Abstract
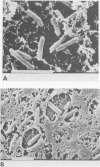
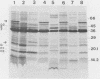
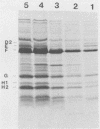
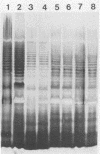
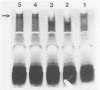
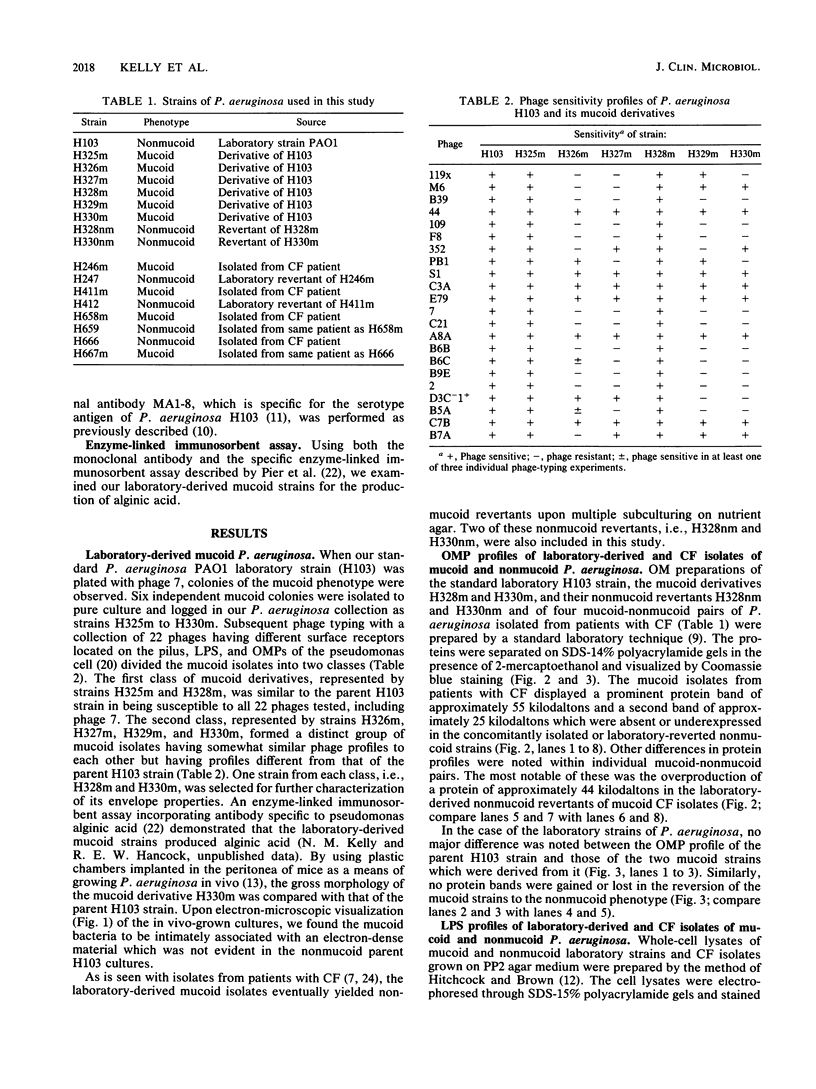
Laboratory-derived mucoid variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were selected by plating the standard PAO1 laboratory strain with bacteriophage. These mucoid variants formed two distinct groups of strains on the basis of phage typing. The first group had the same phage-typing pattern as the parent PAO1 strain, while the second group had a distinctly different phage-typing pattern. One strain from each group was assessed along with the parent PAO1 strain for its outer membrane protein (OMP) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) profiles by sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis followed by appropriate staining. The mucoid derivatives were found to differ from the parent PAO1 nonmucoid strain in having lost a high-molecular-weight LPS species. Furthermore, the reversion of the mucoid strains to the nonmucoid phenotype was accompanied by a return of the missing high-molecular-weight LPS species. No observable difference between the mucoid derivatives and the parent nonmucoid strain was noted in the OMP profiles. The opposite was found in the case of four isolates of mucoid P. aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. Two OMP bands (of approximately 55 and 25 kilodaltons) were present in the mucoid isolates but missing in their sister nonmucoid strains. In the case of the cystic fibrosis isolates, no difference in the LPS profiles within mucoid-nonmucoid pairs was noted.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckmire F. L. Influence of nutrient media on the characteristics of the exopolysaccharide produced by three mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Microbios. 1984;41(163):49–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R., Lam J. S., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Influence of culture conditions on expression of the mucoid mode of growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):8–16. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.8-16.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne W. M., Jr, Buckmire F. L. Partial purification and characterization of a polymannuronic acid depolymerase produced by a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from a patient with cystic fibrosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):562–567. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.562-567.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. R., Linker A. Production and characterization of the slime polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):915–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.915-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Govan J. R. Alginate synthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a chromosomal locus involved in control. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Aug;119(2):443–450. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabert E., Wingender J., Winkler U. K. An outer membrane protein characteristic of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):83–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mouat E. C., Speert D. P. Quantitation and identification of antibodies to outer-membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in sera of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):220–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wieczorek A. A., Mutharia L. M., Poole K. Monoclonal antibodies against Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane antigens: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.166-171.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Bell A., Hancock R. E. Surface characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in a chamber implant model in mice and rats. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):344–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.344-350.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Rawling E. G., Hancock R. E. Determinants of the efficacy of tobramycin therapy against isogenic nonmucoid and mucoid derivatives of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 growing in peritoneal chambers in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1207–1211. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knirel YuA, Vinogradov E. V., Shashkov A. A., Dmitriev B. A., Kochetkov N. K., Stanislavsky E. S., Mashilova G. M. Somatic antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The structure of O-specific polysaccharide chains of P. aeruginosa O:3(a),c and O:3a,d,e lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):289–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGeorge J., Korolik V., Morgan A. F., Asche V., Holloway B. W. Transfer of a chromosomal locus responsible for mucoid colony morphology in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from cystic fibrosis patients to P. aeruginosa PAO. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Jun;21(4):331–336. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-4-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R. Mucoid variation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced by the action of phage. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Rubero V. J. Mucoid conversion by phages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):717–719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.717-719.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype strains. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):770–779. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., McGroarty E. J. High-molecular-weight components in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella minnesota, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):738–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.738-745.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Desjardins D., Aguilar T., Barnard M., Speert D. P. Polysaccharide surface antigens expressed by nonmucoid isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.189-196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugashetti B. K., Metzger H. M., Jr, Vadas L., Feingold D. S. Phenotypic differences among clinically isolated mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.686-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Schmidt P. J. Dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1003-1010.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]