Abstract
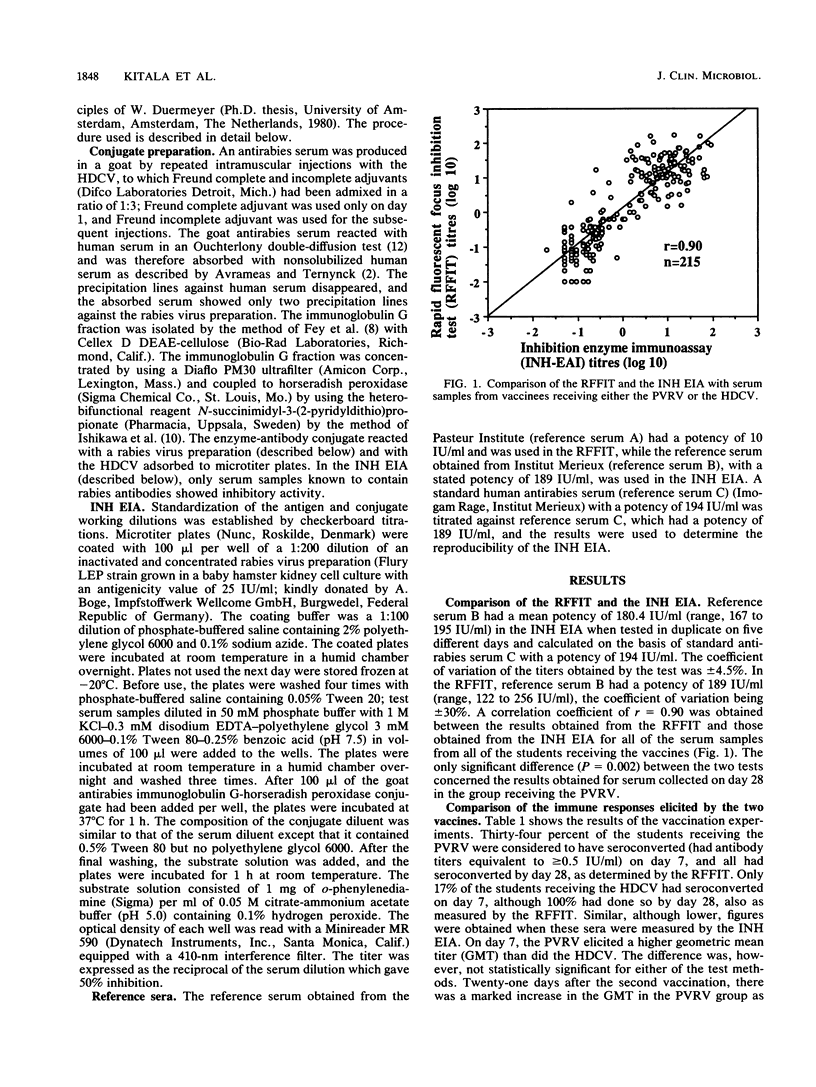
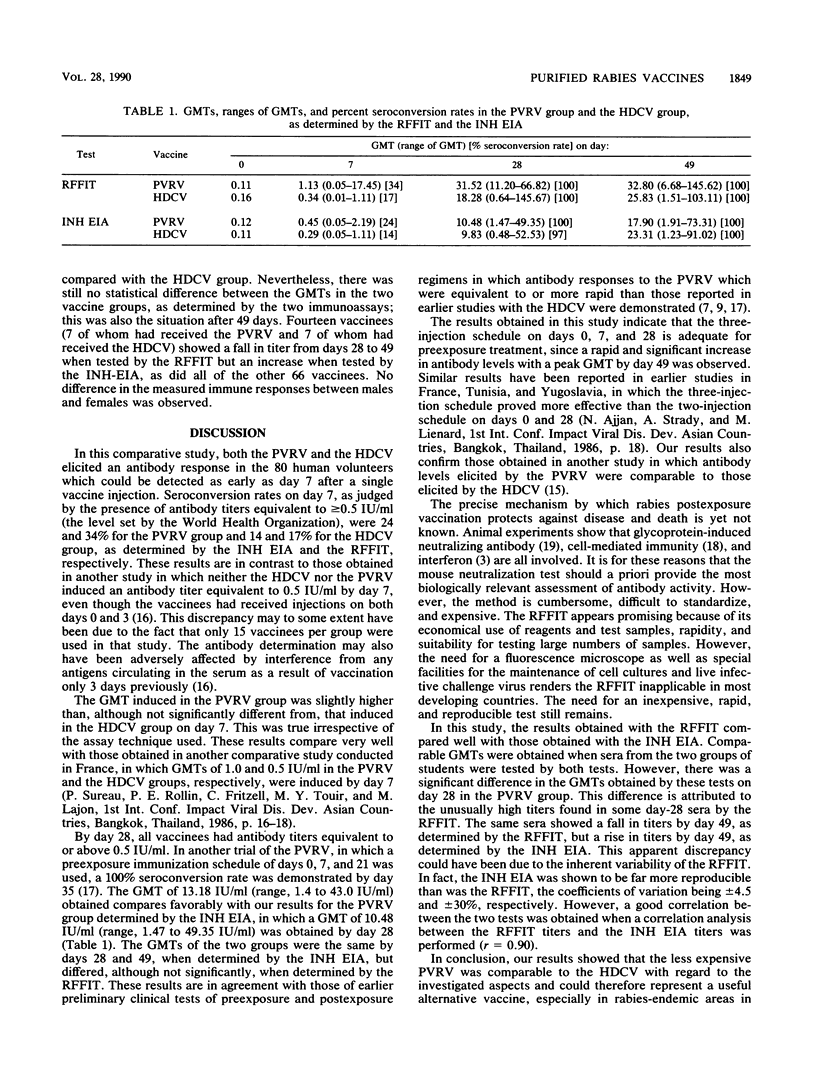
Antibody responses to a conventional rabies preexposure regimen of a new purified Vero cell rabies vaccine (PVRV) and a human diploid cell vaccine (HDCV) were compared in 80 healthy Kenyan veterinary students. Forty-three of the students received the PVRV and 37 received the HDCV on days 0, 7, and 28. Antibody responses were monitored by using the rapid fluorescent-focus inhibition test (RFFIT) and an inhibition enzyme immunoassay (INH EIA) on days 0, 7, 28, and 49. Both vaccines elicited a rapid antibody response. A good correlation between the RFFIT titers and the INH EIA titers was obtained (r = 0.90). Our results also showed that the INH EIA was more reproducible and might therefore be a suitable substitute for the more expensive and less reproducible RFFIT. The geometric mean titers determined by both tests in the two groups of students were statistically similar during the test period. The RFFIT and the INH EIA gave comparable geometric mean titers, which differed significantly only on day 28 in the PVRV group. The effect of the new PVRV is comparable to that of the more expensive HDCV, as determined by the present test systems. The PVRV could therefore be the vaccine of choice, especially in tropical rabies-endemic areas, where the high cost of the HDCV has confined its use to a privileged few.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atanasiu P. Quantitative assay and potency test of antirabies serum and immunoglobulin. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):314–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. Biologically active water-insoluble protein polymers. I. Their use for isolation of antigens and antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer G. M., Moore S. A., Shaddock J. H., Levy H. B. An effective rabies treatment in exposed monkeys: a single dose of interferon inducer and vaccine. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57(5):807–813. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard K. W., Fishbein D. B., Miller K. D., Parker R. A., Waterman S., Sumner J. W., Reid F. L., Johnson B. K., Rollins A. J., Oster C. N. Pre-exposure rabies immunization with human diploid cell vaccine: decreased antibody responses in persons immunized in developing countries. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):633–647. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard K. W., Roberts M. A., Sumner J., Winkler W. G., Mallonee J., Baer G. M., Chaney R. Human diploid cell rabies vaccine. Effectiveness of immunization with small intradermal or subcutaneous doses. JAMA. 1982 Feb 26;247(8):1138–1142. doi: 10.1001/jama.247.8.