Abstract
Although chemically defined media have been developed and widely used to study the expression of virulence factors in the model plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae, it has been difficult to link specific medium components to the induction response. Using a chemostat system, we found that iron is the limiting nutrient for growth in the standard hrp-inducing minimal medium and plays an important role in inducing several virulence-related genes in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. With various concentrations of iron oxalate, growth was found to follow Monod-type kinetics for low to moderate iron concentrations. Observable toxicity due to iron began at 400 μM Fe3+. The kinetics of virulence factor gene induction can be expressed mathematically in terms of supplemented-iron concentration. We conclude that studies of induction of virulence-related genes in P. syringae should control iron levels carefully to reduce variations in the availability of this essential nutrient.
The type III secretion system (T3SS) is used by diverse plant and animal pathogens to invade and colonize their hosts (1). This secretion system translocates bacterial proteins (effectors) from the bacterial cytoplasm directly into the eukaryotic host cell cytosol, where the effectors subvert host cell processes to the advantage of the pathogen. In Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000, the T3SS is responsible for the elicitation of hypersensitive reactions of nonhost plants and is essential for disease on host plants (14). Many T3SS genes in plant pathogens are denoted hrp, for hypersensitive response and pathogenicity. We know of several regulatory elements that control T3SS genes in P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (7, 27), including HrpL, an alternative sigma factor. However, the exact environmental signals that the bacteria respond to are unknown.
The expression of avrB, a T3SS effector, varies depending on the carbon source in Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea race 0 (9). Other environmental factors affecting the expression of virulence-related genes have also been studied. Nitrogen and osmolarity are important for the expression of the Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae 61 hrp genes (28). Osmotic strength, pH, and carbon source differentially affected the expression of T3SS genes in Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola (18). These results imply that catabolite repression by the tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates may be involved in the induction process. With other pathogenic bacteria, nutritional conditions are reported to be an important factor for the induction of virulence. For example, the Xanthomonas hrp genes are induced by sucrose and sulfur-containing amino acids (21). The optimal condition for hrp gene expression may simulate leaf apoplast environmental factors, including hypo-osmotic pressure, low pH, and limited nutrient concentration (18).
Iron is a micronutrient (required in concentrations less than 10−4 M) for in vitro cultures (22), and the typical concentration needed for optimal bacterial growth is 0.3 to 1.8 μM (24). Iron is an essential element for bacteria due to its participation in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, electron transport, amino acid and pyrimidine biosynthesis, DNA synthesis, and other critical functions (3). Iron uptake must also be regulated due to its lethal effect through the Fenton reaction (2). The effect of iron limitation on bacterial growth has been documented for Escherichia coli cultures (6, 19, 20). Two studies have shown that production of the phytotoxins, syringomycin, and syringotoxin from P. syringae responds in batch culture to iron supplementation (5, 15). Iron is known to alter the physiology of other pseudomonads in both batch and chemostat cultures (11, 16). Although iron is the fourth most abundant element in the earth's crust, its availability is very low due to its low solubility in aqueous solution ([Fe3+] at pH 7, 10−18 μM) (24). Bacteria have evolved complex mechanisms to ensure that iron requirements are met but not exceeded. Siderophore-mediated transport of iron is one of the mechanisms used by bacteria to uptake iron from their environment (17).
In this study, medium components in hrp-inducing minimal medium were evaluated systematically with a chemostat culture. Iron was found to be both a growth-limiting nutrient in hrp-inducing minimal medium and a mediator of virulence gene expression in the model plant pathogen P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacteria and media.
P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 and DC3000 hopA1::mini-Tn5 lux Cmr were obtained from Philip A. Bronstein, USDA ARS, Ithaca, NY. King's B (KB) medium (12) was used for the seed culture. hrp-inducing minimal medium is composed of 0.2% carbon source (e.g., 2.000 g/liter fructose), 5.500 g/liter KH2PO4, 1.500 g/liter K2HPO4, 1.000 g/liter (NH4)2SO4, 0.344 g/liter MgCl2, 0.100 g/liter NaCl, and 0.01% antifoam 204, pH 5.5 (hrpMM0.2F, modified from a medium described in reference 9). The differences between hrpMM0.2F and the original medium described by Huynh et al. (9) involve the amounts of MgCl2 (3.6 versus 1.7 mM), the pHs (5.5 versus 5.7), and the amounts of antifoam 204. Increased magnesium chloride improved growth, and decreased pH made medium preparation easier (personal communication with Dacheng Ren, Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY). Antifoam 204 (0.01%) inhibits formation of foam in long-term cultures. In experiments with and without antifoam, the doubling time of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 growth was not affected by addition of 0.01% antifoam 204 (data not shown). Rifampin (stock of 25 mg/ml in DMSO) was used at 50 μg/ml for the sterility of cell lines in the seed culture. All the iron solutions were prepared as a concentrated solution (2.50 or 3.75 mM ferric citrate, 3.75 or 5 mM iron oxalate, and 37.5 mM iron EDTA) in distilled water with filtration. For pulse injection, concentrated ammonium sulfate solution (0.075 g/ml) and citric acid solution (3.75 mM) were prepared in distilled water with filtration. All the chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. (St Louis, MO).
