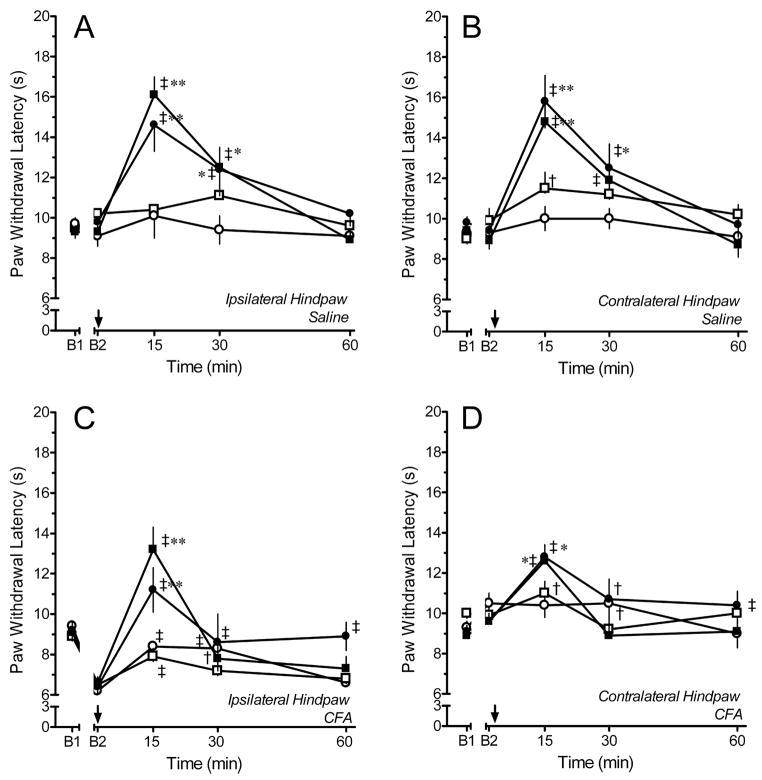
Fig. 3.
Time course of paw withdrawal latency (PWL) after microinjection of saline (open circles; N=4–7), 0.3 ng (open squares; N=3–4), 1 ng (filled circles; N=7 each), or 3 ng (filled squares; N=8–10) of DAMGO into the locus coeruleus (LC) of rats that had received an injection of saline (A, B) or CFA (C,D) in the left hindpaw four days earlier. Note that the increase in contralateral PWL produced by 1 and 3 ng DAMGO in CFA-treated rats is less than that observed in saline-treated rats. Comparisons of the ipsilateral PWL are confounded by differing baselines. B1 represents the baseline PWL determined before hindpaw injection of saline or CFA. B2 represents the baseline PWL determined 4 days later and before microinjection of saline or DAMGO in the LC. Arrow denotes time of microinjection. † p < 0.05, ‡ p < 0.01 compared to B2; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared to saline at the corresponding time point.