Abstract
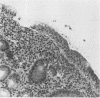
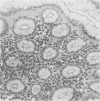
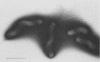
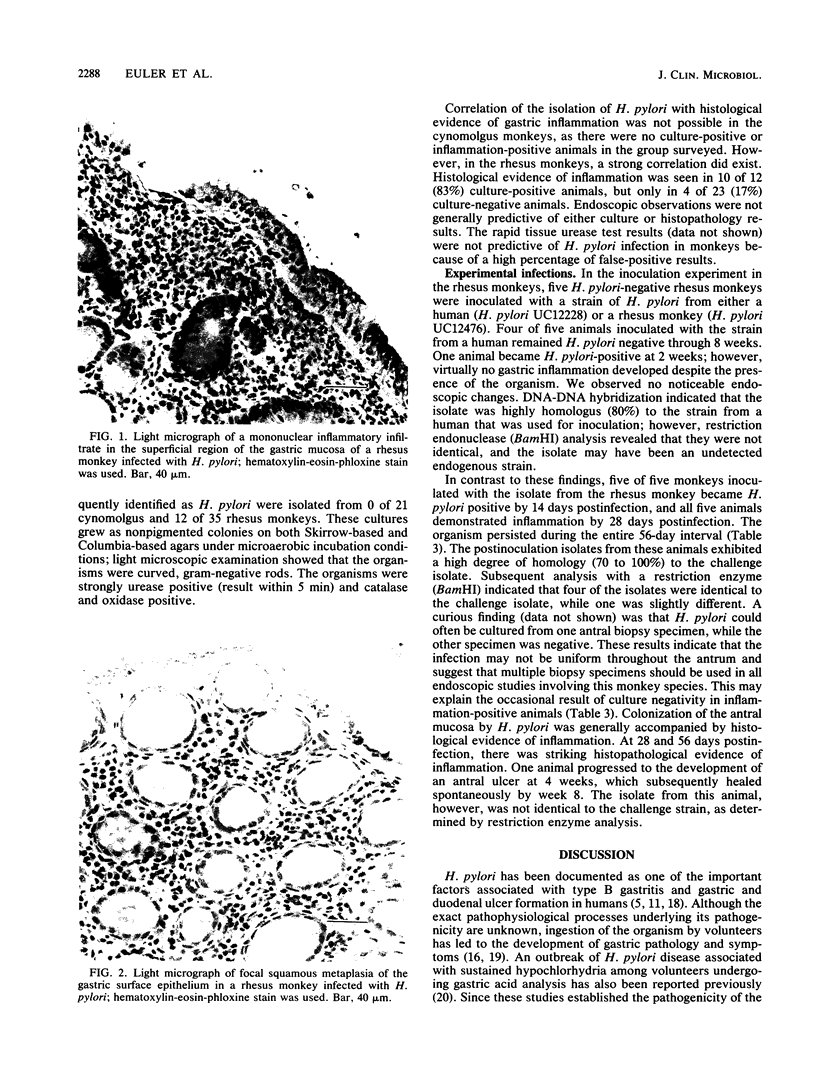
Endoscopic, histologic, and microbiologic evaluations of 21 cynomolgus and 34 rhesus monkeys for naturally occurring Helicobacter pylori infection were done. H. pylori was never isolated from any cynomolgus monkey, but was found in 12 rhesus monkeys. A general correlation existed between a positive culture and a gastric inflammatory response. Inoculation challenges were then undertaken. Four cynomolgus and five rhesus monkeys received two different H. pylori strains isolated from humans. Five rhesus monkeys received an isolate obtained from rhesus monkeys. Evaluation of the cynomolgus monkeys 7 and 14 days later revealed no H. pylori. Endoscopies of the rhesus monkeys were done 7, 14, 21, 28, and 56 days later. One rhesus monkey, which received the isolate from humans, became H. pylori positive at day 21 and remained positive through day 56. Restriction enzyme analysis of genomic DNA at day 56 revealed that the isolate was not identical to the challenge strain isolated from humans. All five rhesus monkeys that received the strain isolated from rhesus monkeys became H. pylori positive by day 14 and remained positive through day 56 Antral inflammation developed in all monkeys. Restriction enzyme analysis of genomic DNA on day 56 confirmed that four of five isolates were identical to the challenge strain isolated from rhesus monkeys. DNA hybridization documented homology between the challenge strains isolated from humans and rhesus monkeys plus those isolated at day 56. In this study, we showed that the rhesus monkey, if given a strain of H. pylori isolated from rhesus monkeys, develops a gastric infection with accompanying histological changes, making this model suitable for further development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskerville A., Newell D. G. Naturally occurring chronic gastritis and C pylori infection in the rhesus monkey: a potential model for gastritis in man. Gut. 1988 Apr;29(4):465–472. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.4.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowry S. C., Chhuttani P. M., Chakravarti R. N., Sehgal A. K. Study of oesophagus, stomach and duodenum of 100 Rhesus monkeys. J Assoc Physicians India. 1966 Apr;14(4):235–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronsdon M. A., Schoenknecht F. D. Campylobacter pylori isolated from the stomach of the monkey, Macaca nemestrina. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1725–1728. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1725-1728.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Dunny G. M., Schultz S. K. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a strain of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid determining erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):283–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.283-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan J. G., Gilligan D., Humphries H., McKenna D., Dooley C., Sweeney E., Keane C., O'Morain C. Campylobacter pylori and recurrence of duodenal ulcers--a 12-month follow-up study. Lancet. 1987 Nov 14;2(8568):1109–1111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91545-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Burette A., Labbe M., Deprez C., De Reuck M., Deltenre M. Campylobacter pylori-associated gastritis: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial with amoxycillin. