Abstract
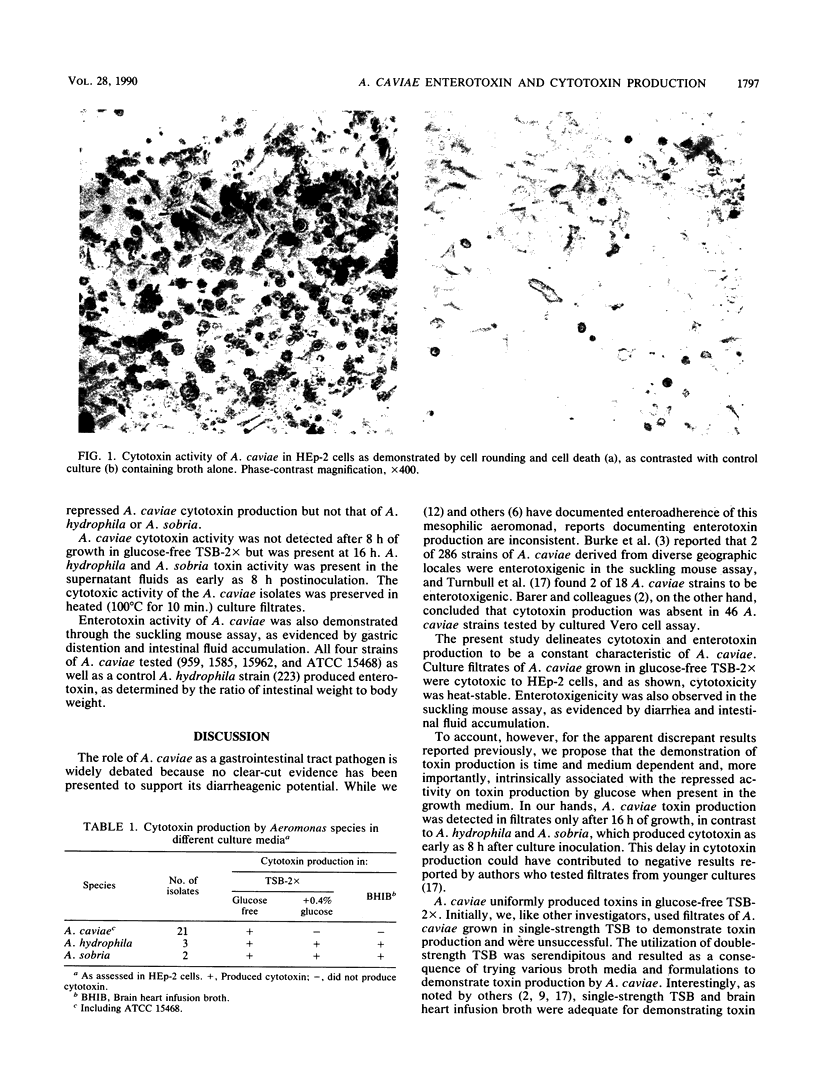
Twenty-one stool and environmental Aeromonas caviae isolates were studied for cytopathogenicity for cultured HEp-2 cells. Cytotoxic activity was demonstrated by the 21 A. caviae strains and by A. caviae ATCC 15468 after challenging HEp-2 cells with filtrates from a 24-h-old broth shake culture composed of double-strength, glucose-free Trypticase soy broth, incubated at 35 degrees C. Heat-stable cytotoxicity was observed 5 h after the addition of 1/5 and 1/10 concentrations of filtrates and consisted of cell rounding and cell detachment. Enterotoxin activity was also demonstrated through the suckling mouse assay. These data advance the role of A. caviae as a gastrointestinal pathogen.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altwegg M. Aeromonas caviae: an enteric pathogen? Infection. 1985 Sep-Oct;13(5):228–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01667217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barer M. R., Millership S. E., Tabaqchali S. Relationship of toxin production to species in the genus Aeromonas. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Dec;22(4):303–309. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-4-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Beaman J., Gracey M., Lesmana M., Rockhill R., Echeverria P., Janda J. M. Correlation of enterotoxicity with biotype in Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1196–1200. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1196-1200.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Berry R. J., Gracey M. Detection of enterotoxins of Aeromonas hydrophila by a suckling-mouse test. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):401–408. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrello A., Silburn K. A., Budden J. R., Chang B. J. Adhesion of clinical and environmental Aeromonas isolates to HEp-2 cells. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):19–27. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Montenegro M. A., Sanyal S. C., Helmuth R., Bulling E., Timmis K. N. Cloning of enterotoxin gene from Aeromonas hydrophila provides conclusive evidence of production of a cytotonic enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.435-441.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challapalli M., Tess B. R., Cunningham D. G., Chopra A. K., Houston C. W. Aeromonas-associated diarrhea in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Oct;7(10):693–698. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198810000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millership S. E., Barer M. R., Tabaqchali S. Toxin production by Aeromonas spp. from different sources. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Dec;22(4):311–314. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-4-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namdari H., Bottone E. J. Correlation of the suicide phenomenon in Aeromonas species with virulence and enteropathogenicity. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2615–2619. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2615-2619.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namdari H., Bottone E. J. Microbiologic and clinical evidence supporting the role of Aeromonas caviae as a pediatric enteric pathogen. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):837–840. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.837-840.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namdari H., Bottone E. J. Suicide phenomenon in mesophilic aeromonads as a basis for species identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):788–789. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.788-789.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namdari H., Cabelli V. J. The suicide phenomenon in motile aeromonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):543–547. doi: 10.1093/benz/9780199773787.article.b00013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Havelaar A., Jansen W., Kozaki S., Guinée P. Production of "Asao toxin" by Aeromonas strains isolated from feces and drinking water. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1140–1142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1140-1142.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitarangsi C., Echeverria P., Whitmire R., Tirapat C., Formal S., Dammin G. J., Tingtalapong M. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides: prevalence among individuals with and without diarrhea in Thailand. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.666-673.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Joaquin V. H., Pickett D. A. Aeromonas-associated gastroenteritis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Jan;7(1):53–57. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198801000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]