Abstract
Thromboxane A2 (TxA2), the principle product of platelet COX-1-dependent arachidonic acid metabolism, directs multiple pro-atherogenic processes via its receptor, TP. Oxidative challenge offsets TP degradation, a key component in limiting TxA2's actions. Following TP activation, we observed cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation coincident with increased TP expression. We examined the link between TP-evoked ROS and TP regulation. TP expression was augmented in TPα-transfected cells treated with a TxA2 analog [1S-1α,2β(5Z),3α(1E,3R*),4α]]-7-[3-(3-hydroxy-4-(4′-iodophenoxy)-1-butenyl)-7-oxabicyclo-[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-5-heptenoic acid (IBOP). This was reduced with a cellular antioxidant, N-acetyl cysteine, or two distinct NADPH oxidase inhibitors, diphenyleneiodonium and apocynin. Homologous upregulation of the native TP was also reduced in apocynin-treated aortic smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) and was absent in ASMCs lacking an NADPH oxidase subunit (p47−/−). TP transcription was not increased in IBOP-treated cells, indicating a posttranscriptional mechanism. IBOP induced translocation of TPα to the Golgi and reduced degradation of the immature form of the receptor. These data are consistent with a ROS-dependent mechanism whereby TP activation enhanced TP stability early in posttranscriptional biogenesis. Given the significant role played by TP and ROS in perturbed cardiovascular function, the convergence of TP on ROS-generating pathways for regulation of TxA2-dependent events may be critical for cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase, prostanoids, vascular smooth muscle cells, cardiovascular disease
Thromboxane A2 (TxA2), derived predominantly from platelet COX-1-dependent metabolism of arachidonic acid, is integral to cardiovascular disease (CVD). TxA2 directs multiple processes, including vasoconstriction, platelet aggregation, and smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation via its cell surface G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), the TP (1). Antagonism or deletion of TP retarded atherogenesis (2, 3) and blunted the proliferative response to vascular injury (4) or remodeling (5) in mice.
Regulation of TP expression, which is augmented in human CVD (6, 7), has received less attention compared with the coincident increase in the biosynthesis of its ligand, TxA2 (3, 8). Indeed, despite the diversity of platelet agonists, the cardioprotective effects of aspirin are realized through irreversible inhibition of platelet COX-1-derived TxA2 (9). Conversely, the unrestricted TxA2 generation, with concomitant depression of its opposing mediator prostacyclin, associated with selective COX-2 inhibitors, is the leading explanation for the cardiovascular hazard associated with that class of drugs (10), underscoring the central role played by this eicosanoid during cardiovascular function and disease. However, a TP antagonist was more effective in offsetting lesion formation compared with inhibitors of TxA2 synthesis in atherosclerotic mice (2, 3), warranting examination of receptor-specific events in CVD.
In addition to their role as signaling intermediates (11), reactive oxygen species (ROS) may regulate GPCR function and expression. Exogenous hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) promoted desensitization of the dopamine D1 receptor (12). In contrast, the sphingnosine 1-phosphate S1P1 receptor (13) and the TP (14) are posttranslationally upregulated by H2O2. These observations suggest a role for intracellular ROS in controlling protein expression and represent a potential mechanism for regulating TP expression. This currently untested hypothesis is especially interesting given that NADPH oxidase, a major source of vascular ROS (15), is an effector for TP (16, 17), while antagonism of the TP offset NADPH oxidase expression and renal oxidant stress in diabetic hyperlipidemic mice (18). Indeed, similar to other vasoactive mediators (15), NADPH oxidase-derived cellular ROS may be integral to TxA2's cardiovascular actions (16, 17).
We examined the role of TP-generated cellular oxidants in regulation of TP expression. We report a novel feed-forward loop in which TP activation promotes upregulation of TP expression through a ROS-dependent mechanism of enhanced receptor stability early in biogenesis.
METHODS
Cell Culture and Transfection
Hemagglutinin (HA) epitope tagged human (h) TPα was generated as described (19). hTPα, triple (3x) HA-tagged, was from the Missouri S and T cDNA Resource Center. HEK 293 cells (ATCC, Rockville, MD) and human (h) aortic (A) SMCs (Biowhittaker, MD) were maintained as described (20). SMCs were isolated from wild-type or p47−/− mouse aortic explants as described (19). HEK 293 cells were transfected with HAhTPα, for stable expression (hereafter termed TPα-HEK), or transiently with 3xHAhTPα (hereafter termed 3xHAhTPα-HEK) as described (21). Experiments were carried out 48 h after transfection.
Radioligand binding
TPα-HEK were scraped into buffer (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 1 mM EDTA, and protease inhibitors) and homogenized (TissueLyser™; Qiagen; 2 x 3 min at 30 MHz). Intact cells and nuclei were removed (2 x 1,800 g, 10 min). The crude membrane fraction was isolated from the resulting supernatant by ultracentrifugation (100,000 g, 1 h at 4°C) and resuspended in buffer. TP radiolabeled using a saturating concentration (150 nM) of the TP antagonist 3H-SQ 29548 (Perkin-Elmer, MA) as described (21). For saturation binding, increasing concentrations of 3H-SQ 29548 were used. Nonspecific binding was quantified using excess unlabeled SQ 29548.
To measure binding to intact human aortic smooth muscle cells (hASMCs), cells were detached (0.02% EDTA) and resuspended in HBSS containing 0.2% BSA. Cells (∼20,000) were incubated with a saturating concentration of 3H-SQ 29548 (250 nM) overnight at 4°C. The reaction was stopped with ice-cold HBSS/BSA and GF/C filter (Whatmann) filtration. Radioactivity associated with washed filters was quantified.
Measurement of ROS
Intracellular ROs were measured by carboxy methyl dichloroflourescein fluorescence. Cells were seeded into 96-well plates or coverslips, grown for 24 h, and loaded with 10 μM carboxy methyl dichloroflourescein in HBSS for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were washed and fluorescence measurements taken, before and after [1S-1α,2β(5Z),3α(1E,3R*),4α]]-7-[3-(3-hydroxy-4-(4′-iodophenoxy)-1-butenyl)-7-oxabicyclo-[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl]-5-heptenoic acid (IBOP) treatment, using a Victor spectrophotometer (Perkin-Elmer), with excitation and emission at 485 and 535 nm, respectively. Images were captured with a Hamamatsu camera (Hamamatsu City, Japan) using Metamorph software V6.0 (Universal Imaging Corporation, PA) on an Inverted Olympus IX70 microscope (Tokyo, Japan).
Western blotting
Whole-cell lysates were resolved (NuPAGE; Invitrogen, CA). HA-tagged or native TP receptors were visualized with anti-HA (Covance; 1:1,000 dilution) or anti-TP (Cayman Chemicals, MI; 1:100) as previously described (19).
Quantitative real-time PCR
Cells, in 12-well (TPα-HEK) or 6-well (hASMC) dishes, were treated with IBOP. Total RNA was extracted (RNeasy™; Qiagen, CA), reverse transcribed into cDNA (TaqMan™ reverse transcriptase; Applied Biosystems, CA), and TP mRNA quantified by real-time PCR analysis. Primers and probes were from Ambion, CA (Hs00169054_m1). mRNA levels were normalized by subtracting the Ct for β-actin or 18S from the Ct for TP, producing a ΔCt value. The ΔCt was compared with control using the relative quantitation 2–(ΔCt) method (22) to determine fold change.
Membrane fractionation
TPα-HEK were scraped into buffer (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 0.25 M sucrose, and protease inhibitors) and homogenized (TissueLyser™; Qiagen; 2 x 3 min at 30 MHz). Intact cells and nuclei were removed (2 x 1,800 g, 10 min). The membrane fraction was isolated by ultracentrifugation (65,000 g, 1 h at 4°C) and resuspended in buffer.
Discontinuous density gradients (2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5, 15, 17.5, 20, and 30%) were prepared using Optiprep™ (Axis-Shield, Norway) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Membrane homogenates were loaded onto the gradient and centrifuged (97,000 g for 2.5 h at 4°C). Fractions (1 ml) were collected from the bottom of the tube. The distribution of 3xHAhTPα, calnexin [endoplasmic reticulum (ER)], and golgin-97 (Golgi) was determined by immunoblotting.
Immunofluorescence microscopy
3xHAhTPα-HEK were fixed (4% paraformaldehyde, 30 min, 4°C) and permeabilized (0.1% Triton X-100, 10 min, room temperature). Slides were blocked in PBS containing 5% goat serum and 2% BSA. 3xHAhTPα and Golgin-97 were stained with rat anti-HA (1:500 dilution; Roche Biochemicals, IN) and mouse anti-human golgin-97 (1:200 dilution; Invitrogen) overnight at 4°C. Staining was visualized with Alexi-Fluor 555-labeled anti-rat and Alexi-Fluor 488-labeled anti-mouse (1:1,000 dilution; Invitrogen) for 30 min using an Olympus AX60 microscope.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using Graphpad Prism software. Comparisons were made using a one-sample t-test or by ANOVA, with suitable post hoc multiple comparison testing as appropriate.
