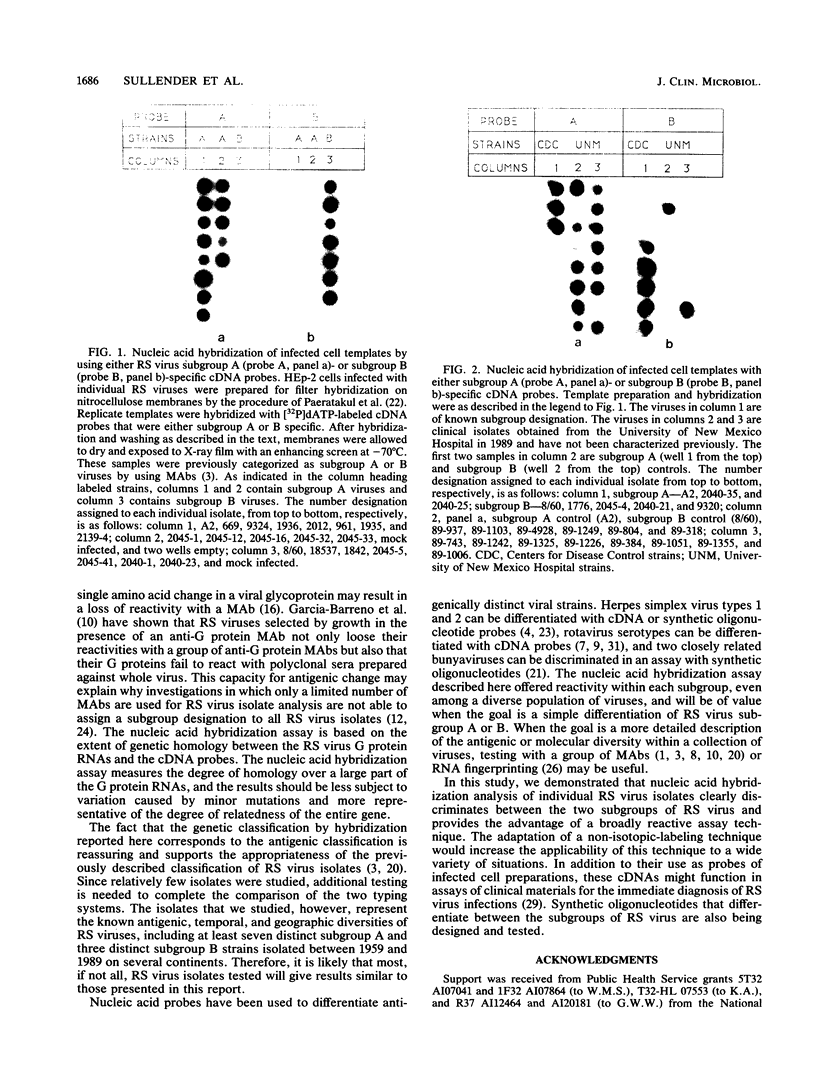
A new approach to respiratory syncytial (RS) virus subgroup determination was developed by using a simple nucleic acid filter hybridization technique. By this method, virus-infected cells are bound and fixed in a single step, and the viral RNA in the fixed-cell preparation is characterized directly by its ability to hybridize to cDNA probes specific for either the A or B subgroups of RS virus. The subgroup-specific probes were constructed from cDNA clones that corresponded to a portion of the extracellular domain of the RS virus G protein of either a subgroup B RS virus (8/60) or a subgroup A RS virus (A2). The cDNA probes were labeled with 32P and used to analyze RS virus isolates collected over a period of three decades. Replicate templates of infected cell preparations were hybridized with either the subgroup A or B probe. The subgroup assignments of 40 viruses tested by nucleic acid hybridization were in agreement with the results of subgroup determinations based on their reactivities with monoclonal antibodies, which previously has been the only method available for determining the subgroup classification of RS virus isolates. The nucleic acid hybridization assay has the advantage of providing broad-based discrimination of the two subgroups on the basis of nucleic acid homology, irrespective of minor antigenic differences that are detected in assays in which monoclonal antibodies are used. The nucleic acid hybridization technique provides a reliable method for RS virus subgroup characterization.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerlind B., Norrby E., Orvell C., Mufson M. A. Respiratory syncytial virus: heterogeneity of subgroup B strains. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2145–2154. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. J., Bingham P., Hierholzer J. C. Neutralization of respiratory syncytial virus by individual and mixtures of F and G protein monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4232–4238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4232-4238.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. J., Hierholzer J. C., Tsou C., Hendry R. M., Fernie B. F., Stone Y., McIntosh K. Antigenic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus strains with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):626–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigam A. R., Richman D. D., Oxman M. N. Rapid typing of herpes simplex virus isolates by deoxyribonucleic acid:deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):226–234. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.226-234.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. cDNA cloning and transcriptional mapping of nine polyadenylylated RNAs encoded by the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J. J., Firoozmand F., Sato S., Vonderfecht S. L., Yin F. Z., Yolken R. H. Detection of group B rotavirus in fecal specimens by dot hybridization with a cloned cDNA probe. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.422-426.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger R., Anderson L. J., Dicker R. C., Harrison B., Doan R., Downing A., Corey L. Epidemic infections caused by respiratory syncytial virus in institutionalized young adults. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1335–1339. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Green K. Y., Garcia D., Sears J., Perez-Schael I., Avendaño L. F., Rodriguez W. B., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z. Dot hybridization assay for distinction of rotavirus serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.29-34.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Barreno B., Palomo C., Peñas C., Delgado T., Perez-Breña P., Melero J. A. Marked differences in the antigenic structure of human respiratory syncytial virus F and G glycoproteins. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):925–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.925-932.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry R. M., Burns J. C., Walsh E. E., Graham B. S., Wright P. F., Hemming V. G., Rodriguez W. J., Kim H. W., Prince G. A., McIntosh K. Strain-specific serum antibody responses in infants undergoing primary infection with respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):640–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry R. M., Talis A. L., Godfrey E., Anderson L. J., Fernie B. F., McIntosh K. Concurrent circulation of antigenically distinct strains of respiratory syncytial virus during community outbreaks. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):291–297. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Bingham P. G., Coombs R. A., Johansson K. H., Anderson L. J., Halonen P. E. Comparison of monoclonal antibody time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay with monoclonal antibody capture-biotinylated detector enzyme immunoassay for respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus antigen detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1243–1249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1243-1249.