Abstract
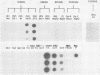
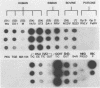
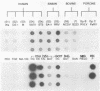
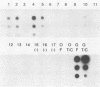
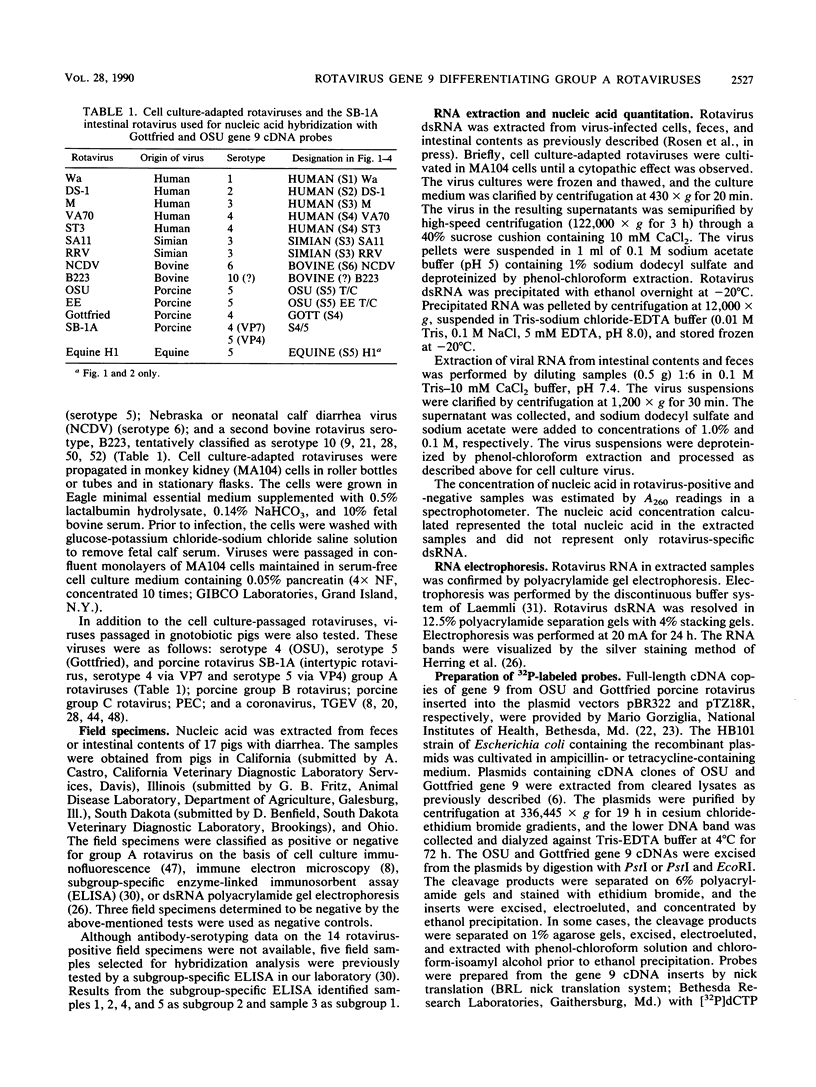
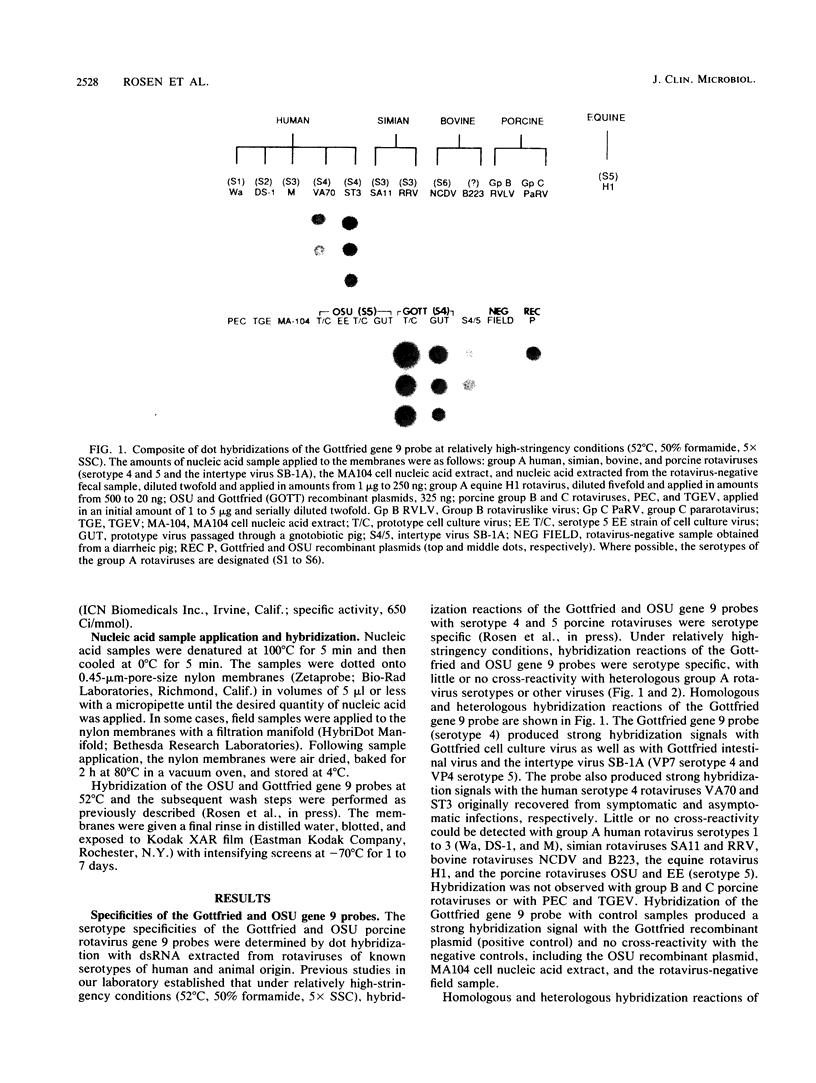
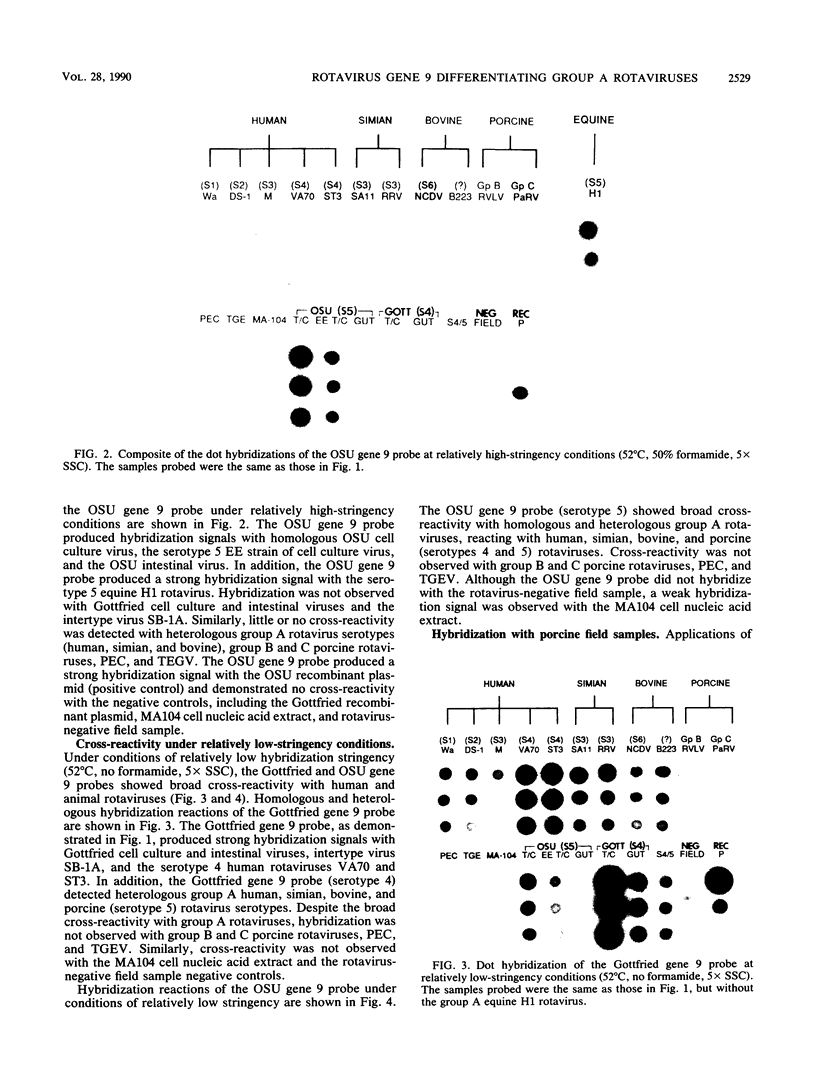
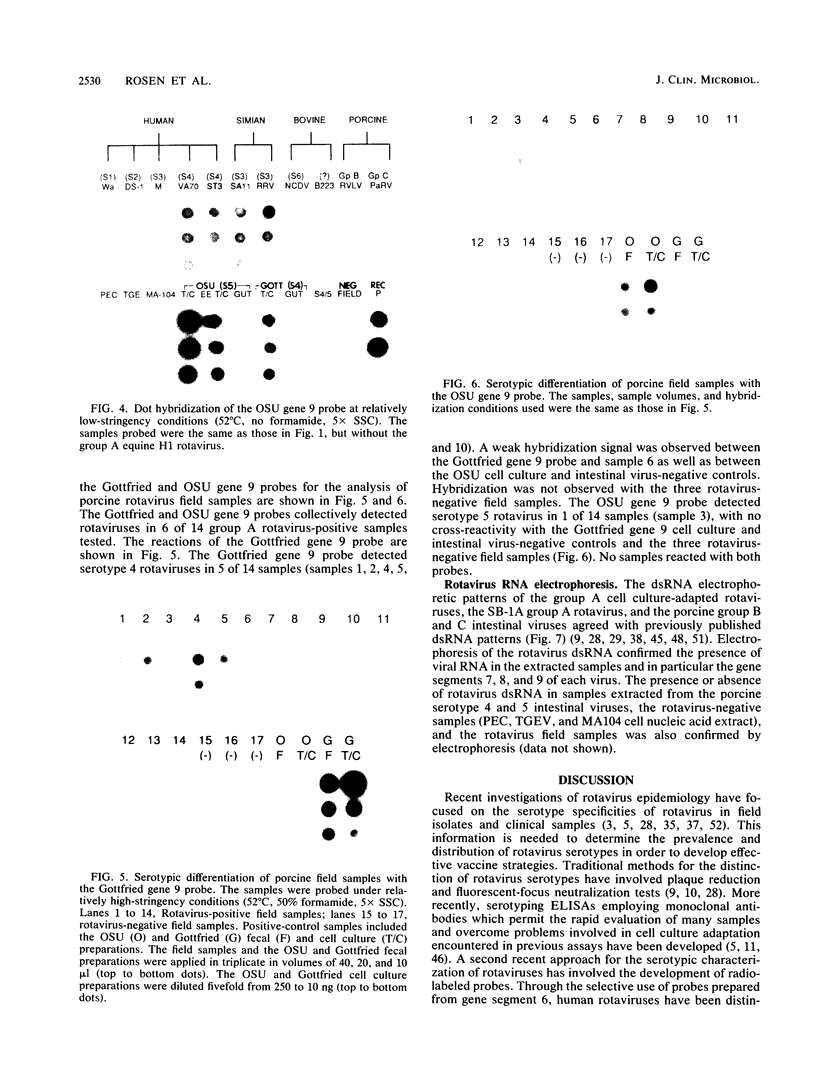
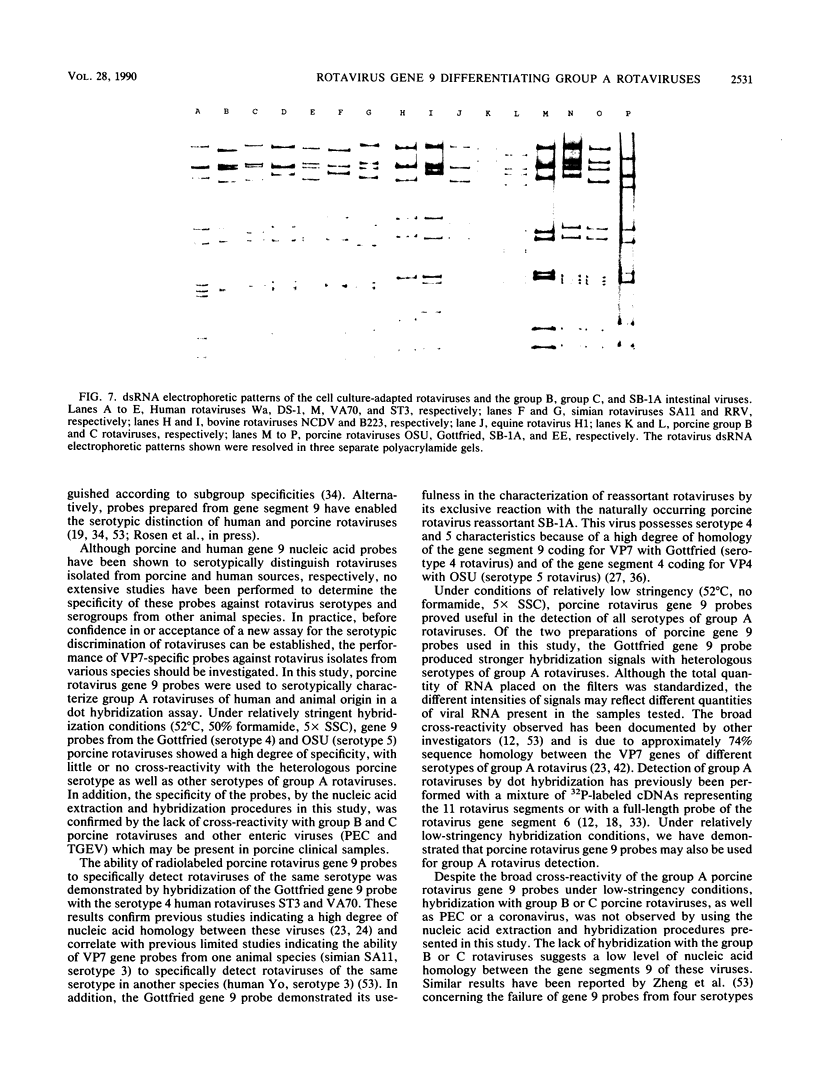
The serotypic specificities of Gottfried and OSU porcine rotavirus gene 9 probes were investigated in a dot hybridization assay. The probes were reacted with homologous and heterologous serotypes of group A rotaviruses of human and animal origin. Hybridizations were conducted under relatively low-stringency (52 degrees C, no formamide, 5 x SSC) and high-stringency (52 degrees C, 