RESULTS
TP is coupled to ROS generation
We first confirmed intracellular ROS generation following TP activation. ROS generation was increased in human (h; Fig. 1A, B) and mouse (m; Fig. 1C) ASMC treated with the TP agonist IBOP. Consistent with other reports (16, 18), this was inhibited by either diphenyleneiodonium (DPI), a general inhibitor of flavoenzymes, including NADPH oxidase, or apocynin, a nonselective NADPH oxidase inhibitor. IBOP did not induce ROS in mASMC lacking the p47phox subunit of NADPH oxidase (p47−/−; Fig. 1C). Taken together, these internally consistent data place one or more NADPH oxidases downstream of TP activation.
Fig. 1.
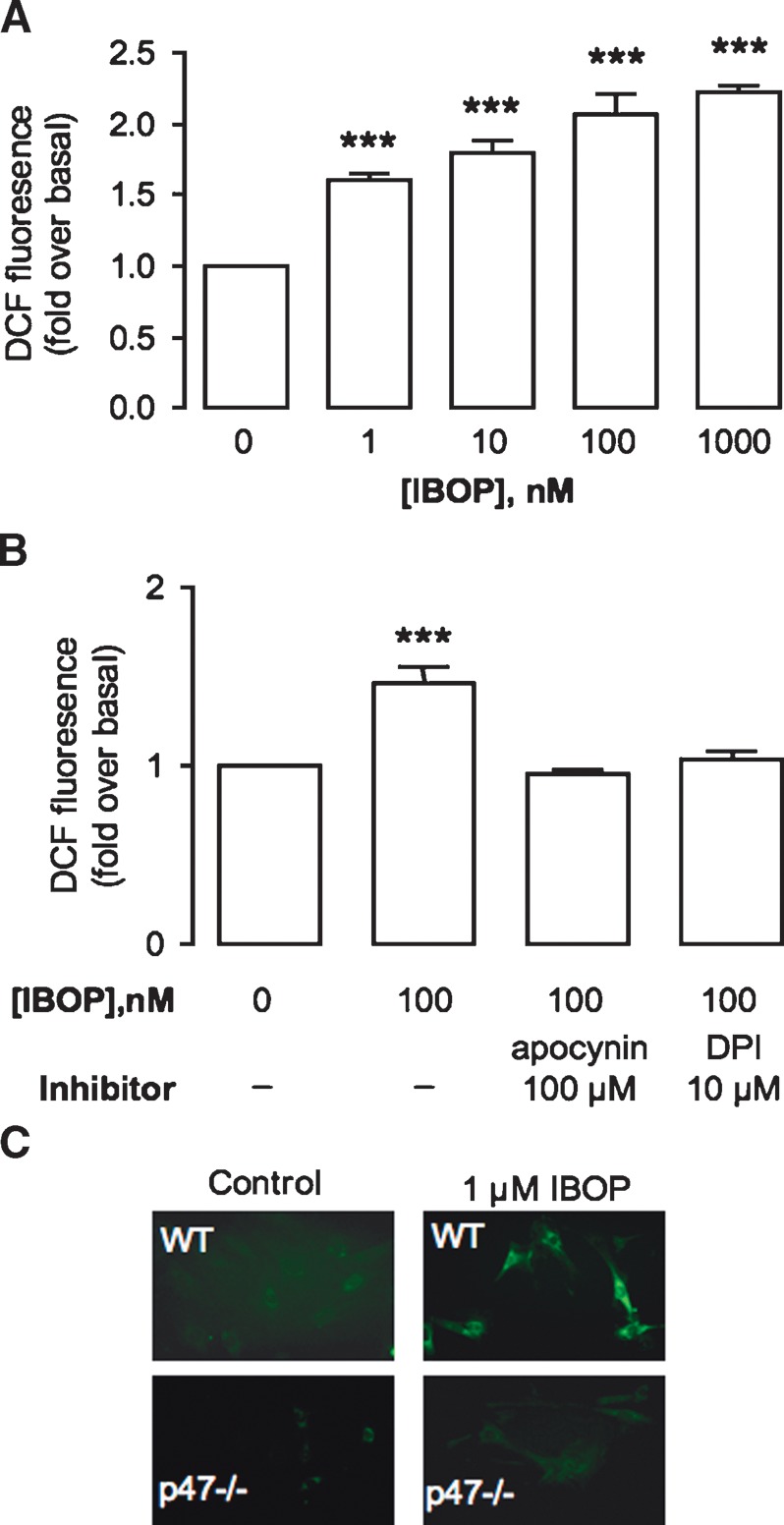
TP-mediated ROS generation. hASMC were treated with IBOP for 3 h (A) or pretreated with NADPH oxidase inhibitors (B) (DPI, 10 μM, or apocynin, 100 μM) for 30 min prior to IBOP (100 nM; 3 h). C: mASMC from wild-type (WT) mice or p47−/− mice were treated with IBOP (1 μM) for 3 h. ROS generation was assessed by fluorescent spectrophotometry or microscopy. Data in A and B are fold over basal ± SE (n = 3). *** P < 0.001 with reference to (w.r.t.) control. Data in C are a representative experiment that was repeated with similar results.
Homologous regulation of TP expression
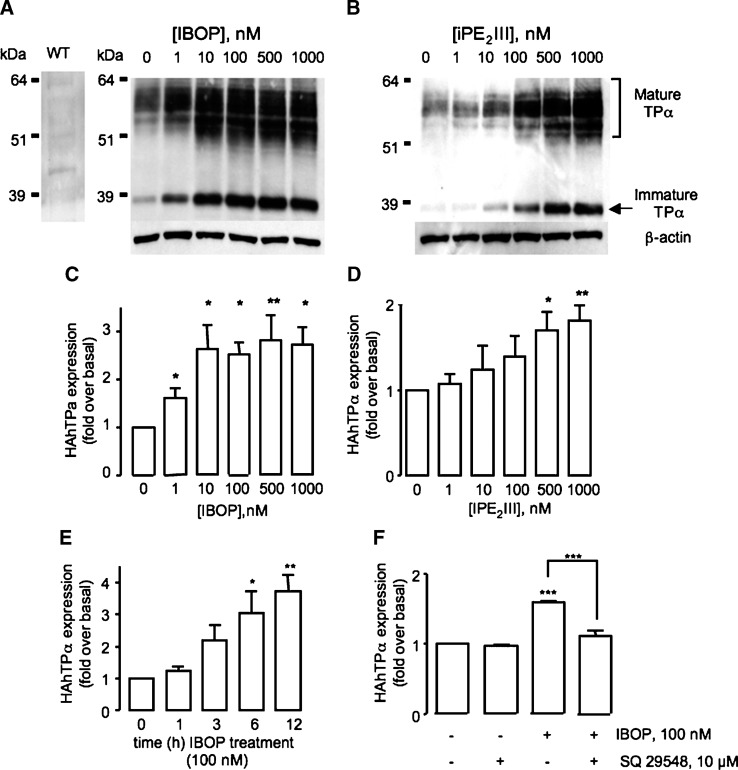
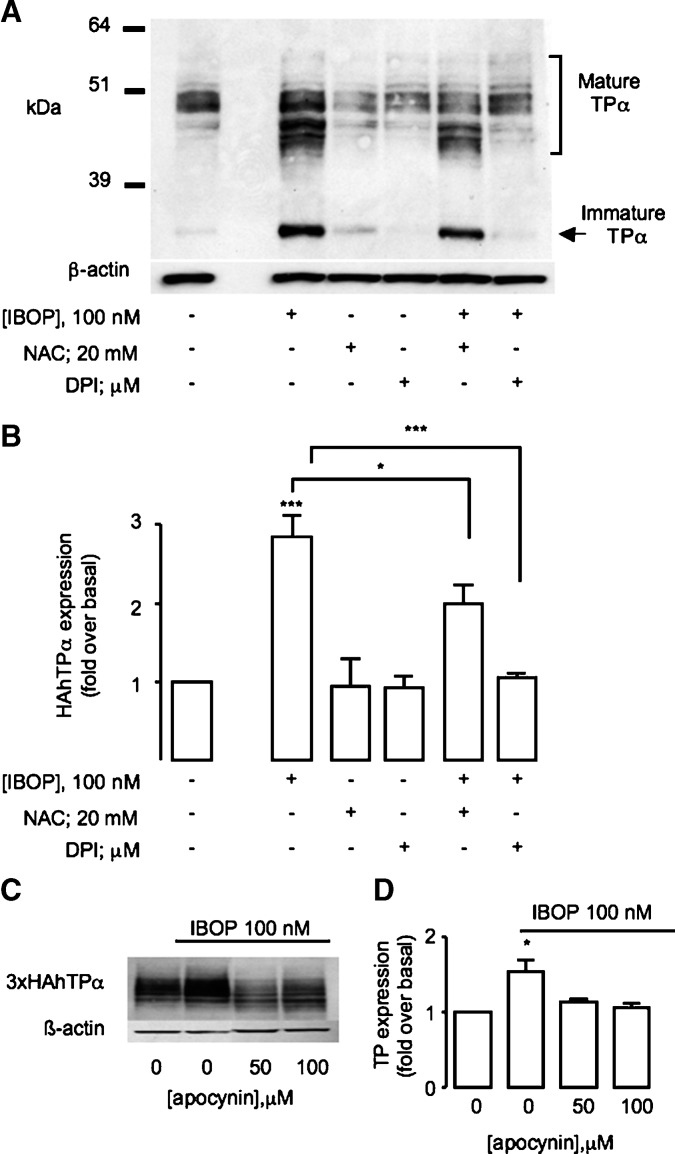
Oxidative challenge of cells with H2O2 increased TP expression (14). We considered whether TP expression was similarly enhanced by ROS generated as part of the TP signaling cascade. This concept deviates from the classical notion of GPCR regulation, in which the activated receptor becomes downregulated (23), and may be highly relevant to increased TP responsiveness in settings of platelet activation, when biosynthesis of TxA2 is markedly increased (24, 25). HEK 293 cells stably expressing HAhTPα (TPα-HEK) were treated for 12 h with increasing concentrations of either IBOP, a TxA2 analog, or iPE2III, a free-radical generated arachidonic acid metabolite that activates the TP in vitro (19) and in vivo (26). TP expression was determined by Western blot analysis. Similar to other GPCRs, differential glycosylation of the TPα (27) gives rise to two major species: the mature, fully glycosylated receptor appears as a broad complex species from 45–60 kDa, while the immature unglycosylated form appears at 39 kDa. These multiple bands were not due to nonspecific antibody binding because neither the mature nor immature TPα species were evident in Western blots of untransfected wild-type HEK cells (Fig. 2A, left panel). Treatment with IBOP (Fig. 2A, C) or iPE2III (Fig. 2B, D) increased expression of both the forms of TPα in a concentration-dependent manner. Maximum induction was evident