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Jr, Olmsted R. A., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Alling D. W., Walsh E. E., Collins P. L. Antigenic relatedness between glycoproteins of human respiratory syncytial virus subgroups A and B: evaluation of the contributions of F and G glycoproteins to immunity. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3163–3166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3163-3166.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Spriggs M. K., Olmsted R. A., Collins P. L. The G glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial viruses of subgroups A and B: extensive sequence divergence between antigenically related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5625–5629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Gerhard W., Ward C. W., Dopheide T. A. Antigenic drift in type A influenza virus: sequence differences in the hemagglutinin of Hong Kong (H3N2) variants selected with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson M. A., Belshe R. B., Orvell C., Norrby E. Subgroup characteristics of respiratory syncytial virus strains recovered from children with two consecutive infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1535–1539. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1535-1539.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson M. A., Orvell C., Rafnar B., Norrby E. Two distinct subtypes of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Oct;66(Pt 10):2111–2124. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-10-2111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan K. F., Urquidi V., Emery V. C., Bishop D. H. The design and use of specific genetic probes to identify closely related bunyaviruses and to determine the genotype of their recombinants. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2201–2207. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paeratakul U., De Stasio P. R., Taylor M. W. A fast and sensitive method for detecting specific viral RNA in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1132–1135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1132-1135.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., Aarnaes S. L., Bryan R. N., Ruth J. L., de la Maza L. M. Typing of herpes simplex virus with synthetic DNA probes. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):757–762. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russi J. C., Delfraro A., Arbiza J. R., Chiparelli H., Orvell C., Grandien M., Hortal M. Antigenic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus associated with acute respiratory infections in Uruguayan children from 1985 to 1987. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1464–1466. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1464-1466.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch G. A., Park C. S., Dohner D. E. RNA fingerprinting of respiratory syncytial virus using ribonuclease protection. Application to molecular epidemiology. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1894–1902. doi: 10.1172/JCI114096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch G. A., Park C. S. Monoclonal antibodies demonstrate heterogeneity in the G glycoprotein of prototype strains and clinical isolates of respiratory syncytial virus. J Med Virol. 1987 Aug;22(4):345–356. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Ball L. A., Young K. K., Furze J., Wertz G. W. Human respiratory syncytial virus glycoprotein G expressed from a recombinant vaccinia virus vector protects mice against live-virus challenge. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):607–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.607-613.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Taylor G., Ball L. A., Anderson K., Young K. K., King A. M., Wertz G. W. Immune and histopathological responses in animals vaccinated with recombinant vaccinia viruses that express individual genes of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3855–3861. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3855-3861.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke R. B., Murphy-Corb M. Detection of respiratory syncytial virus in nasopharyngeal secretions by DNA-RNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1739–1743. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1739-1743.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Collins P. L., Huang Y., Gruber C., Levine S., Ball L. A. Nucleotide sequence of the G protein gene of human respiratory syncytial virus reveals an unusual type of viral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4075–4079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B. J., Lam W. P., Yan Y. K., Lo S. K., Lung M. L., Ng M. H. Direct identification of serotypes of natural human rotavirus isolates by hybridization using cDNA probes derived from segment 9 of the rotavirus genome. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):552–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.552-557.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]