Abstract
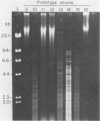
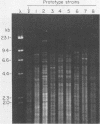
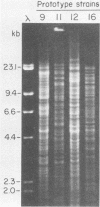
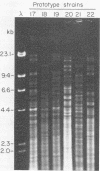
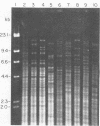
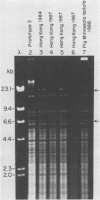
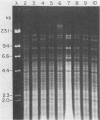
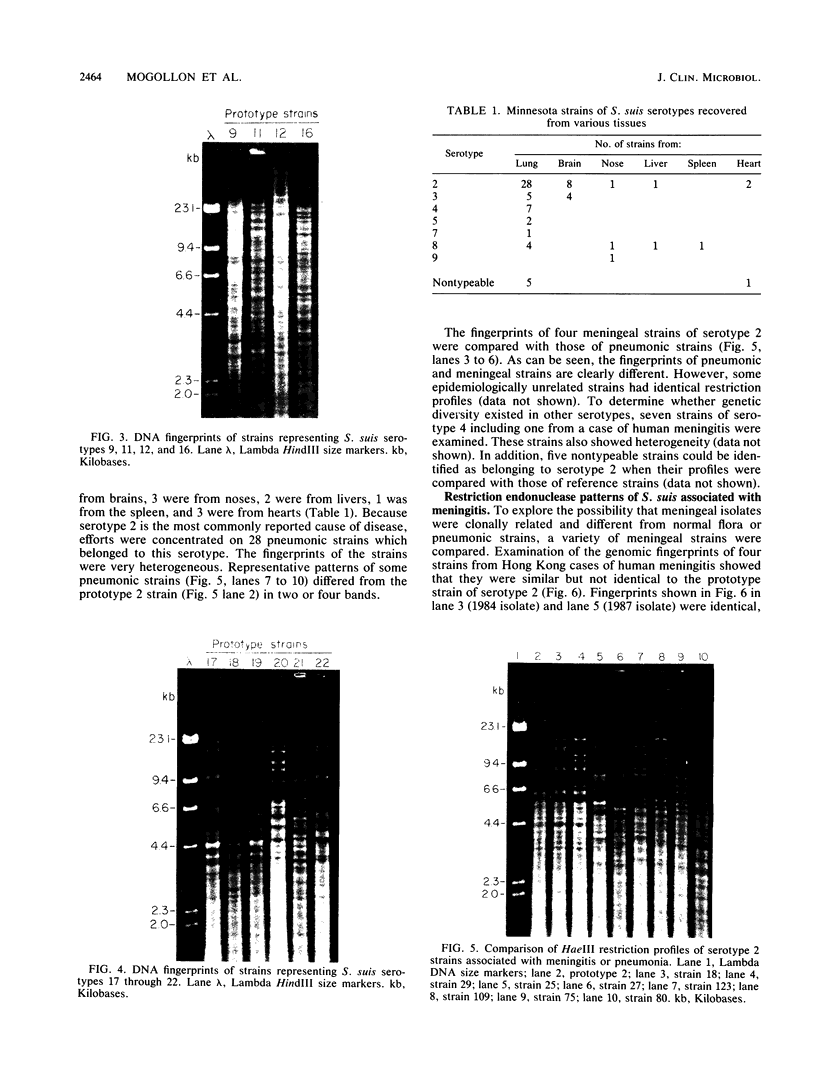
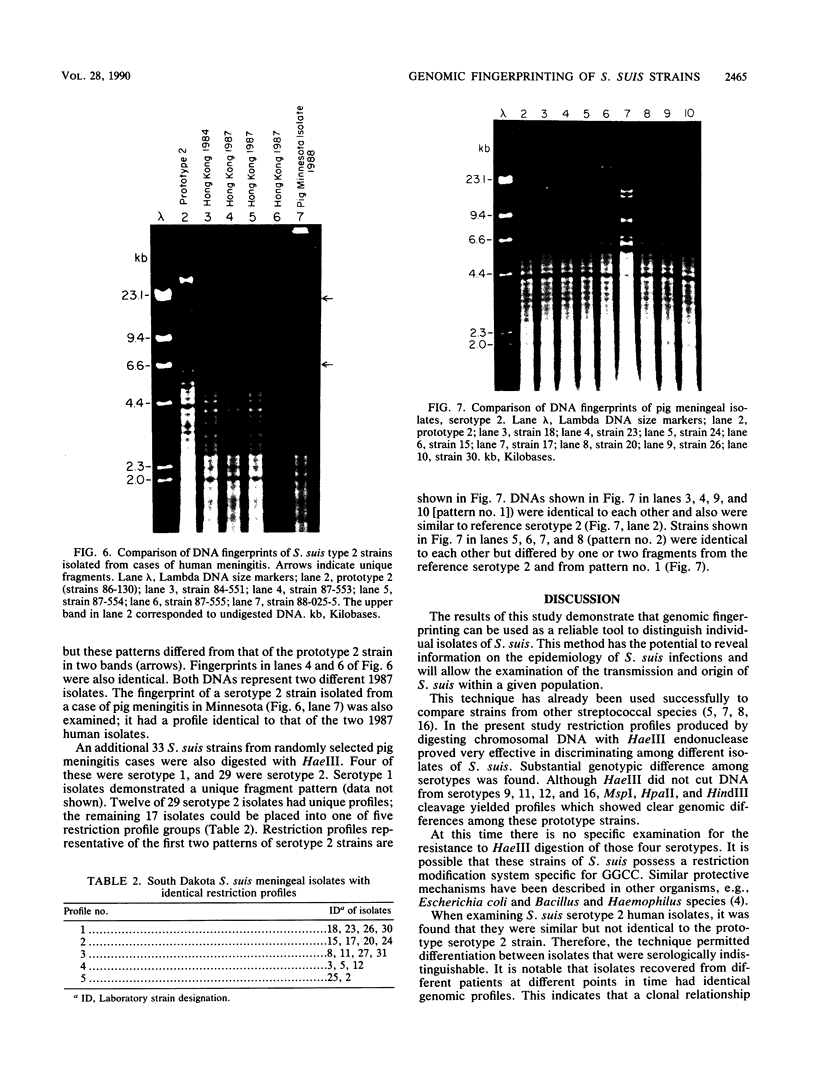
A collection of Streptococcus suis strains from animal and human infections was examined for DNA-banding patterns after restriction endonuclease digestion and agarose gel electrophoresis. The endonuclease HaeIII produced the most discriminating restriction profiles among 23 serotypes studied. DNA from serotypes 9, 11, 12, and 16 was resistant to HaeIII cleavage. DNA from serotypes 9 through 16 was cleaved with HindIII and showed substantial genomic differences. We also examined 106 epidemiologically unrelated strains isolated from cases of pig meningitis or pneumonia and 5 strains isolated from cases of human meningitis in order to compare genomic fingerprinting and serotyping as epidemiological tools. Heterogeneity was found among fingerprints of serologically identical isolates, indicating genetic diversity within some serotypes. DNA fingerprints of some serotype 2 strains from different sources appeared identical, suggesting a clonal relationship among strains of this serotype. The data suggest that this technique represents an important tool for examining the natural history of disease caused by S. suis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends J. P., Hartwig N., Rudolphy M., Zanen H. C. Carrier rate of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 in palatine tonsils of slaughtered pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):945–947. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.945-947.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends J. P., Zanen H. C. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):131–137. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorvatn B., Lund V., Kristiansen B. E., Korsnes L., Spanne O., Lindqvist B. Applications of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of chromosomal DNA of Neisseria meningitidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):763–765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.763-765.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. E., Roberts R. J. Modification profiles of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):913–934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caufield P. W., Walker T. M. Genetic diversity within Streptococcus mutans evident from chromosomal DNA restriction fragment polymorphisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):274–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.274-278.