Batch culture.
A 250-ml Erlenmeyer flask with a Bellco cap (no. 6; Vineland, NJ) was used for 50.0 ml culture. Seed culture (1.0 ml at an optical density at 600 nm [OD600] of 2.500) was washed with fresh, cold hrp-inducing minimal medium prior to inoculation, if necessary. Batch culture was shaken at 250 rpm in a shaking incubator (G24 environmental incubator shaker; New Brunswick Scientific Co., Inc., Edison, NJ) at 30°C. One milliliter of suspension culture was withdrawn for growth measurement in OD600 units by using a spectrophotometer (SmartSpec 3000; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). Two hundred microliters of suspension culture was withdrawn into a 96-well plate (Costar 3912; Corning, Inc., Corning, NY) for luminescence measurement with a luminometer (Veritas Microplate Luminometer, Turner BioSystems, Sunnyvale, CA).
Serial subculture.
Serial batch culture was performed to assess the carryover effect from the seed culture occurring when hrp-inducing minimal medium itself is used. Seed culture was initiated from a frozen stock, and the first inoculation was performed when the seed culture reached an early stationary phase (OD600, ∼2.5). The cell growth was recorded at intervals of 6 h. When the first series of batch culture in a hrp-inducing minimal medium reached an early stationary phase, the second series of batch culture in a hrp-inducing minimal medium was initiated by inoculating the same quantity of cells from the first series. The third series was generated in the same way.
Continuous culture.
A custom-made continuous-culture system was used. Spinner flasks (Bellco Biotechnology) were used as a reactor (reaction volume, 75.0 ml). Agitation (∼300 rpm) was controlled with a magnetic stirrer (Bell Stir Magnetic Stir 9; Bellco Biotechnology). Temperature was controlled at 30 ± 1°C in an incubator (Forma Scientific, Inc., Marietta, OH). Feed and harvest flow rates were controlled using P625 peristaltic pumps and tubings (P625/TSD015S or P625/TSD020S) (Instech Lab., Plymouth Meeting, PA) from a part of a Cellstation high-throughput bioreactor (Fluorometrix Corp., Baltimore, MD) or a four-channel 205S peristaltic pump (Watson-Marlow Bredel, Inc., Wilmington, MA) with Ismatec PharMed BPT pump tubings (0.51 mm; Cole-Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL). One arm of the spinner flask was capped with a silicon stopper (no. 00; Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) with stainless steel tubing for sparging. Compressed air was fed through a compressed-air filter (B547-02AGCGX33; Watts Fluidair, Richland, MI) and filtered through a venting filter (Whatman, Inc., Florham Park, NJ). Sparging was controlled with flow meters (no. 7262; Matheson Tri-Gas, Montgomeryville, PA) at an airflow rate of 1.00 standard cubic feet/hour (472 ml/min) for six spinner flasks. All the silicone tubings (various sizes, primarily 0.79-mm inside diameter) and fittings (various types, sizes, and materials) were purchased from Cole-Parmer. All the stainless steel tubings (0.79- and 4.8-mm inside diameters) were obtained from McMaster-Carr (New Brunswick, NJ). After a seed culture was inoculated into hrp-inducing minimal medium, a batch culture was initiated. When the culture reached an appropriate level of cell mass (OD600, ∼0.5), pumps were initiated for a continuous culture. The other arm of the spinner flask was capped with a Bellco cap (no. 00), providing flow of sterile air in and out. Fluid could be added or samples removed using a syringe and needle through this cap. Approximately 1.3 ml of suspension culture was withdrawn from a reactor to measure OD600 and luminescence.
RNA transcription comparison.
