Abstract
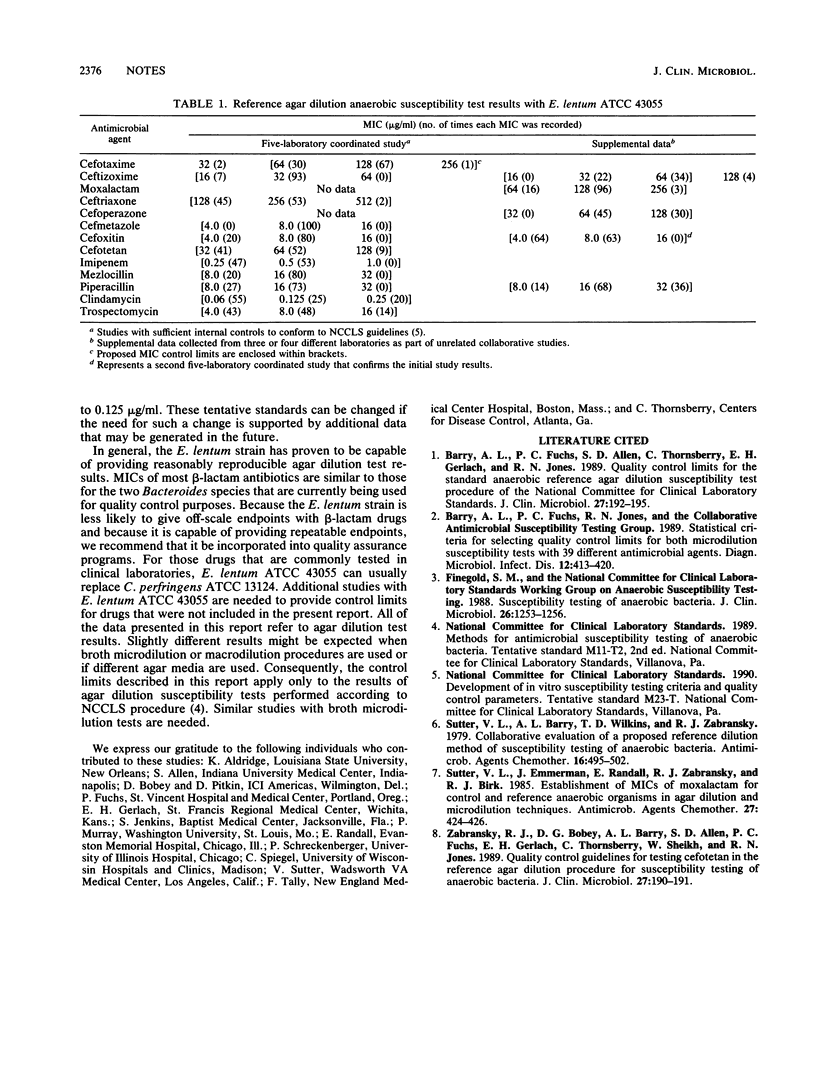
A strain of Eubacterium lentum (ATCC 43055) was selected for quality control of anaerobic susceptibility tests. Multilaboratory collaborative studies with 13 different antimicrobial agents were reviewed, and MIC control limits were proposed for agar dilution tests with the new control strain.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Allen S. D., Thornsberry C., Gerlach E. H., Jones R. N. Quality control limits for the standard anaerobic reference agar dilution susceptibility test procedure of the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):192–195. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.192-195.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C., Jones R. N. Statistical criteria for selecting quality control limits for broth microdilution susceptibility tests with 39 different antimicrobial agents. Collaborative Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Group. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;12(5):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Barry A. L., Wilkins T. D., Zabransky R. J. Collaborative evaluation of a proposed reference dilution method of susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):495–502. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Emmerman J., Randall E., Zabransky R. J., Birk R. J. Establishment of MICs of moxalactam for control and reference anaerobic organisms in agar dilution and microdilution techniques. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):424–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabransky R. J., Bobey D. G., Barry A. L., Allen S. D., Fuchs P. C., Gerlach E. H., Thornsberry C., Sheikh W., Jones R. N. Quality control guidelines for testing cefotetan in the reference agar dilution procedure for susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):190–191. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.190-191.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