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Huang C. Y., Kay R. Streptococcus suis meningitis. An important underdiagnosed disease in Hong Kong. Med J Aust. 1983 Apr 30;1(9):414-6, 417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Kaplan E. L., Livdahl C., Skjold S. DNA fingerprints of Streptococcus pyogenes are M type specific. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1317–1323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Baker C. J., Troup N. J., Tompkins L. S. Restriction endonuclease analysis of human and bovine group B streptococci for epidemiologic study. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1352–1356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1352-1356.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. I. An immunochemical study of the causative agent (PM streptococcus). J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):205–212. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Ward G. E., Murtaugh M. P. Species-specific cloned DNA probes for the identification of Campylobacter hyointestinalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2717–2723. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2717-2723.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk M., Higgins R., Jacques M., Mittal K. R., Henrichsen J. Description of 14 new capsular types of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2633–2636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2633-2636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommez J., Devriese L. A., Henrichsen J., Castryck F. Identification and characterization of Streptococcus suis. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Apr;11(4):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Kjems E., Ravn T. Biochemical and serological properties of Streptococcus mutans from various human and animal sources. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):357–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Pedersen K. B., Henrichsen J. Serology of capsulated streptococci pathogenic for pigs: six new serotypes of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):993–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.993-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold S. A., Quie P. G., Fries L. A., Barnham M., Cleary P. P. DNA fingerprinting of Streptococcus zooepidemicus (Lancefield group C) as an aid to epidemiological study. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1145–1150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touil F., Higgins R., Nadeau M. Isolation of Streptococcus suis from diseased pigs in Canada. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Jun;17(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor R. S. Meningitis in pigs caused by Streptococcus suis type II. Vet Rec. 1977 Nov 5;101(19):378–379. doi: 10.1136/vr.101.19.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]