After a chemostat culture of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 in hrpMM0.2F reached a steady state (D = 0.070 ± 0.003 h−1), the culture from the system outlet was collected for 3 h (time preinjection of −10 to −7 h). Filter-sterilized iron oxalate was injected at 50 μM into the reactor, and then the culture was collected for 3 h (0 to 3 h or 3 to 6 h, with time zero corresponding to the time of iron injection). Ten milliliters of the cultures was pelleted by centrifugation at room temperature for 5 min at 10,000 × g, and the supernatant was removed. RNA was isolated from the samples by using an RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Carlsbad, CA) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. RNA was treated with Turbo DNase (Ambion, Austin, TX) to remove residual DNA and then cleaned and concentrated using a MinElute kit (Qiagen). Removal of DNA was verified by quantitative real-time PCR (23). Real-time PCR was performed by using the IQ5 sequence detection system (Bio-Rad) and iQ SYBR green Supermix (Bio-Rad) in accordance with the manufacturer's protocols. One hundred nanograms of total RNA was reverse transcribed in a thermocycler with an iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad) according to the manufacturer's instructions. One milliliter of the resulting total cDNA population was mixed with 0.4 μM concentrations of each primer previously reported (23, 25) and 10 μl of iQ SYBR green Supermix (Bio-Rad) in a 20-μl final volume. The PCR assay was carried out with one cycle at 95°C for 2 minutes and 30 seconds, followed by 32 cycles at 95°C for 15 s and 60°C for 30 s. The amount of double-stranded DNA in each sample was determined at the end of every PCR cycle by measuring fluorescence, which is generated by the incorporation of SYBR green dye. Controls without reverse transcription and without a template were used to assess DNA contamination and the formation of primer dimmers. The production of nonspecific products was determined by the dissociation protocol included in the software provided with the IQ5 real-time-PCR machine. The resulting threshold cycle (CT) values were calculated by the IQ5 software and analyzed using the relative-standard-curve method (for separate tubes) described in ABI user bulletin no. 2. For each strain, the CT values of each gene tested were normalized to the CT values of gyrA housekeeping genes. Another housekeeping gene, gap-1, was also tested, as a negative control.
RESULTS
Reduction of growth in hrp-inducing minimal medium by use of serial subcultures.
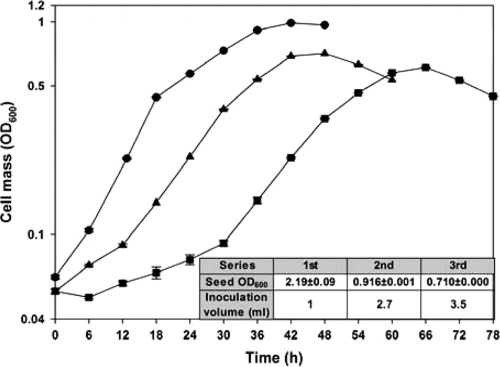
The T3SS genes in P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 are induced in hrp-inducing minimal medium with 0.2% fructose (hrpMM0.2F) (9). The medium is widely used to culture P. syringae and is thought to mimic the apoplastic environment, the major route through which plant pathogens attack the host plants (18). In order to evaluate the reproducibility of growth in hrp-inducing minimal medium under typical laboratory culture protocols, a serial subculture in hrpMM0.2F was performed using seed culture grown in rich KB medium (12). To maintain the same quantity of inoculated cells from the corresponding parental culture, the inoculation volume was varied (Fig. 1, inset table). Figure 1 shows that both maximum growth yield and growth rate are reduced and that adaptation periods, including a lag phase, are prolonged as the subculture number increases. To enter the maximal-specific-growth-rate phase, the first series required 0 to 6 h, the second 12 h, and the third 30 h. The maximum specific growth rate (Fig. 1) decreases with each transfer, from 0.127 ± 0.002 h−1 at the first transfer to 0.077 ± 0.007 h−1 by the third transfer. This result suggests that some critical nutrient(s) may be absent in hrpMM0.2F and that nutrients carried over from the seed culture in rich KB medium support more-rapid growth and reduce the adaptation periods.
FIG. 1.
Serial batch subculture of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 in hrp-inducing minimal medium with 0.2% fructose demonstrates a carryover effect from seed culture grown in KB medium. The first serial culture was derived by transferring 1.0 ml of seed culture into KB medium (OD600, 2.19 ± 0.09) to 50.0 ml of freshly prepared hrp-inducing minimal medium without a washing step. The second and third serial cultures were generated by inoculating the same amount (OD600) of the corresponding parental cultures to 50.0 ml of freshly prepared hrp-inducing minimal medium (see inset table). •, first serial culture; ▴, second serial culture; ▪, third serial culture.
Identification of the growth-limiting nutrient in hrp-inducing minimal medium.
