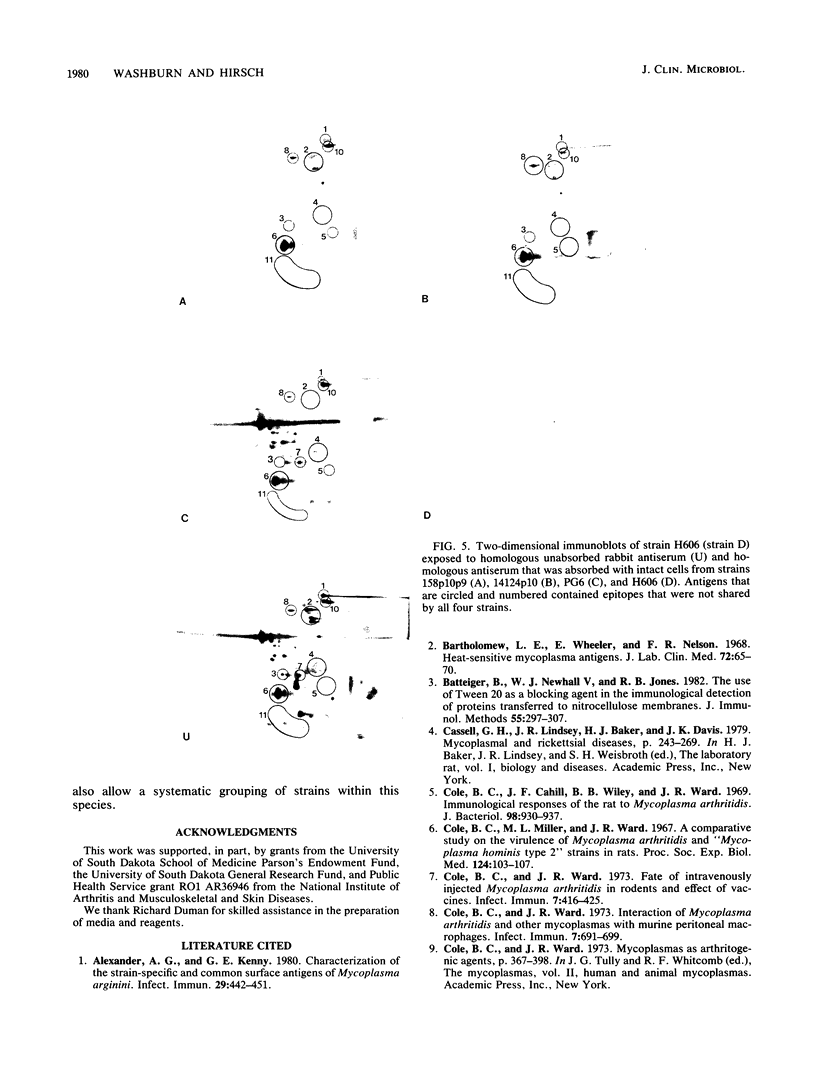
Abstract
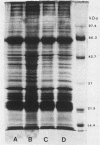
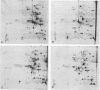
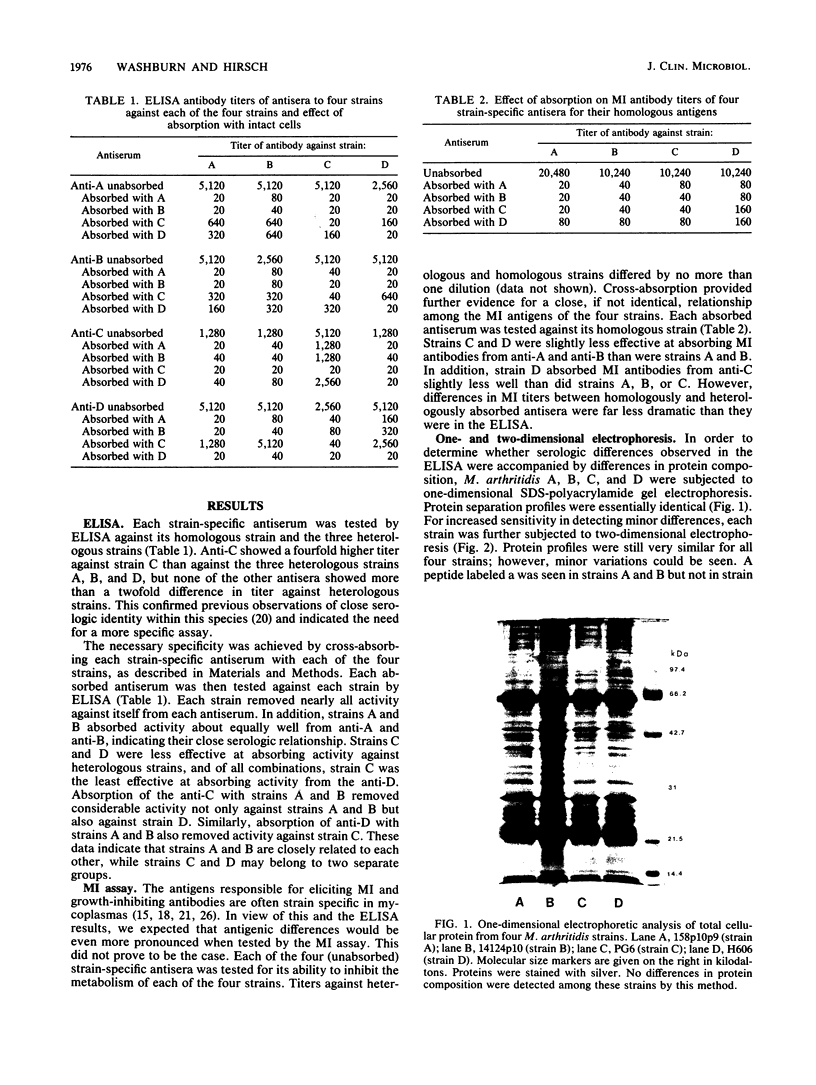
Four Mycoplasma arthritidis strains, two virulent (158p10p9 and 14124p10) and two avirulent (PG6 and H606), were examined for differences in their antigenic compositions. Rabbit antisera prepared against each strain were compared for their reactivities against both homologous and heterologous strains by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and metabolism inhibition assay. These tests confirmed a close serologic relationship among the four strains. Only by cross-absorbing each antiserum with intact cells from both homologous and heterologous strains could serologic differences be detected. Interestingly, antigenic variability was minimal among those antigens involved in the metabolism inhibition reaction, suggesting that they may be highly conserved within this species. No differences in protein composition could be detected by one-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. However, slight variation was apparent on two-dimensional gels, and antigens possessing strain-specific epitopes were detected by two-dimensional immunoblotting experiments performed with cross-absorbed antisera. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, two-dimensional electrophoresis, and immunoblotting experiments showed that the two virulent strains were closely related to each other, while the avirulent strains were more distantly related to each other and to the other two strains. The relationship of M. arthritidis serologic diversity to virulence remains unclear: however, this study has demonstrated that it may be possible to subdivide M. arthritidis into serogroups on the basis of cross-absorption patterns and to identify those antigens bearing strain-specific epitopes by immunoblotting with cross-absorbed antisera.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of the strain-specific and common surface antigens of Mycoplasma arginini. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):442–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.442-451.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew L. E., Wheeler E., Nelson F. R. Heat-sensitive mycoplasma antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Cahill J. F., Wiley B. B., Ward J. R. Immunological responses of the rat to Mycoplasma arthritidis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.930-937.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Miller M. L., Ward J. R. A comparative study on the virulence of Mycoplasma arthritidis and "Mycoplasma hominis, type 2" strains in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):103–107. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Fate of intravenously injected Mycoplasma arthritidis in rodents and effect of vaccines. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):416–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.416-425.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Interaction of Mycoplasma arthritidis and other mycoplasmas with murine peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):691–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.691-699.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R., Jones R. S., Cahill J. F. Chronic proliferative arthritis of mice induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. I. Induction of disease and histopathological characteristics. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):344–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.344-355.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson L. S., Duthie J. J., Sugar M. Focal Infection in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comparison of the Incidence of Foci of Infections in the Upper Respiratory Tract in One Hundred Cases of Rheumatoid Arthritis and One Hundred Controls. Ann Rheum Dis. 1949 Sep;8(3):205–208. doi: 10.1136/ard.8.