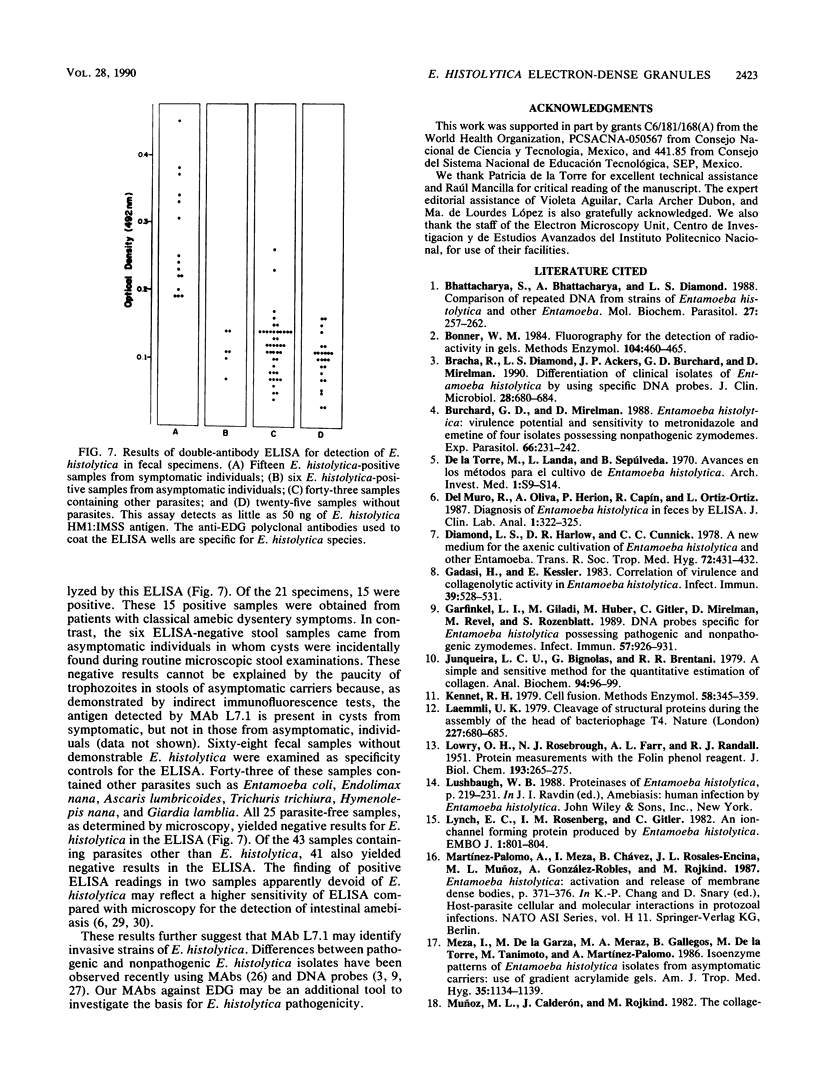
Abstract
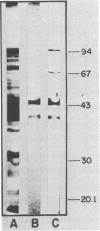
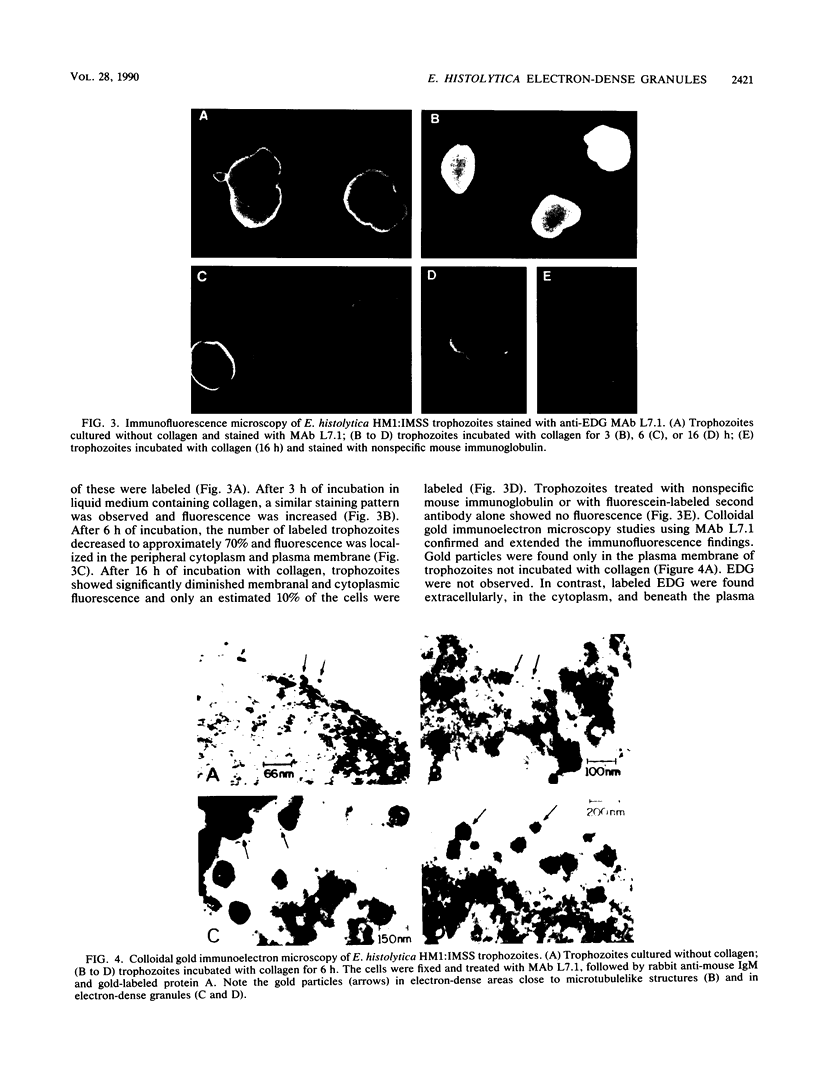
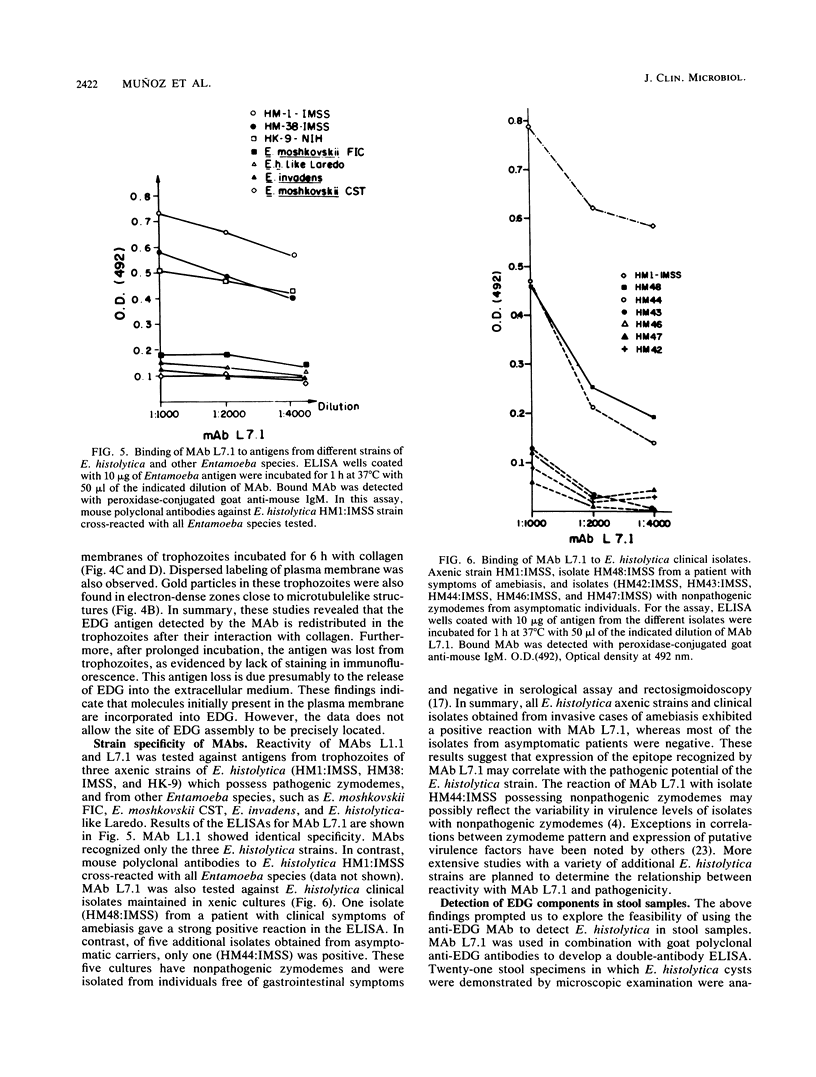
In vitro interaction of Entamoeba histolytica with collagen induces intracellular formation and release of electron-dense granules (EDG) and stimulation of collagenolytic activity. Purified EDG contain 1.66 U of collagenase per mg of protein. Thus, EDG may participate in tissue destruction during invasive amebiasis. Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) L1.1 and L7.1 reacted specifically with EDG in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy. MAb L7.1 immunoprecipitated three polypeptides with molecular weights of 95,000, 68,000, and 28,000 from lysates of biosynthetically labeled E. histolytica. Both MAbs recognized the pathogenic E. histolytica axenic strains HM1:IMSS, HM38:IMSS, and HK-9 but failed to react in ELISA with Entamoeba moshkovskii, Entamoeba invadens, and E. histolytica-like Laredo. In addition, MAb L7.1 reacted with one E. histolytica isolate from a symptomatic patient but did not react with four of five isolates from asymptomatic patients. EDG antigens were detected by a MAb L7.1-based ELISA in E. histolytica-containing fecal samples from symptomatic, but not asymptomatic, individuals. These results suggest that the EDG antigen detected with MAb L7.1 may be differentially expressed in pathogenic and nonpathogenic E. histolytica.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya S., Bhattacharya A., Diamond L. S. Comparison of repeated DNA from strains of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Fluorography for the detection of radioactivity in gels. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:460–465. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha R., Diamond L. S., Ackers J. P., Burchard G. D., Mirelman D. Differentiation of clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica by using specific DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):680–684. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.680-684.