The medium components in hrpMM0.2F were evaluated to identify possible limiting nutrients. Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur, phosphorous, magnesium, and potassium are generally thought to be macronutrients. Since hrpMM0.2F is basically a phosphate-buffered medium, phosphorous and potassium are unlikely to be limiting nutrients. In P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 batch cultures, the residual concentration of fructose was found to be about 30% of the initial concentration (618 ± 262 mg/liter; n = 4). For chemostat cultures (dilution rate range, 0.061 to 0.086 h−1), the residual concentration of fructose in the reactor was about 90% of the feed concentration after the culture reached a steady state. Both results indicate that fructose is not the limiting factor. We used pulse injection experiments with chemostat cultures (4, 13, 29) to evaluate if the nitrogen source or other components were limiting for growth. After a steady state was reached, candidate compounds were directly pulse injected into the reactor by using a syringe. Culture density (OD600) was recorded to assess the effect of the pulse of the given compound. Pulse injection with ammonium sulfate (final concentration, 2.0 g/liter [twice the level found in hrpMM0.2F]) resulted in no changes in growth (Fig. 2), indicating that nitrogen and sulfur sources are not limiting nutrients.
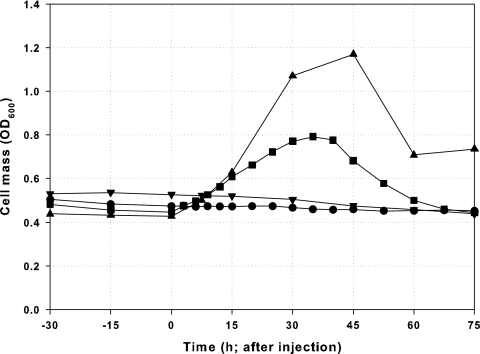
FIG. 2.
Pulse injection of various medium components from hrp-inducing minimal medium with 0.2% fructose by use of continuous cultures of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 to identify limiting nutrients. •, ammonium sulfate (2.0 g/liter [twice the level found in hrpMM0.2F]; dilution rate, 0.061 ± 0.002 h−1); ▪, iron citrate (50 μM; [Fe3+], 50 μM; dilution rate = 0.071 ± 0.001 h−1); ▾, citric acid (50 μM; dilution rate, 0.068 ± 0.001 h−1); ▴, iron oxalate (50 μM; [Fe3+], 100 μM; dilution rate, 0.068 ± 0.001 h−1).
Among trace metals, iron was suggested as a candidate because of its relation to virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its low solubility. Iron citrate was injected at 50 μM, resulting in a strong positive response in growth (Fig. 2). To distinguish the contribution of iron from that of citrate, citric acid was injected at the same concentration (50 μM), resulting in no growth enhancement (Fig. 2), while the injection of an alternative iron source, iron oxalate (100 μM Fe3+), resulted in a similar growth-enhancing response (Fig. 2). A comparison of the effects of different amounts of ferric ion shows a dose-dependent growth enhancement, with a change in OD600 (ΔOD600) of 0.35 with a pulse of 50 μM Fe3+ and a ΔOD600 of 0.74 with a pulse of 100 μM Fe3+. The stoichiometric ratio of cell mass change to iron addition is consistent with the assumption that iron is the sole growth-limiting nutrient in this medium.
Effect of ferric ion on induction of virulence-related genes.
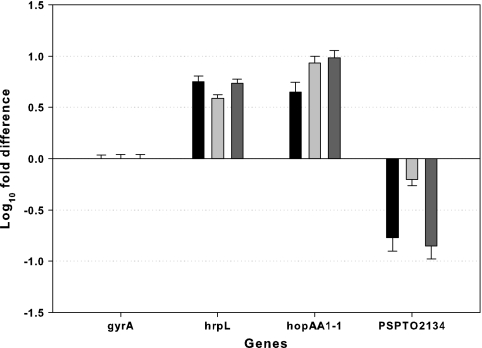
mRNA levels for selected genes were compared using quantitative real-time PCR of wild-type P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 after pulse injection with 50 μM iron oxalate (thus, 100 μM Fe3+). hrpL encodes the major regulator of T3SS genes, hopAA1-1 encodes a T3SS effector protein, and PSPTO2134 is a pyoverdine biosynthesis gene. As a control, a general housekeeping gene, gyrA, was used. The results show that the mRNA levels of the two virulence factors increased in response to elevated iron concentration, whereas PSPTO2134 levels decreased as expected (Fig. 3).
FIG. 3.
The amounts of RNA transcripts for four selected genes are compared between a steady-state culture (the collection time was between −10 and −7 h before the pulse injection) in hrp-inducing minimal medium with 0.2% fructose without iron and a pulse-perturbed continuous culture (the collection time was 0 to 3 h or 3 to 6 h after the pulse injection) by using a pulse of 50 μM iron oxalate with a dilution rate of 0.070 ± 0.003 h−1. The amounts of mRNA of each gene were normalized to gyrA mRNA levels. Log10 difference was calculated as log10 (normalized amounts of RNA of test gene from pulse/normalized amounts of RNA of test gene from steady state). Each column bar represents an independent experiment set (three biological replicates). Error bars represent the standard deviations for three technical replicates for each independent experiment set. gyrA, a general housekeeping gene; hrpL, the major regulatory gene for T3SS; hopAA1-1, a T3SS effector gene; PSPTO2134, a pyoverdine biosynthesis gene.
