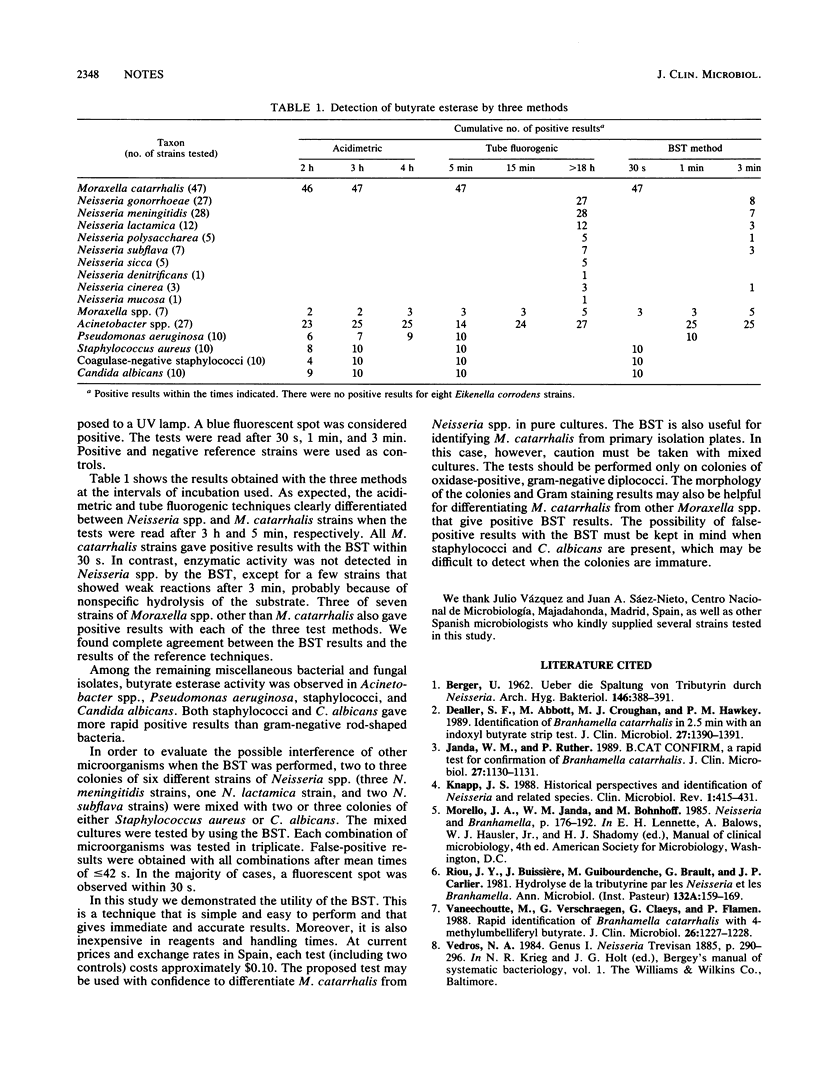
Abstract
A total of 47 Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis strains, 89 strains of Neisseria spp., and 82 strains of miscellaneous bacteria and yeasts were studied by using a fluorogenic spot method which detects butyrate esterase. A positive butyrate esterase spot test correctly differentiated M. catarrhalis from Neisseria spp., which had a negative butyrate esterase spot test reaction. The test is rapid, simple, and easy to perform. The butyrate esterase spot test was useful for direct identification of M. catarrhalis from primary cultures. However, false-positive reactions may occur with mixed cultures.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dealler S. F., Abbott M., Croughan M. J., Hawkey P. M. Identification of Branhamella catarrhalis in 2.5 min with an indoxyl butyrate strip test. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1390–1391. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1390-1391.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda W. M., Ruther P. B.CAT CONFIRM, a rapid test for confirmation of Branhamella catarrhalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1130–1131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1130-1131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S. Historical perspectives and identification of Neisseria and related species. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):415–431. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. Y., Buissière J., Guibourdenche M., Brault G., Carlier J. P. Hydrolyse de la tributyrine par les Neisseria et les Branhamella. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Mar-Apr;132(2):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaneechoutte M., Verschraegen G., Claeys G., Flamen P. Rapid identification of Branhamella catarrhalis with 4-methylumbelliferyl butyrate. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1227–1228. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1227-1228.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