following treatment with 10–100 nM IBOP (2.63 ± 0.52-fold over basal; P < 0.05, n = 5), consistent with the dose response for TP signaling in these cells (19). A higher concentration of iPE2III (500 nM) was required for TP upregulation (1.7 ± 0.21-fold over basal; P < 0.05, n = 3), consistent with its lower affinity for the receptor (19, 26). TP upregulation was time dependent, with increased expression observed within 6 h (3.03 ± 0.68-fold over basal; P < 0.05, n = 3; Fig. 2E). Pretreatment with the TP antagonist SQ 29548 inhibited IBOP-induced TP upregulation (Fig. 2F).
Fig. 2.
Effect of TP activation on TP expression. TPα-HEK cells were treated with IBOP (A, C) or iPE2III (B, D) for 12 h. Alternatively, HEK 293 cells transiently transfected with 3xHAhTPα were treated with 100 nM IBOP for 1–12 h (E) or pretreated with vehicle or 1 μM SQ 29548 for 30 min (F) prior to 100 nM IBOP for 6 h. Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and HAhTPα detected using an anti-HA antibody. A and B are representative Western blots. Untransfected wild-type (WT) HEK 293 cells, probed for the anti-HA antibody, are shown as a control for nonspecific antibody binding (left panel, A). C–F are mean fold over basal expression of the mature TP ± SEM from densitometric analysis normalized to β-actin (n = 3–5). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.005, and *** P < 0.001 w.r.t. control unless otherwise indicated.
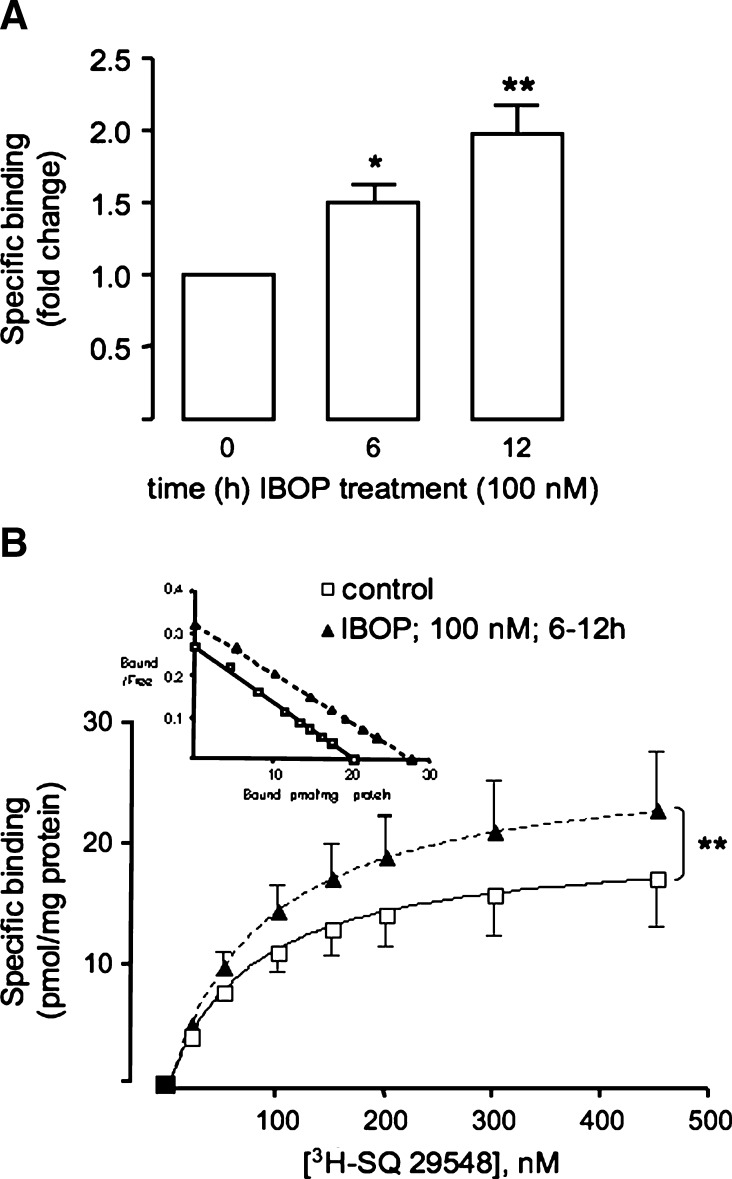
Increased TP expression in IBOP-treated TPα-HEK was confirmed by radioligand binding of 3H-SQ 29548 to crude cell membrane (Fig. 3A). The saturation binding isotherm showed a ∼40% increase in the Bmax (P < 0.05, n = 5), without alteration of the dissociation constant (∼70 nM; Fig. 3B), following IBOP treatment. Importantly, increased TP expression following TP activation was not restricted to HEK 293 cells: IBOP (100 nM) increased expression of the native TP in both human, as assessed by binding of 3H-SQ 29548 to intact cells (2.6 ± 0.5-fold over basal; P < 0.05, n = 3), and mASMC (see Fig. 6).
Fig. 3.
Radioligand binding to TP following IBOP treatment. Crude membranes were prepared from TPα-HEK, treated with or without IBOP (100 nM, 6–12 h). Membrane proteins were incubated with 150 nM (A) or increasing concentrations (B) of 3H-SQ 29548 for 30 min at 30°C. Nonspecific binding was measured using a 500-fold excess of unlabeled SQ 29548. Data are fold change in specific binding compared with control (no IBOP) (A) or specific binding per mg of protein (Scatchard plot in inset) (B). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5–7). *P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01 w.r.t. control.
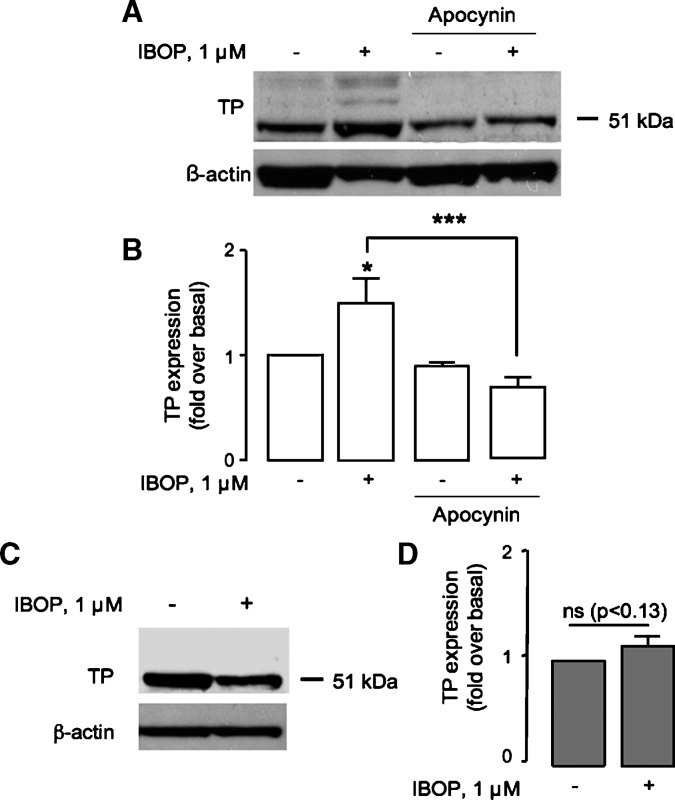
Fig. 6.