To further explore the induction of T3SS genes in response to iron, we utilized a mutant DC3000 strain in which a promoterless luxCDABE transposon was inserted into hopA1, a T3SS effector gene (P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 hopA1::mini-Tn5 lux Cmr). This strain is referred to below as DC3000-lux. When the continuous culture with DC3000-lux reached a steady state, 500 μM Fe3+ (iron EDTA) was pulse injected, resulting in growth enhancement and the induction of hopA1, as reported by luminescence (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). Both the luminescence and the RNA transcript responses indicate that iron modulates virulence factor induction of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 and DC3000-lux when they are grown in hrp-inducing minimal medium. Thus, DC3000-lux can be used as a reporter of hopA1 induction and responds similarly to P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000.
Kinetic study of the effect of iron on the growth and expression of hopA1.
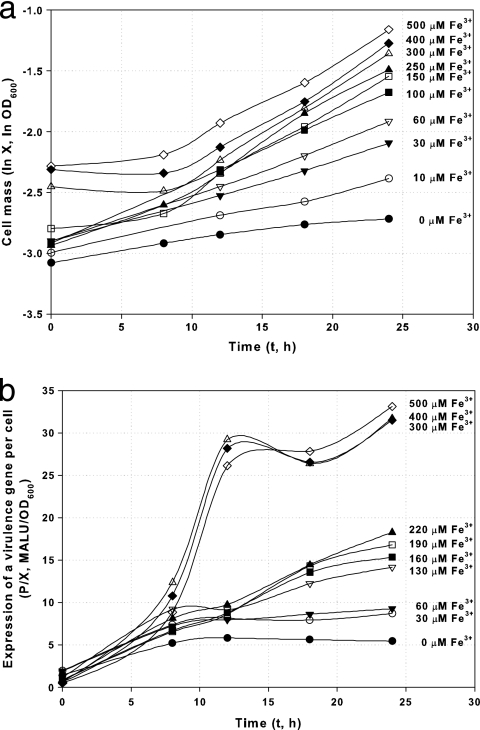
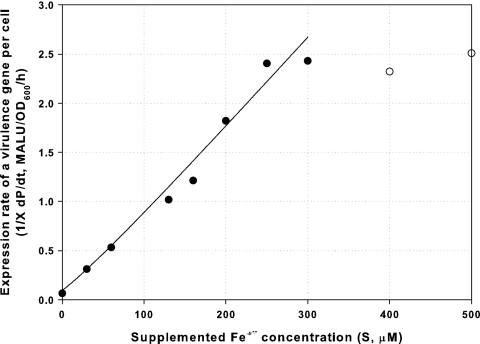
To quantitatively evaluate the dependency of growth and expression of virulence factors on iron, a batch kinetic study was performed with DC3000-lux at various iron concentrations. For this experiment, an additional washing step was performed before inoculation to remove medium component carryover from the KB seed culture. Cells showed exponential growth during the first 24 h, as shown in Fig. 4a. Although identical amounts of inocula were used, the observed initial OD600s in medium with higher concentrations of Fe3+ (such as 400 and 500 μM) were higher than the OD600s observed in medium with lower levels of Fe3+. We attribute this effect to light scattering and absorption due to the formation of precipitates initiated by high levels of Fe3+ and confirmed this by measuring the OD600 of uninoculated medium with high concentrations of Fe3+. However, the specific growth rate increases with Fe3+ concentration, as indicated by the slope of each line in this logarithmic plot.
FIG. 4.
Growth (a) and expression kinetics (b) of a reporter for a virulence gene per cell in DC3000-lux (P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 hopA1::mini-Tn5 lux Cmr). Cells were harvested from batch culture in hrp-inducing minimal medium with various concentrations of Fe3+. Note that Fe3+ levels above 300 μM are growth inhibitory (Fig. 5) but that the expression of the virulence gene is enhanced significantly after 10 h by addition of iron at levels greater than 300 μM. MALU, mega-ALU; X, cell mass measured by optical density; P, expression of a virulence gene as measured by luminescence.
The expression of a virulence gene was assayed by measuring the luminescence of DC3000-lux as a proxy for general virulence factor expression, assuming that the level of expression is correlated with luminescence in this mutant. The profile of specific luminescence (in arbitrary luminescence units [ALU]/OD600 unit) is dependent on Fe3+ concentration, as shown in Fig. 4b.
Evaluation of kinetic data.
