Abstract
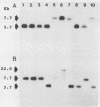
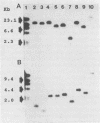
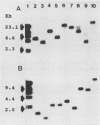
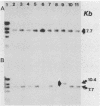
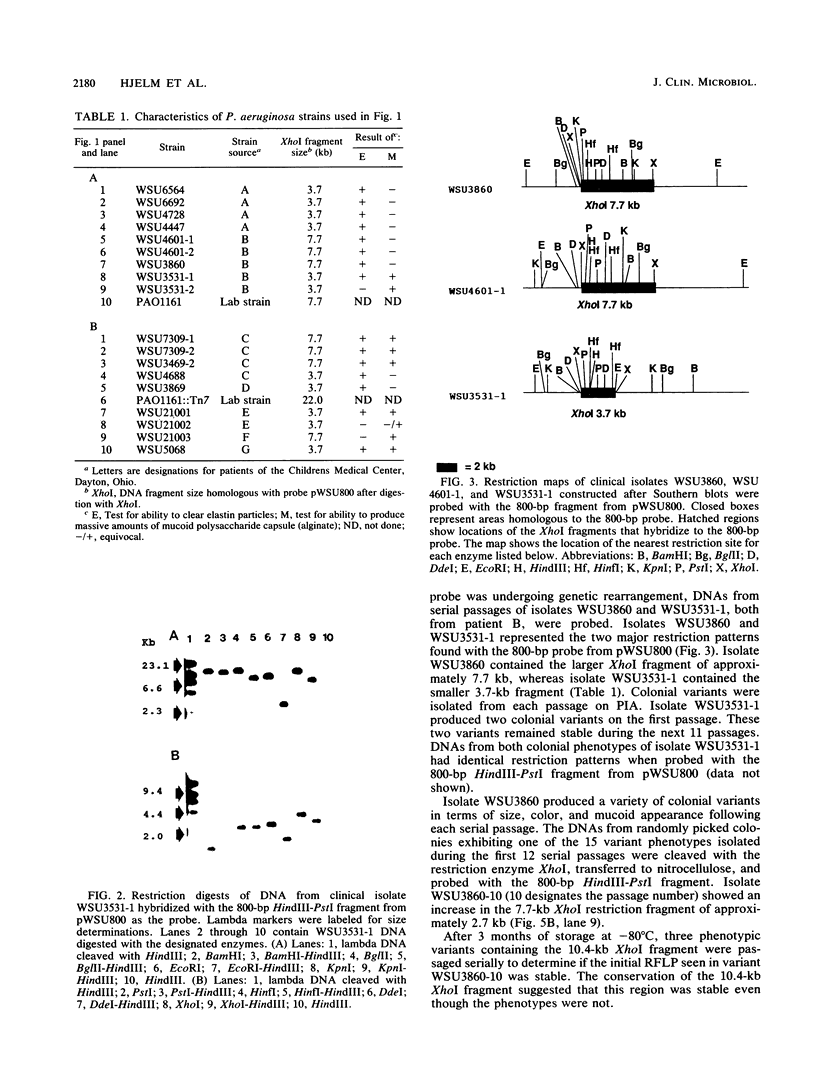
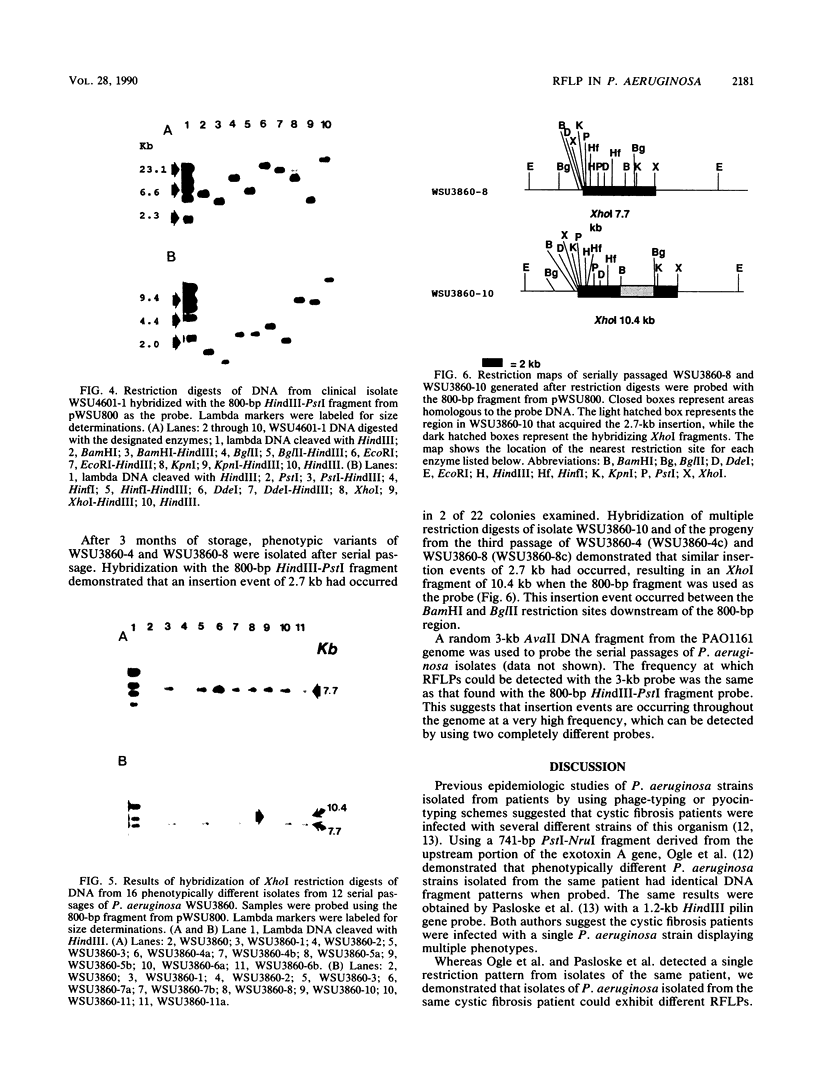
An 800-base-pair HindIII-PstI fragment that flanks a hot spot for Tn7 insertion was isolated from the chromosome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cloned into pUC12. The fragment was used to probe XhoI digests of genomic DNA from 18 P. aeruginosa isolates collected from sputum samples of seven cystic fibrosis patients. Only two XhoI restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), of 3.7 and 7.7 kilobases (kb), were detected. Isolate WSU3531-1 (3.7-kb XhoI fragment) and WSU3860 (7.7-kb XhoI fragment), while isolated from the same patient, showed different RFLPs. Serial passages of isolate WSU3531-1 demonstrated that this strain was phenotypically stable. In contrast, colony and pigment variants were readily isolated at a frequency of 1% from serial passages of isolate WSU3860. When XhoI-digested genomic DNA from phenotypic variants of serially passaged WSU3860 were probed with the 800-base-pair HindIII-PstI fragment, the probe hybridized to a 10.4-kb XhoI fragment from three isolates. Restriction analysis of the genomic DNA digested with a variety of restriction enzymes showed that a 2.7-kb insertion occurred in the same region for all three isolates. There appeared to be no correlation between changes in the RFLP and changes in colony morphology.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. R., Williams P. The influence of environment on envelope properties affecting survival of bacteria in infections. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:527–556. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Tomasek P., Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Gene amplification induces mucoid phenotype in rec-2 Pseudomonas aeruginosa exposed to kanamycin. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):510–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.510-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaby W. L. Study of Dissociative Behavior of Pseudomonas aeruginos. J Bacteriol. 1946 Feb;51(2):217–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosti-Testu F., Norris V., Brevet J. Restriction map of Tn7. Plasmid. 1983 Jul;10(1):96–99. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R. Mucoid variation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced by the action of phage. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Joffe A. M., Sun Q., Volpel K., Paranchych W., Eftekhar F., Speert D. P. Serial isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a cystic fibrosis patient have identical pilin sequences. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):665–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.665-672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. The virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6 (Suppl 3):S617–S626. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_3.s617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D. Biochemical and physiologic basis for susceptibility and resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antimicrobial agents. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6 (Suppl 3):S643–S656. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_3.s643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Schmidt P. J. Dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1003-1010.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Williams R. L. Serotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):521–526. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.521-526.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]