TP-NADPH oxidase regulates TP expression in mASMC. A, B: Wild-type mASMC were pretreated with vehicle or apocynin (100 μM, 30 min) prior to IBOP (1 μM, 24 h). C, D: p47−/− mASMC were treated with or without IBOP (1 μM. 24 h). Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and TP detected using an anti-TP antibody. A, C: Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. B, D: Mean fold over basal expression ± SEM from densitometric analysis normalized to β-actin (n = 3). ns, nonspecific. * P < 0.05 and *** P < 0.001 w.r.t. control unless otherwise indicated.
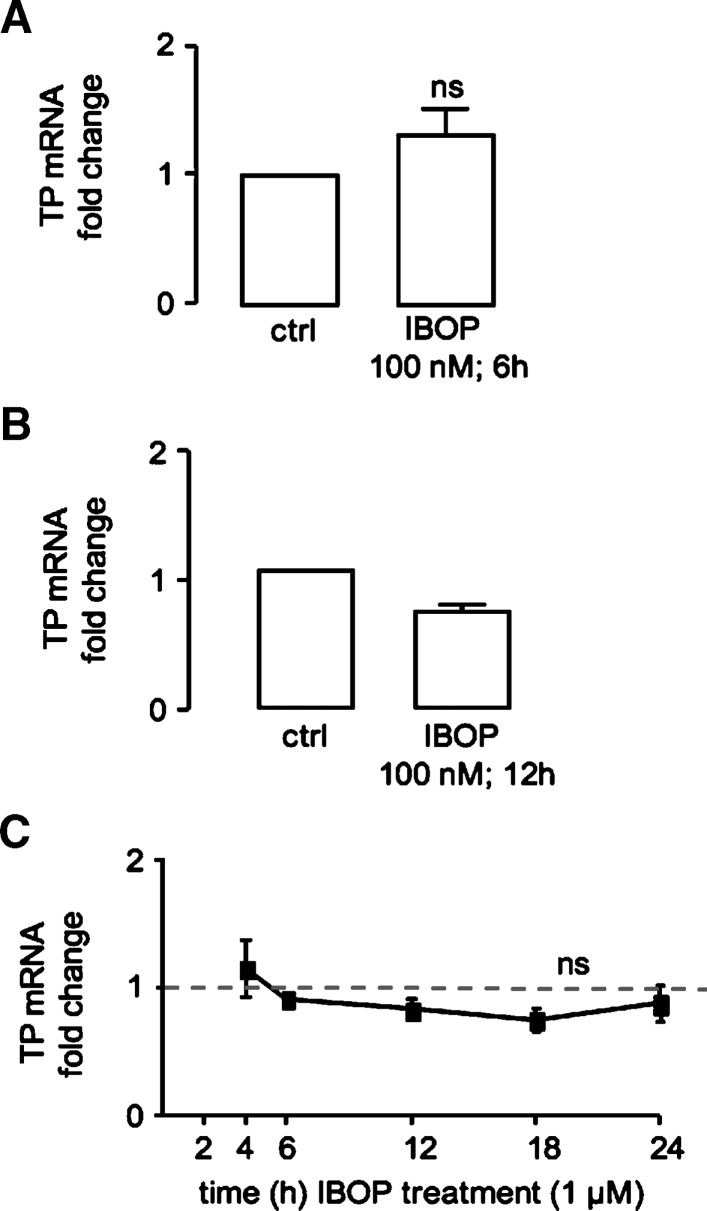
In our HEK 293 cell model, TPα expression is under control of the constitutive cytomegalovirus promoter, making it unlikely that transcriptional changes contributed to TP expression. Indeed, we observed no significant increase in TP mRNA levels in TPα-HEK cells treated with IBOP for 6 h (Fig. 4A) or 12 h (data not shown). Similarly, we observed no increase in TP mRNA in hASMC treated with IBOP (100 nM) for 12 h or 1μM for up to 24 h (Fig. 4B, C). These data argue against contribution of a gene transcriptional event to ROS-dependent upregulation of TP expression.
Fig. 4.
Activation of the TP does not alter TP transcription. TPα-HEK (A) or hASMC (B, C) were serum starved (24 h) before IBOP treatment. Total RNA was extracted and reverse transcribed into cDNA, and TP expression was examined by real-time PCR. Values were normalized to either β-actin or 18S levels and are expressed as the fold change compared with control (no IBOP). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3–5). ns, nonsignificant w.r.t control.
The role of ROS in homologous regulation of TP expression
We next examined whether a redox-dependent mechanism was involved in upregulation of the activated TP. Pretreatment of TPα-HEK with a cell-permeable antioxidant, n-acetyl-cysteine (NAC; 20 mM), abrogated the IBOP-induced (Fig. 5A, B) and iPE2III-induced (data not shown) increase in TPα expression, implicating intracellular ROS generation in TP-dependent TP upregulation. Similarly, DPI or apocynin significantly inhibited IBOP-induced TP upregulation in TPα-HEK (Fig. 5A–D) or ASMC (Fig. 6A, B). Furthermore, IBOP-induced TP upregulation in mASMC was abolished in p47−/− mASMC (Fig. 6C, D). These results indicate that ROS, generated via TP-dependent activation of an NADPH oxidase, underlies TP-dependent increase TP expression.
Fig. 5.
Role of ROS in TP upregulation. A, B: TPα-HEK cells were pretreated with or without an antioxidant (NAC, 20 mM) or flavoprotein inhibitor (DPI, 10 μM), prior to IBOP (100 nM, 12 h). C, D: Transfected transient 3xHAhTPα-HEK were pretreated with or without apocynin, a nonselective NADPH oxidase inhibitor, for 30 min prior to IBOP (100 nM, 12 h). Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and HAhTPα detected using an anti-HA antibody. A, C: Representative Western blot. B, D: Mean fold over basal expression ± SEM from densitometric analysis of the mature TP, normalized to β-actin (n = 5). *P < 0.05 and *** P < 0.001 w.r.t. control unless otherwise indicated.
TP activation induces translocation of TP from the ER to the Golgi
Following synthesis in the ER, correctly folded GPCRs traffic to the Golgi and on to the plasma membrane in their mature form. Posttranslational modifications that occur during this process include glycosylation of the immature receptor, a step that is essential for ER export, and membrane localization of the mature TP (27). The presence of an intracellular receptor reserve has been reported for some GPCRs, including the TP (14) and thrombin receptors (28). Exogenous H2O2 facilitated TP mobilization from the ER to the Golgi (14). We examined whether mobilization of the TP along its biogenic pathways coincided with its upregulation via the TP-derived intracellular ROS pathway. Cell lysates were prepared from TPα-HEK cells, treated (100 nM IBOP; 3 h), and fractionated on discontinuous density gradients optimized for resolution of ER and Golgi membrane fractions (29). In untreated cells, the majority of HAhTPα resided in the heavier fractions (Fig. 7A, fractions 3–8) and colocalized with the ER marker calnexin; little HAhTPα was present in lighter fractions that costained for the Golgi marker, golgin-97. IBOP treatment shifted this distribution, with increased proportion of HAhTPα found in the Golgi fractions (Fig. 7B, fractions 10–12). Similarly, prominent colocalization of HAhTPα with golgin-97 was evident in IBOP-treated cells (Fig. 7C). These data strongly support the concept that activation of the TP facilitates its translocation from the ER to the Golgi along the receptor's biogenic pathway.
Fig. 7.