The kinetic data support the development of a mathematical model as described in the supplemental material. The growth rate for up to 300 μM added iron can be described by a Monod-type equation. At higher values of iron, growth inhibition becomes apparent. Because unsupplemented hrp-inducing minimal medium has some iron, the Monod equation is modified by a term, μ0, as shown in equation 1.
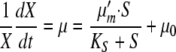 |
(1) |
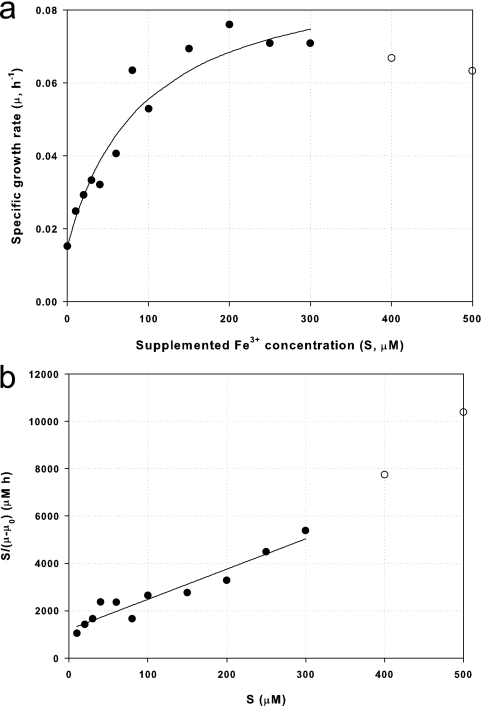
where X is cell mass (as measured by OD600), μ is the specific growth rate (h−1), μm′ is the maximum growth rate increase due to iron supplementation (h−1), KS is the saturation constant for growth on Fe3+ (μM), S is the concentration (μM) of supplemented Fe3+, and μ0 is the growth rate with no supplemental Fe3+, equaling 0.15 h−1 (see the supplemental material). By use of the data from Fig. 5, the value of μm′ was determined to be 0.078 h−1 and the value of KS to be 94.1 μM (see the supplemental material).
FIG. 5.
Effect of Fe3+ concentration on specific growth rate of DC3000-lux (P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 hopA1::mini-Tn5 lux Cmr) (data are obtained from Fig. 4a). (a) Saturation curve, μ = (μ′m·S)/(KS + S) + μ0, where μm′ is 0.078 (h−1), μ0 is 0.015 (h−1), and KS is 94.1 (μM). (b) Hanes-Woolf plot, S/(μ − μ0) = (1/μ′m)·S + (KS/μ′m). •, experimental results up to 300 μM Fe3+; ○, experimental results over 400 μM Fe3+; —, prediction from Monod-type equation 1 or the Hanes-Woolf plot (see equation S2 in the supplemental material) up to 300 μM Fe3+ (the equation is not valid at higher iron concentrations).
The rate of increased luminescence to increased biomass (dP/dX) is linearly related to iron concentration (S) and two parameters, α and β, according to the following equation:
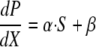 |
(2) |
As shown in the supplemental material, α is 9.91 × 104 ALU/OD600 unit/μM and β is 6.19 × 106 ALU/OD600 unit.
Equations 1 and 2 can be combined (see the supplemental material) to yield the following:
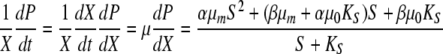 |
(3) |
where μm is μm′ + μ0, which is 0.093 h−1.
As shown in Fig. 6, the data fit equation 3 very well for Fe3+ concentrations up to 300 μM initial supplementation. This relation should prove useful for predicting potential virulence induction by P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 under iron-limited conditions.
FIG. 6.
Relationship between supplemented-iron concentration and the expression rate of the virulence reporter gene per cell 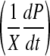 for DC3000-lux (P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 hopA1::mini-Tn5 lux Cmr), as described by equation 3. The equation is valid for supplemented-iron concentrations up to 300 μM (data points are obtained from Fig. 5a and Fig. S4 in the supplemental material by the equation
for DC3000-lux (P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 hopA1::mini-Tn5 lux Cmr), as described by equation 3. The equation is valid for supplemented-iron concentrations up to 300 μM (data points are obtained from Fig. 5a and Fig. S4 in the supplemental material by the equation 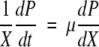 ). •, experimental results up to 300 μM Fe3+; ○, experimental results over 400 μM Fe3+; —, prediction from equation 3 up to 300 μM Fe3+.
). •, experimental results up to 300 μM Fe3+; ○, experimental results over 400 μM Fe3+; —, prediction from equation 3 up to 300 μM Fe3+.