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard G. D., Mirelman D. Entamoeba histolytica: virulence potential and sensitivity to metronidazole and emetine of four isolates possessing nonpathogenic zymodemes. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Aug;66(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadasi H., Kessler E. Correlation of virulence and collagenolytic activity in Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):528–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.528-531.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Giladi M., Huber M., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. DNA probes specific for Entamoeba histolytica possessing pathogenic and nonpathogenic zymodemes. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):926–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.926-931.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junquiera L. C., Junqueira L. C., Brentani R. R. A simple and sensitive method for the quantitative estimation of collagen. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 1;94(1):96–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90795-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H. Cell fusion. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:345–359. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch E. C., Rosenberg I. M., Gitler C. An ion-channel forming protein produced by Entamoeba histolytica. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):801–804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meza I., De la Garza I. M., Meraz M. A., Gallegos B., De la Torre M., Tanimoto M., Martínez-Palomo A. Isoenzyme patterns of Entamoeba histolytica isolates from asymptomatic carriers: use of gradient acrylamide gels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Nov;35(6):1134–1139. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz M. L., Rojkind M., Calderón J., Tanimoto M., Arias-Negrete S., Martínez-Palomo A. Entamoeba histolytica: collagenolytic activity and virulence. J Protozool. 1984 Aug;31(3):468–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Smith R. D., Schlesinger P. H., Murphy C. F., Ravdin J. I. Isolation of the galactose-binding lectin that mediates the in vitro adherence of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1238–1244. doi: 10.1172/JCI113198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. L., Keene W. E., McKerrow J. H. Thiol proteinase expression and pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2772–2777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2772-2777.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan W. D., Chiodini P. L., Spice W. M., Moody A. H., Ackers J. P. Immunological differentiation of pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. Lancet. 1988 Mar 12;1(8585):561–563. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Horstmann R. D., Knobloch J., Arnold H. H. Genomic DNA differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5118–5122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Yolken R. H., Nash T. E., Quinn T. C. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of Giardia lamblia in fecal specimens. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jan;149(1):90–97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Yolken R. H., Quinn T. C. Use of a monoclonal antibody in an enzyme immunoassay for the detection of Entamoeba histolytica in fecal specimens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):465–472. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Young T. M., Lu L. P., Unkeless J. C., Cohn Z. A. Characterization of a membrane pore-forming protein from Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1677–1690. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Barriocanal J. G., Bonifacino J. S., Sandoval I. V. Two integral membrane proteins located in the cis-middle and trans-part of the Golgi system acquire sialylated N-linked carbohydrates and display different turnovers and sensitivity to cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):215–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Tønnessen T. I., Petersen O. W., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Routing of internalized ricin and ricin conjugates to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):37–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]