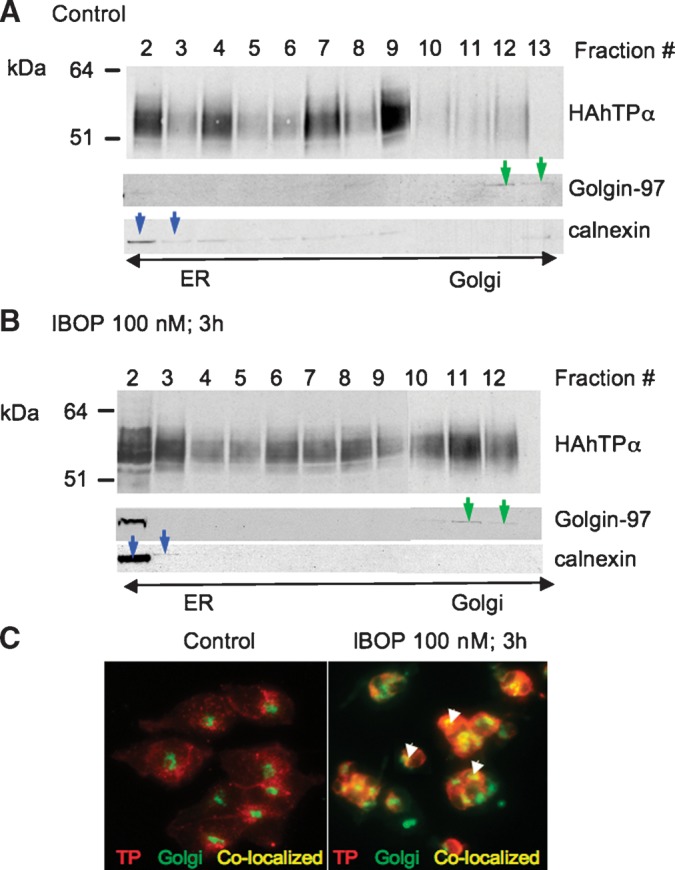
IBOP induces translocation of 3xHAhTPα from the ER to the Golgi. TPα-HEK cells were treated with vehicle or IBOP (100 nM, 3 h). A, B: Cell lysates were fractionated on a discontinous density gradient and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Fractions were identified with marker proteins for Golgi (golgin-97; green arrows) and ER (calnexin; blue arrows). Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. C: HAhTP (red staining) and Golgi (green staining) were visualized in intact cells by immunofluoresence microscopy. Perinuclear staining for TPα was observed in untreated cells, consistent with localization to the ER. Colocalization of HAhTPα and Golgi is in yellow (arrows). Images are from a representative experiment that was repeated with similar results.
Homologous stabilization of TPα
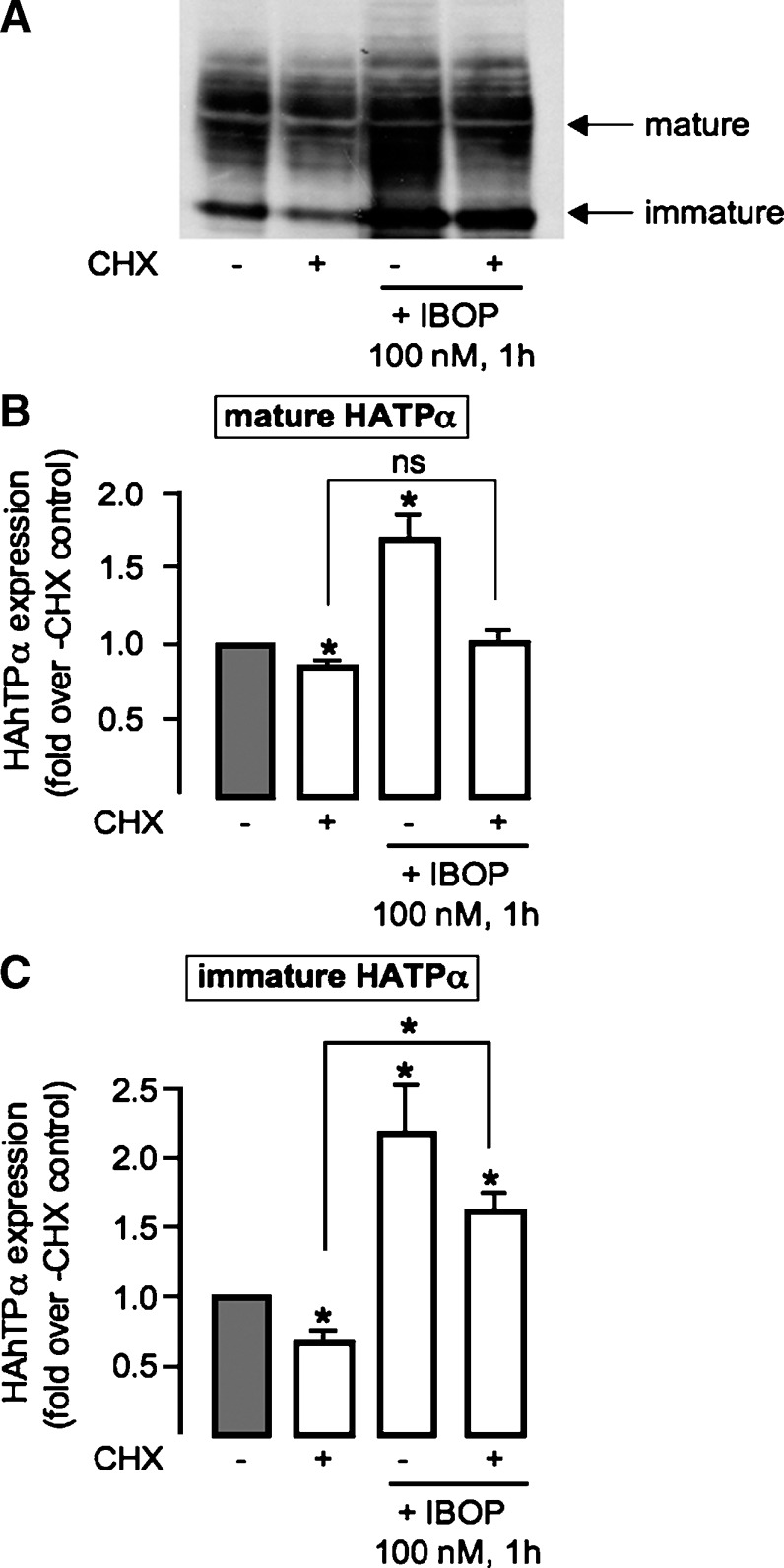
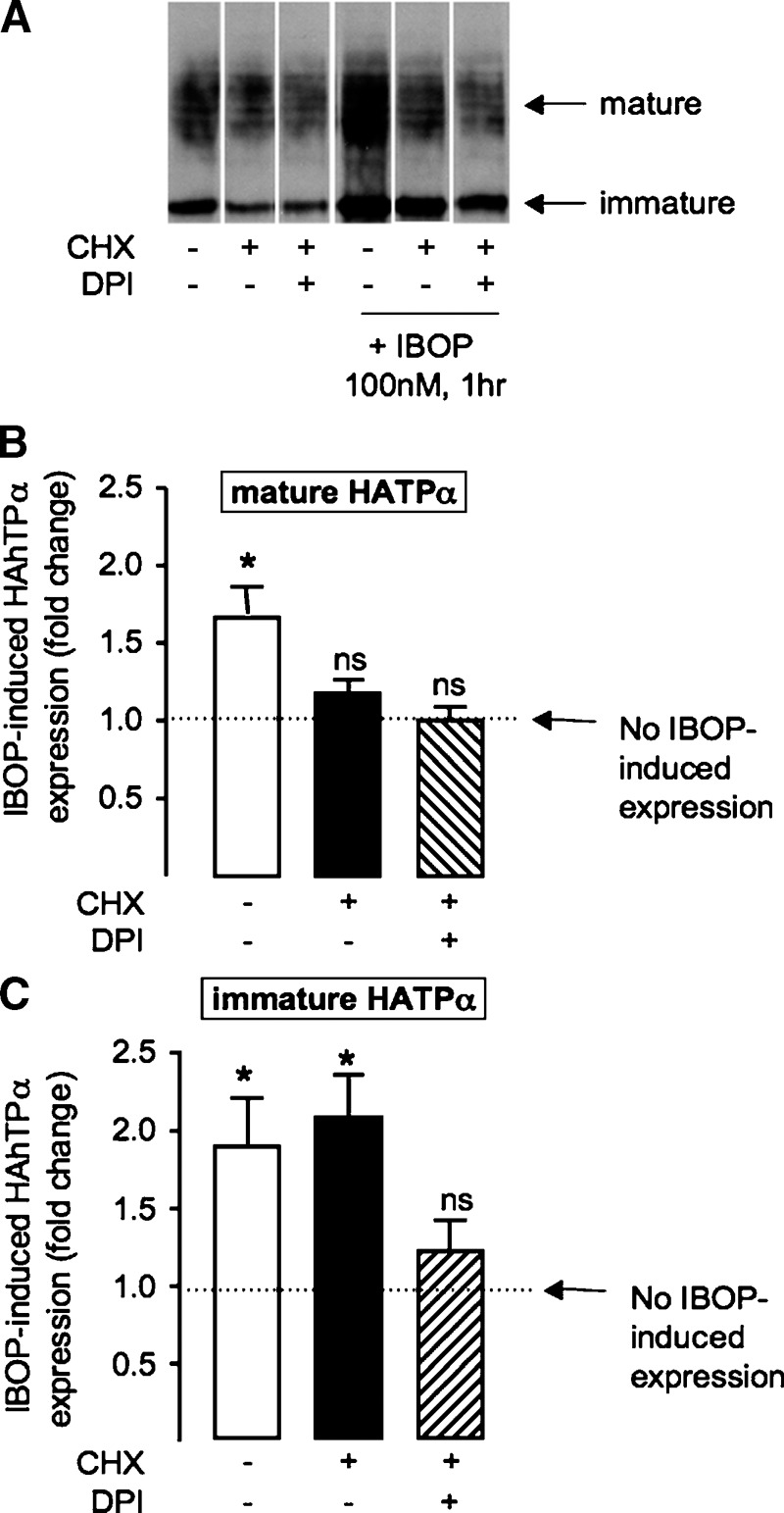
Degradation of TPα was slowed substantially in cells treated with exogenous H2O2 (14). We examined whether the TP-ROS-TP feed-forward cycle involved such a posttranslational mechanism of receptor stabilization. HEK 293 cells, transiently transfected with 3xHahTPα, were pretreated with or without IBOP for 1 h before treatment with cycloheximide, to inhibit de novo protein synthesis and unmask receptor degradation. Conventional pulse-chase methods, which require metabolic labeling with 35S-methionine/cysteine, were not successful, probably because of the small number of these residues in the hTP (data not shown). Therefore, we examined the mature glycosylated, and immature unglycosylated, form of the TP by Western blot. In control cells, levels of the mature and immature TPα were significantly reduced, following cyclohexamide treatment, reflecting degradation. Following pretreatment with IBOP (100 nM, 1 h), degradation of mature TP was unchanged (Fig. 8B). In contrast, degradation of the immature TP form was significantly offset (Fig. 8C) with sustained upregulation despite the presence of cycloheximide. These data are consistent with IBOP-induced stabilization of the TP, early in the receptor's posttranslational processing. This IBOP-induced early stabilization event was reduced in cells treated with DPI (Fig. 9C); in the presence of cyclohexamide, the immature TP band was significantly degraded in cells pretreated with DPI prior to addition of IBOP. These data implicate the TP-ROS signaling pathway in promoting TP biogenesis.