DISCUSSION
Environmental factors such as nutrients influence the induction of virulence factors (9, 18, 28). The chemostat, when operated at steady state, makes it possible to study the effects of individual environmental factors in a constant environment. By use of pulse injection experiments with a chemostat (4, 13, 29), iron was found to be a limiting nutrient for P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 growth in hrp-inducing minimal medium, showing a dose-dependent response. In the absence of cells, the initial concentration of a chemical provided in a pulse is expected to be reduced to less than 5% of the original dose after three residence times (1/D) (4, 13). However, the effect of iron addition lasted for 10 residence times, with the maximum response recorded at about 3 residence times following pulse injection. This delay probably represents dynamics of iron uptake, sequestration in the cell, and dynamics of utilization.
Our growth results match well with those for E. coli growth in an iron-deficient medium (20). Iron deficiency has been reported to alter respiration and energy coupling in E. coli, reducing respiration rates and levels of nonhaem iron (8, 19). In P. syringae pv. glycinea race 0, growth is inversely correlated with avr and hrp induction (9). Our results for P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 indicate that iron enhances both growth and the expression of virulence factors. The dependency of P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 growth on various concentrations of initial iron and the fact that the dependency follows a Monod equation (for up to 300 μM of supplemented iron) show that iron is a true limiting nutrient. Unlike for other bacterial systems, where optimal growth can be attained with a micromolar amount of iron (6, 8, 20, 24), we observe that for P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000, the iron-rich condition is around 200 μM and iron toxicity begins at over 400 μM. The toxicity was expected because iron catalyzes the Fenton reaction, producing the highly reactive hydroxyl radical, which can cause damage to bacterial cell membranes (2). To model this iron toxicity, experiments with higher concentrations of iron are required. For iron concentrations up to 300 μM, a simple Monod equation describes the culture's response.
Induction of the virulence factor hopA1 by ferric ion was measured using the lux system for both batch and continuous cultures. Luminescence induction increased 20-fold between the iron-supplemented and control media. We also determined that the virulence factors hrpL and hopAA1-1 were differentially transcribed with iron supplementation. In contrast, a component of an iron-scavenging system (PSPTO2134) appears to be repressed under high-iron-concentration conditions. From these results, we conclude that iron appears to be involved in the transcriptional control of virulence-related factors in P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000. While virulence control by iron has been well illustrated for the Fur system in P. aeruginosa, the Fur system is a negative regulator, indicating that the system represses the uptake of iron when iron is rich. PvdS, an alternative sigma factor in the Fur system, has been described for negative regulation of the iron uptake system (10). Recently, positive regulation of iron through small RNAs has been reported (26). Our results suggest that an iron-related mechanism may be a limiting factor in virulence-related induction. Although the results of luminescence induction were dependent on the extracellular-iron concentration, the underlying molecular mechanism of iron control is likely very complicated.
Prior work using P. syringae with hrp-inducing minimal medium has not fully recognized the role iron may play in the growth and induction of virulence-related genes. This observation is particularly important in studies with some types of continuous or semicontinuous culture (e.g., chemostat or repeated batch culture), where the effects of carryover of iron from rich media are minimized. Given the important role iron plays in many of the relevant ecological conditions, a full understanding of iron effects on P. syringae may be fundamental to understanding the physiology of this organism in its natural environment. Finally, we suggest that iron levels in in vitro cultures should be carefully controlled in any experiments designed to model virulence-related gene expression and that protocols should be reviewed to reduce potential problems arising from varying concentrations of iron.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Tai Hyun Park was supported by the NBS-ERC (Nano Bioelectronics and Systems Research Center)/KOSEF (Korea Science and Engineering Foundation) international collaboration program. The New York State Office of Science, Technology and Academic Research (NYSTAR) provided support, in part, to M. L. Shuler through a NYSTAR distinguished professorship.