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Messerli J., Sturzenegger N., Grolimund F. Methods of isolation, purification and quantitation of bovine immunoglobulins: a technical review. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1976 May;23(4):269–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1976.tb00682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa E., Imagawa M., Hashida S., Yoshitake S., Hamaguchi Y., Ueno T. Enzyme-labeling of antibodies and their fragments for enzyme immunoassay and immunohistochemical staining. J Immunoassay. 1983;4(3):209–327. doi: 10.1080/15321818308057011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie R. E., Dobkin M. B., Meyer P., Chin B., Roby R. E., Hammar A. H., Cabasso V. J. Measurement of rabies antibody: comparison of the mouse neutralization test (MNT) with the rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test (RFFIT). J Biol Stand. 1975;3(4):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(75)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Yager P. A., Baer G. M. A rapid reproducible test for determining rabies neutralizing antibody. Bull World Health Organ. 1973 May;48(5):535–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suntharasamai P., Chanthavanich P., Warrell M. J., Looareesuwan S., Karbwang J., Supanaranond W., Phillips R. E., Jansawan W., Xueref C., Pouradier-Duteil X. Purified Vero cell rabies vaccine and human diploid cell strain vaccine: comparison of neutralizing antibody responses to post-exposure regimens. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Jun;96(3):483–489. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suntharasamai P., Warrell M. J., Warrell D. A., Chanthavanich P., Looareesuwan S., Supapochana A., Phanuphak P., Jittapalapongsa S., Yager P. A., Baer G. M. Early antibody responses to rabies post-exposure vaccine regimens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):160–165. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J. Cell-mediated immunity and postexposure protection from rabies by inactivated vaccines of tissue culture origin. Dev Biol Stand. 1978;40:255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., György E., Schlumberger D., Sokol F., Koprowski H. Antigenic properties of rabies virus components. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Plotkin S. A., Grella D. W. Human cell culture rabies vaccine. Antibody response in man. JAMA. 1973 May 21;224(8):1170–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