Fig. 8.
Effect of IBOP treatment on TP stabilization. Transiently transfected 3xHAhTPα−HEK were treated with vehicle or IBOP (100 nM) for 1 h. Cells were then treated with or without cycloheximide (CHX; 50 μg/ml) for 6 h to unmask TP degradation. A: Representative Western blot. Data from densitometric analysis of mature TP (B) and immature TP (C) degradation, normalized to β-actin, were expressed as fold change compared with control (cells that received neither IBOP nor CHX; gray bar). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 7). * P < 0.05 w.r.t. control unless otherwise indicated.
Fig. 9.
Role of ROS in homologous TP stabilization. Transiently transfected 3xHAhTPα−HEK were treated with vehicle or IBOP (100 nM) for 1 h in the absence or presence (hatched bars) of DPI (10 μM; 30 min pretreatment). Cells were then treated with (black bars or hatched bars) or without cyclohexamide (CHX; 50 μg/ml) for 6 h to unmask TP degradation. A: Representative Western blot. B and C show densitometric analysis of mature TP (B) and immature TP (C), normalized to β-actin. Fold change in IBOP-induced TP expression was calculated as the ratio of expression in IBOP-treated/non-IBOP-treated cells, with all other treatments being identical. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5). ns, nonsignificant. * P < 0.05 w.r.t. 1-fold (i.e., no effect).
DISCUSSION
Oxidative stress and TxA2 are established mediators of CVD that contribute to vascular injury (4), atherosclerotic lesion formation, and plaque destabilization (3). Our study confirms that, similar to other vasoactive mediators, such as thrombin (30) and angiotensin II (31), TxA2 activates NADPH oxidases (16). However, the relevance of TP-induced ROS generation in mediating the physiological and pathophysiological actions of TxA2 has not been elucidated. Application of exogenous H2O2 promotes stabilization of the TP in transfected cells (14), suggesting a role for ROS in regulating TP responsiveness. This study set out to determine if endogenous ROS, generated as signaling intermediates secondary to TP activation, could stabilize TP and, consequently, augment the receptor's expression. This hypothesis is a departure from the classical understanding of GPCR regulation in which the activated GPCR is downregulated. Two isoforms of the hTP have been described (32). We concentrated on the more ubiquitous TPα (33).
TPα was significantly upregulated, in a time- and concentration-dependent manner following treatment with the TP agonist IBOP, in both transiently and stably transfected HEK 293 cells. This reflected an increase in the receptor Bmax, with no significant change in the dissociation constant for binding, indicating that activation of the TPα produced an increase in functional receptor capable of binding agonist. We did not, however, examine whether TPα signaling was similarly augmented because of the confounding issues of receptor activation, desensitization, and internalization (20, 34), during the continued presence of agonist. Indeed, Western blot does not discriminate between receptor that is available for ligand binding at the plasma membrane versus receptor that is trafficking to or from the membrane. This may explain the apparent discrepancy between the levels of TPα quantified by Western blot (∼2- to 3-fold increase) versus radioligand binding (∼40% increase) in TPα-HEK. Importantly, we observed a similar upregulation response of the native TP in two ASMC models (human and mouse), arguing against experimental artifacts due to TPα overexpression. The consistent increase in high-affinity membrane-associated TPα, particularly the 2-fold increase observed in whole-cell binding of SQ 29548 to hASMC, strongly suggests an upregulation of functional receptor at the cell surface in IBOP-treated cells. This is a remarkable finding, given our previous report that exposure to TxA2 analogs, for a shorter time period (2 h), results in TP internalization and that the internalized receptor is not recycled to the plasma membrane (20). Indeed, these data suggest a distinct feed-forward pathway for upregulation of the homologously activated TP that predominates during continual agonist activation. Such continual activation would be expected in many disease settings, including syndromes of platelet activation and inflammation.
Given the sensitivity of TP expression to exogenous H2O2 (14), we considered whether endogenous ROS generation in response to TP activation can drive TP expression. Pretreatment of TPα-HEK cells with the cell-permeable antioxidant NAC inhibited homologous TP upregulation, consistent with a ROS-dependent mechanism. Several cellular sources of ROS have been described (35–37). Of these, NADPH oxidase is reportedly the major source of ROS in the vasculature (15) and has been consistently implicated in models of CVD (38). This oxidase is a multimeric enzyme complex, consisting of membrane-associated (Nox homologs and p22phox) and cytosoplasmic (p47phox homologs, p67phox homologs, and rac) subunits (39). Several variants of NADPH oxidase, expressed in a cell- and tissue-specific manner, have been reported (40). Both Nox-1 and -4 are expressed in human and mouse ASMC (41, 42). Studies implicate NADPH oxidases as TP effectors (16, 18), although the particular isoform that couples with the TP has not been identified.
We used two pharmacological inhibitors of NADPH oxidases. DPI, a general inhibitor of flavoproteins, including NADPH oxidases, and apocynin, a nonselective NADPH oxidase inhibitor, virtually abolished IBOP-induced TP upregulation in TPα-HEK. Moreover, IBOP treatment did not initiate TP upregulation in ASMCs treated with apocynin or derived from mice genetically lacking the functionally critical p47phox subunit. The internal consistency across the cell types, and between the pharmacological and genetic manipulations used, strongly implicates one or more NADPH oxidases in enhanced expression of the activated TP. We did not assess directly which NADPH oxidase isoform was involved. Indeed, given the consistent responses observed across different cells types, it is possible that more than one isozyme can subserve this function. However, since both apocynin and p47phox deletion can inhibit the function of Nox1, but not Nox 4 (38), the former enzyme is a likely candidate. Currently, we are characterizing the particular NADPH oxdiase subunits that are downstream of TPα and that direct regulation of its expression.
TP upregulation was also induced by the isoprostane iPE2III (Fig. 2C, D). Isoprostanes are free radical-catalyzed products of arachidonic acid that activate the TP in vivo (26). Like TxA2 (43), isoprostanes are elevated in syndromes of vascular disease and are thought to act as pro-atherogenic TP ligands (2, 3). Isoprostane formation in vitro (16) and in vivo (44) occurs secondary to activation of the NADPH oxidase ROS-generating complex. Thus, TP-mediated NADPH oxidase activation may augment formation of isoprostanes, incidental TP agonists, and established biomarker of CVD, driving increased TP expression.