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Apr;83(4):365–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Delmee M., Bruck C., Labbe M., Avesani V., Burette A. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of Campylobacter pylori to 24 antimicrobial and anti-ulcer agents. Eur J Epidemiol. 1988 Jun;4(2):154–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00144743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Labbe M., Burette A., Delmee M., Avesani V., Bruck C. Treatment failure of ofloxacin in Campylobacter pylori infection. Lancet. 1987 May 9;1(8541):1096–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90527-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Armstrong J. A., Marshall B. J. Campylobacter pyloridis, gastritis, and peptic ulceration. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Apr;39(4):353–365. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.4.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschl A. M., Stanek G., Rotter M., Pötzi R., Gangl A., Hentschel E., Schütze K., Holzner H. J., Nemec H. Campylobacter pylori, Gastritis und Ulcus pepticum. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1987 Jul 17;99(14):493–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert T., Mégraud F., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Susceptibility of Campylobacter pyloridis to 20 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):510–511. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenberg W., Rauws E. A., Widjojokusumo A., Tytgat G. N., Zanen H. C. Identification of Campylobacter pyloridis isolates by restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):414–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.414-417.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski S. I., Goodwin C. S. Restriction endonuclease analysis of the genome of Campylobacter pylori with a rapid extraction method: evidence for considerable genomic variation. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):465–471. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Armstrong J. A., McGechie D. B., Glancy R. J. Attempt to fulfil Koch's postulates for pyloric Campylobacter. Med J Aust. 1985 Apr 15;142(8):436–439. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb113443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Arthur J., Nicholson G. Campylobacter pyloridis infection in Auckland patients with gastritis. N Z Med J. 1986 May 28;99(802):353–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Nicholson G. Ingestion of Campylobacter pyloridis causes gastritis and raised fasting gastric pH. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey E. J., Carey K. V., Peterson W. L., Jackson J. J., Murphy F. K., Read N. W., Taylor K. B., Trier J. S., Fordtran J. S. Epidemic gastritis with hypochlorhydria. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1449–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. D., Berridge B. R. Campylobacter-like organisms in the gastric mucosa of rhesus monkeys. Lab Anim Sci. 1988 Jun;38(3):329–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiatlo A. L., Attar B., Levendoglu H., Go B., Kocka F. E. Identification of Campylobacter pylori by using the rapID NH system. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):341–342. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.341-342.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]