We thank Monica Mall for helping with RNA analysis.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 6 March 2009.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://aem.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1.Büttner, D., and U. Bonas. 2003. Common infection strategies of plant and animal pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 6:312-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Byers, B. R., and J. E. L. Arceneaux. 1998. Microbial iron transport: iron acquisition by pathogenic microorganisms, p. 37-66. In A. Sigel and H. Sigel (ed.), Metal ions in biological systems: iron transport and storage in microorganisms, plants, and animals, vol. 35. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Earhart, C. F. 1996. Uptake and metabolism of iron and molybdenum, p. 1075-1090. In F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter, and H. E. Umbarger (ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, 2nd ed., vol. 1. ASM Press, Washington, DC. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Goldberg, I., and Z. Er-el. 1981. The chemostat—an efficient technique for medium optimization. Process Biochem. 16:2-8. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gross, D. C. 1985. Regulation of syringomycin synthesis in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae and defined conditions for its production. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 58:167-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hartmann, A., and V. Braun. 1981. Iron uptake and iron limited growth of Escherichia coli K-12. Arch. Microbiol. 130:353-356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Heu, S., and S. W. Hutcheson. 1993. Nucleotide sequence and properties of the hrmA locus associated with the Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae 61 hrp gene cluster. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 6:553-564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hubbard, J. A. M., K. B. Lewandowska, M. N. Hughes, and R. K. Poole. 1986. Effects of iron-limitation of Escherichia coli on growth, the respiratory chains and gallium uptake. Arch. Microbiol. 146:80-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huynh, T. V., D. Dahlbeck, and B. J. Staskawicz. 1989. Bacterial blight of soybean: regulation of a pathogen gene determining host cultivar specificity. Science 245:1374-1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Johnová, A., M. Dobišová, M. A. Abdallah, and P. Kyslík. 2003. Fur mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: phenotypic characterization in terms of iron-dependent pattern of deregulation of pyoverdin synthesis. Biotechnol. Lett. 25:235-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim, E. J., W. Wang, W. D. Deckwer, and A. P. Zeng. 2005. Expression of the quorum-sensing regulatory protein LasR is strongly affected by iron and oxygen concentrations in cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa irrespective of cell density. Microbiology 151:1127-1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.King, E. O., M. K. Ward, and D. E. Raney. 1954. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 44:301-307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kuhn, H., U. Friederich, and A. Fiechter. 1979. Defined minimal medium for a thermophilic Bacillus sp. developed by a chemostat pulse and shift technique. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 6:341-349. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lindgren, P. B. 1997. The role of hrp genes during plant-bacterial interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 35:129-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Morgan, M. K., and A. K. Chatterjee. 1988. Genetic organization and regulation of proteins associated with production of syringotoxin by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. J. Bacteriol. 170:5689-5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ongena, M., E. Jourdan, A. Adam, M. Schäfer, H. Budzikiewicz, and P. Thonart. 2008. Amino acids, iron, and growth rate as key factors influencing production of the Pseudomonas putida BTP1 benzylamine derivative involved in systemic resistance induction in different plants. Microb. Ecol. 55:280-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pattus, F., and M. A. Abdallah. 2000. Siderophores and iron-transport in microorganisms. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 47:1-20. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rahme, L. G., M. N. Mindrinos, and N. J. Panopoulos. 1992. Plant and environmental sensory signals control the expression of hrp genes in Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. J. Bacteriol. 174:3499-3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rainnie, D. J., and P. D. Bragg. 1973. The effect of iron deficiency on respiration and energy-coupling in Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 77:339-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ratledge, C., and F. G. Winder. 1964. Effect of iron and zinc on growth patterns of Escherichia coli in an iron-deficient medium. J. Bacteriol. 87:823-827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schulte, R., and U. Bonas. 1992. A Xanthomonas pathogenicity locus is induced by sucrose and sulfur-containing amino acids. Plant Cell 4:79-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shuler, M. L., and F. Kargi. 2002. Bioprocess engineering: basic concepts, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- 23.Swingle, B., D. Thete, M. Moll, C. R. Myers, D. J. Schneider, and S. Cartinhour. 2008. Characterization of the PvdS-regulated promoter motif in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 reveals regulon members and insights regarding PvdS function in other pseudomonads. Mol. Microbiol. 68:871-889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vasil, M. L., and U. A. Ochsner. 1999. The response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to iron: genetics, biochemistry and virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 34:399-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vencato, M., F. Tian, J. R. Alfano, C. R. Buell, S. Cartinhour, G. A. DeClerck, D. S. Guttman, J. Stavrinides, V. Joardar, M. Lindeberg, P. A. Bronstein, J. W. Mansfield, C. R. Myers, A. Collmer, and D. J. Schneider. 2006. Bioinformatics-enabled identification of the HrpL regulon and type III secretion system effector proteins of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola 1448A. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 19:1193-1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wilderman, P. J., N. A. Sowa, D. J. FitzGerald, P. C. FitzGerald, S. Gottesman, U. A. Ochsner, and M. L. Vasil. 2004. Identification of tandem duplicate regulatory small RNAs in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in iron homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:9792-9797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xiao, Y., S. Heu, J. Yi, Y. Lu, and S. W. Hutcheson. 1994. Identification of a putative alternate sigma factor and characterization of a multicomponent regulatory cascade controlling the expression of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Pss61 hrp and hrmA genes. J. Bacteriol. 176:1025-1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xiao, Y., Y. Lu, S. Heu, and S. W. Hutcheson. 1992. Organization and environmental regulation of the Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae 61 hrp cluster. J. Bacteriol. 174:1734-1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yee, L., and H. W. Blanch. 1993. Defined media optimization for growth of recombinant Escherichia coli X90. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41:221-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.