Homologous upregulation of TPα was not dependent on modulation of TPα transcription, suggesting a posttranscriptional mechanism. We examined changes in stability of the activated TP protein. The ER plays a crucial role in protein biosynthesis and quality control (45). Proteins retained in the ER typically undergo rapid proteosomal degradation. Alternatively, proteins may proceed to the Golgi before localization of the mature protein in its appropriate cellular compartment (46). Maturation of many GPCRs, including the TPα (27), involves glycosylation as the receptors moves along this ER-Golgi biogenic pathway. By subcellular fractionation and immunofluoresence microscopy, we observed mobilization of the TPα from the ER to the Golgi following IBOP treatment, consistent with the concept that agonist activation drives TPα biogenesis.
Using cyclohexamide to inhibit protein biosynthesis, we previously demonstrated agonist-dependent degradation of TPα (20). In this study, activation of the TPα with IBOP, prior to addition of cyclohexamide, allowed us to examine whether agonist activation altered TPα stability. We observed that TPα degradation was significantly offset in IBOP-pretreated cells, but not when DPI was added to the IBOP treatment, consistent with ROS-dependent receptor stabilization. Interestingly, stabilization was evident only for the immature (39 kDa) form of the TPα, which localized to the ER fraction (data not shown). Taken together with the observed cellular localization of agonist-activated TPα in the Golgi, these data suggest that ROS-mediated TPα stabilization occurs early in TPα generation, driving immature receptor into the ER-Golgi biogenic pathway. NADPH oxidase subunits are ER localized in both vascular SMCs (47) and endothelium (48), placing this ROS-generating system in an appropriate cellular compartment for manipulation of ER-localized TP.
Under cyclohexamide-treated conditions, stabilization of immature TPα did not translate into a sustained elevation of mature receptor, perhaps because of simultaneous degradation of the mature receptor. Alternatively, the sensitivity of mature TP to cycloheximide in IBOP-pretreated cells may indicate that a chaperone, or other modifying protein, is required for trafficking of the TPα along its biogenic pathway. Indeed, several candidate mechanistic pathways for ROS-dependent upregulation of TPα expression exist. Exogenous H2O2 increases expression of ER chaperone proteins, such as HSP70 (49), and several members of the 14-3-3 family (50). Interestingly, 14-3-3ζ (51) is one of several reported TPα interacting proteins, along with RACK1 (52), Rab11 (53), and peroxiredoxin-4 (54). Recently, a ROS signaling pathway was implicated in TP-dependent activation of AMP-activated kinase in vascular SMCs (55). The contribution of these potential mechanistic pathways to homologous ROS-dependent TPα upregulation is currently being explored.
Both TxA2 (4, 56) and NADPH oxidases (57, 58) have an established role in atherogenesis and in the proliferative response to vascular injury. This study demonstrates that signaling levels of ROS, derived from one or more NADPH oxidases, drive a novel pathway of TP upregulation. Thus, while the activated receptor is being internalized and degraded (20), a distinct ROS-dependent feed-forward pathway drives enhanced receptor biogenesis to ultimately increase expression of functional TP. Activation of this feed-forward loop may underlie the augmented TP expression observed in CVD (6, 7). In addition, oxidant-dependent mobilization of an intracellular TP reserve, via this novel mechanism, may explain the enhanced response to 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α, another TP-dependent isoprostane (2), in oxidatively stressed isolated rat hearts (59). Conceptually, this feed-forward loop is highly relevant to CVD where the milieu of vasoactive mediators generated includes TxA2, isoprostanes, and other NADPH oxidase activators.
Acknowledgments
The assistance of Ms. Jennifer Bruce is gratefully acknowledged.
Abbreviations
ASMC, aortic smooth muscle cells
CVD, cardiovascular disease
DPI, diphenyleneiodonium
ER, endoplasmic reticulum
GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptor
h, human
HA, hemagglutinin
m, mouse
NAC, n-acetyl-cysteine
ROS, reactive oxygen species
SMC, smooth muscle cell
TP, TxA2 receptor
TxA2, thromboxane A2
w.r.t., with reference to
Published, JLR Papers in Press, January 16, 2009.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health/National Heart Lung and Blood Institute Grant HL-066233 to E.M.S.
References
- 1.Smyth, E. M., and G. A. FitzGerald. 2003. Prostaglandin Mediators. In Handbook of Cell Signaling. R. D. Bradshaw, editor. Academic Press, San Diego, CA. 265–273.
- 2.Cayatte A. J., Y. Du, J. Oliver-Krasinski, G. Lavielle, T. J. Verbeuren, and R. A. Cohen. 2000. The thromboxane receptor antagonist S18886 but not aspirin inhibits atherogenesis in apo E-deficient mice: evidence that eicosanoids other than thromboxane contribute to atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20 1724–1728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Egan K. M., M. Wang, M. B. Lucitt, A. M. Zukas, E. Pure, J. A. Lawson, and G. A. FitzGerald. 2005. Cyclooxygenases, thromboxane, and atherosclerosis: plaque destabilization by cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition combined with thromboxane receptor antagonism. Circulation. 111 334–342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cheng Y., S. C. Austin, B. Rocca, B. H. Koller, T. M. Coffman, T. Grosser, J. A. Lawson, and G. A. FitzGerald. 2002. Role of prostacyclin in the cardiovascular response to thromboxane A2. Science. 296 539–541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rudic R. D., D. Brinster, Y. Cheng, S. Fries, W. L. Song, S. Austin, T. M. Coffman, and G. A. FitzGerald. 2005. COX-2-derived prostacyclin modulates vascular remodeling. Circ. Res. 96 1240–1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Katugampola S. D., and A. P. Davenport. 2001. Thromboxane receptor density is increased in human cardiovascular disease with evidence for inhibition at therapeutic concentrations by the AT(1) receptor antagonist losartan. Br. J. Pharmacol. 134 1385–1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dorn 2nd G. W., N. Liel, J. L. Trask, D. E. Mais, M. E. Assey, and P. V. Halushka. 1990. Increased platelet thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptors in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 81 212–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.FitzGerald G. A., J. Tigges, P. Barry, and J. A. Lawson. 1997. Markers of platelet activation and oxidant stress in atherothrombotic disease. Thromb. Haemost. 78 280–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baigent C., and C. Patrono. 2003. Selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors, aspirin, and cardiovascular disease: a reappraisal. Arthritis Rheum. 48 12–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Grosser T., S. Fries, and G. A. Fitzgerald. 2006. Biological basis for the cardiovascular consequences of COX-2 inhibition: therapeutic challenges and opportunities. J. Clin. Invest. 116 4–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Touyz R. M., G. Yao, and E. L. Schiffrin. 2003. c-Src induces phosphorylation and translocation of p47phox: role in superoxide generation by angiotensin II in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23 981–987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Asghar M., A. A. Banday, R. Z. Fardoun, and M. F. Lokhandwala. 2006. Hydrogen peroxide causes uncoupling of dopamine D1-like receptors from G proteins via a mechanism involving protein kinase C and G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 40 13–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Igarashi J., M. Miyoshi, T. Hashimoto, Y. Kubota, and H. Kosaka. 2007. Hydrogen peroxide induces S1P1 receptors and sensitizes vascular endothelial cells to sphingosine 1-phosphate, a platelet-derived lipid mediator. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 292 C740–C748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Valentin F., M. C. Field, and J. R. Tippins. 2004. The mechanism of oxidative stress stabilization of the thromboxane receptor in COS-7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 279 8316–8324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Madamanchi N. R., A. Vendrov, and M. S. Runge. 2005. Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25 29–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Muzaffar S., N. Shukla, C. Lobo, G. D. Angelini, and J. Y. Jeremy. 2004. Iloprost inhibits superoxide formation and gp91phox expression induced by the thromboxane A2 analogue U46619, 8-isoprostane F2alpha, prostaglandin F2alpha, cytokines and endotoxin in the pig pulmonary artery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 141 488–496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Koupparis A. J., J. Y. Jeremy, S. Muzaffar, R. Persad, and N. Shukla. 2005. Sildenafil inhibits the formation of superoxide and the expression of gp47 NAD[P]H oxidase induced by the thromboxane A2 mimetic, U46619, in corpus cavernosal smooth muscle cells. BJU Int. 96 423–427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu S., B. Jiang, K. A. Maitland, H. Bayat, J. Gu, J. L. Nadler, S. Corda, G. Lavielle, T. J. Verbeuren, A. Zuccollo, et al. 2006. The thromboxane receptor antagonist s18886 attenuates renal oxidant stress and proteinuria in diabetic apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Diabetes. 55 110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wilson S. J., A. M. Roche, E. Kostetskaia, and E. M. Smyth. 2004. Dimerization of the human receptors for prostacyclin and thromboxane facilitates thromboxane receptor-mediated cAMP generation. J. Biol. Chem. 279 53036–53047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wilson S. J., J. K. Dowling, L. Zhao, E. Carnish, and E. M. Smyth. 2007. Regulation of thromboxane receptor trafficking through the prostacyclin receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of receptor heterodimerization. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27 290–296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wilson S. J., K. McGinley, A. J. Huang, and E. M. Smyth. 