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golightly-Rowland L., Cole B. C., Ward J. R., Wiley B. B. Effect of Animal Passage on Arthritogenic and Biological Properties of Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):538–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.538-545.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannan P. C., Hughes B. O. Reproducible polyarthritis in rats caused by Mycoplasma arthritidis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):316–321. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Dagnall G. J. Experimental polyarthritis in rats produced by Mycoplasma arthritidis. J Comp Pathol. 1975 Jan;85(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(75)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. Antigenic differences within the species Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Sep;68(3):469–477. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S. An antigenic analysis for membranes of Mycoplasma hominis by cross-absorption. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jan;116(1):187–193. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Immunochemical characterization of a heat-stable surface antigen of Mycoplasma pulmonis expressing both species-specific and strain-specific determinants. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):355–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.355-363.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A color test for the measurement of antibody to the non-acid-forming human Mycoplasma species. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Jul;84(1):51–66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLY J. G. BIOCHEMICAL, MORPHOLOGICAL, AND SEROLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MYCOPLASMA OF MURINE ORIGIN. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:171–185. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkill C. E., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of three strains of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1107–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkill C. E., Kenny G. E. Serological comparison of five arginine-utilizing Mycoplasma species by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):624–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.624-632.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Cathey W. J., Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Chronic arthritis of rabbits induced by mycoplasmas. IV. Protective effect of immunization and prior infection. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1985 Jul-Sep;3(3):195–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Cole B. C., Gelman M. I., Ward J. R. Chronic arthritis of rabbits induced by mycoplasmas. I. Clinical microbiologic, and histologic features. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jul;23(7):825–836. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Chronic arthritis of rabbits induced by mycoplasmas. III. Induction with nonviable Mycoplasma arthritidis antigens. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Aug;25(8):937–946. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Ramsay J. R., Andrews M. B. Recognition of Mycoplasma arthritidis membrane antigens by rats and rabbits: comparison by immunoblotting and radioimmunoprecipitation. Vet Microbiol. 1988 May;17(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Ramsay J. R. Experimental induction of arthritis in LEW rats and antibody response to four Mycoplasma arthritidis strains. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Nov;21(1):41–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Ramsay J. R., Roberts L. K. Characterization of the metabolism inhibition antigen of Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):357–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.357-364.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R. Spectrophotometric method for determining titers of antimycoplasma metabolism inhibition antibody. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):343–346. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.343-346.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]