2007. Heterodimerization of the alpha and beta isoforms of the human thromboxane receptor enhances isoprostane signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 352 397–403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pfaffl M. W. 2001. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29 e45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tsao P., and M. von Zastrow. 2000. Downregulation of G protein-coupled receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10 365–369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fitzgerald D. J., F. Wright, and G. A. FitzGerald. 1989. Increased thromboxane biosynthesis during coronary thrombolysis. Evidence that platelet activation and thromboxane A2 modulate the response to tissue-type plasminogen activator in vivo. Circ. Res. 65 83–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fitzgerald D. J., L. Roy, F. Catella, and G. A. FitzGerald. 1986. Platelet activation in unstable coronary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 315 983–989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Audoly L. P., B. Rocca, J. E. Fabre, B. H. Koller, D. Thomas, A. L. Loeb, T. M. Coffman, and G. A. FitzGerald. 2000. Cardiovascular responses to the isoprostanes iPF(2alpha)-III and iPE(2)- III are mediated via the thromboxane A(2) receptor in vivo. Circulation. 101 2833–2840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kelley L. P., and B. T. Kinsella. 2003. The role of N-linked glycosylation in determining the surface expression, G protein interaction and effector coupling of the alpha (alpha) isoform of the human thromboxane A(2) receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1621 192–203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hein L., K. Ishii, S. R. Coughlin, and B. K. Kobilka. 1994. Intracellular targeting and trafficking of thrombin receptors. A novel mechanism for resensitization of a G protein-coupled receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 269 27719–27726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Xia W., J. Zhang, B. L. Ostaszewski, W. T. Kimberly, P. Seubert, E. H. Koo, J. Shen, and D. J. Selkoe. 1998. Presenilin 1 regulates the processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments and the generation of amyloid beta-protein in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Biochemistry. 37 16465–16471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brandes R. P., F. J. Miller, S. Beer, J. Haendeler, J. Hoffmann, T. Ha, S. M. Holland, A. Gorlach, and R. Busse. 2002. The vascular NADPH oxidase subunit p47phox is involved in redox-mediated gene expression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 32 1116–1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ushio-Fukai M., R. W. Alexander, M. Akers, Q. Yin, Y. Fujio, K. Walsh, and K. K. Griendling. 1999. Reactive oxygen species mediate the activation of Akt/protein kinase B by angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274 22699–22704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Raychowdhury M. K., M. Yukawa, L. J. Collins, S. H. McGrail, K. C. Kent, and J. A. Ware. 1994. Alternative splicing produces a divergent cytoplasmic tail in the human endothelial thromboxane A2 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 269 19256–19261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miggin S. M., and B. T. Kinsella. 1998. Expression and tissue distribution of the mRNAs encoding the human thromboxane A2 receptor (TP) alpha and beta isoforms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1425 543–559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Habib A., G. A. FitzGerald, and J. Maclouf. 1999. Phosphorylation of the thromboxane receptor alpha, the predominant isoform expressed in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 274 2645–2651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McNally J. S., A. Saxena, H. Cai, S. Dikalov, and D. G. Harrison. 2005. Regulation of xanthine oxidoreductase protein expression by hydrogen peroxide and calcium. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25 1623–1628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kukreja R. C., H. A. Kontos, M. L. Hess, and E. F. Ellis. 1986. PGH synthase and lipoxygenase generate superoxide in the presence of NADH or NADPH. Circ. Res. 59 612–619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Harrison D., K. K. Griendling, U. Landmesser, B. Hornig, and H. Drexler. 2003. Role of oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 91 7A–11A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Williams H. C., and K. K. Griendling. 2007. NADPH oxidase inhibitors: new antihypertensive agents? J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 50 9–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lyle A. N., and K. K. Griendling. 2006. Modulation of vascular smooth muscle signaling by reactive oxygen species. Physiology (Bethesda). 21 269–280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nauseef W. M. 2008. Biological roles for the NOX family NADPH oxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 283 16961–16965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lassegue B., D. Sorescu, K. Szocs, Q. Yin, M. Akers, Y. Zhang, S. L. Grant, J. D. Lambeth, and K. K. Griendling. 2001. Novel gp91(phox) homologues in vascular smooth muscle cells: nox1 mediates angiotensin II-induced superoxide formation and redox-sensitive signaling pathways. Circ. Res. 88 888–894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ellmark S. H., G. J. Dusting, M. N. Fui, N. Guzzo-Pernell, and G. R. Drummond. 2005. The contribution of Nox4 to NADPH oxidase activity in mouse vascular smooth muscle. Cardiovasc. Res. 65 495–504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pratico D., T. Cyrus, H. Li, and G. A. FitzGerald. 2000. Endogenous biosynthesis of thromboxane and prostacyclin in 2 distinct murine models of atherosclerosis. Blood. 96 3823–3826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Modlinger P., T. Chabrashvili, P. S. Gill, M. Mendonca, D. G. Harrison, K. K. Griendling, M. Li, J. Raggio, A. Wellstein, Y. Chen, et al. 2006. RNA silencing in vivo reveals role of p22phox in rat angiotensin slow pressor response. Hypertension.. 47 238–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Van Craenenbroeck K., S. D. Clark, M. J. Cox, J. N. Oak, F. Liu, and H. H. Van Tol. 2005. Folding efficiency is rate-limiting in dopamine D4 receptor biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 280 19350–19357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sitia R., and I. Braakman. 2003. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum protein factory. Nature. 426 891–894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pedruzzi E., C. Guichard, V. Ollivier, F. Driss, M. Fay, C. Prunet, J. C. Marie, C. Pouzet, M. Samadi, C. Elbim, et al. 2004. NAD(P)H oxidase Nox-4 mediates 7-ketocholesterol-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 10703–10717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Petry A., T. Djordjevic, M. Weitnauer, T. Kietzmann, J. Hess, and A. Gorlach. 2006. NOX2 and NOX4 mediate proliferative response in endothelial cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 8 1473–1484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Madamanchi N. R., S. Li, C. Patterson, and M. S. Runge. 2001. Thrombin regulates vascular smooth muscle cell growth and heat shock proteins via the JAK-STAT pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276 18915–18924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ha M. K., K. Y. Chung, D. Bang, Y. K. Park, and K. H. Lee. 2005. Proteomic analysis of the proteins expressed by hydrogen peroxide treated cultured human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Proteomics. 5 1507–1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yan W., Y. Ding, and H. H. Tai. 2006. 14–3-3zeta interacts with human thromboxane receptors and is involved in the agonist-induced activation of the extracellular-signal-regulated kinase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 71 624–633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Parent A., G. Laroche, E. Hamelin, and J. L. Parent. 2008. RACK1 regulates the cell surface expression of the G protein-coupled receptor for thromboxane A(2). Traffic. 9 394–407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hamelin E., C. Theriault, G. Laroche, and J. L. Parent. 2005. The intracellular trafficking of the G protein-coupled receptor TPbeta depends on a direct interaction with Rab11. J. Biol. Chem. 280 36195–36205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Giguere P., M. E. Turcotte, E. Hamelin, A. Parent, J. Brisson, G. Laroche, P. Labrecque, G. Dupuis, and J. L. Parent. 2007. Peroxiredoxin-4 interacts with and regulates the thromboxane A(2) receptor. FEBS Lett. 581 3863–3868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhang M., Y. Dong, J. Xu, Z. Xie, Y. Wu, P. Song, M. Guzman, J. Wu, and M. H. Zou. 2008. Thromboxane receptor activates the AMP-activated protein kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells via hydrogen peroxide. Circ. Res. 102 328–337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kobayashi T., Y. Tahara, M. Matsumoto, M. Iguchi, H. Sano, T. Murayama, H. Arai, H. Oida, T. Yurugi-Kobayashi, J. K. Yamashita, et al. 2004. Roles of thromboxane A(2) and prostacyclin in the development of atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 114 784–794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Vendrov A. E., N. R. Madamanchi, Z. S. Hakim, M. Rojas, and M. S. Runge. 2006. Thrombin and NAD(P)H oxidase-mediated regulation of CD44 and BMP4-Id pathway in VSMC, restenosis, and atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 98 1254–1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Barry-Lane P. A., C. Patterson, M. van der Merwe, Z. Hu, S. M. Holland, E. T. Yeh, and M. S. Runge. 2001. p47phox is required for atherosclerotic lesion progression in ApoE(−/−) mice. J. Clin. Invest. 108 1513–1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kromer B. M., and J. R. Tippins. 1999. The vasoconstrictor effect of 8-epi prostaglandin F2alpha in the hypoxic rat heart. Br. J. Pharmacol. 126 1171–1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]