50% formamide, formamide, 5 x SSC) conditions (1 x SSC is 0.15 M NaCl plus 0.015 M sodium citrate). Under conditions of relatively low stringency, the Gottfried and OSU gene 9 probes demonstrated broad cross-reactivity and were useful in the detection of homologous and heterologous serotypes of group A rotaviruses. Under conditions of relatively high stringency, the Gottfried and OSU gene 9 probes were serotype specific. The Gottfried gene 9 probe (serotype 4) hybridized with homologous Gottfried porcine rotavirus as well as the serotype 4 human rotaviruses ST3 and VA70. The OSU gene 9 probe (serotype 5) hybridized with homologous OSU porcine rotavirus and the serotype 5 equine rotavirus H1. Hybridization was not observed with the antigenically distinct group B and C porcine rotaviruses or with other porcine enteric viruses, including calicivirus and a coronavirus, transmissible gastroenteritis virus, regardless of stringency conditions. Analysis of 14 group A rotavirus-positive field samples resulted in the serotypic differentiation, collectively, of six serotype 4 or 5 porcine rotaviruses. No field samples reacted with both the Gottfried and OSU gene 9 probes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambinder R. F., Charache P., Staal S., Wright P., Forman M., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. The vector homology problem in diagnostic nucleic acid hybridization of clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):16–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.16-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias C. F., Ruiz A. M., López S. Further antigenic characterization of porcine rotavirus YM. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2871–2873. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2871-2873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M., Pilfold J. N., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus serotypes by serum neutralisation. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):231–237. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinzoni R. B., Mattion N. M., Matson D. O., Blackhall J., La Torre J. L., Scodeller E. A., Urasawa S., Taniguchi K., Estes M. K. Porcine rotaviruses antigenically related to human rotavirus serotypes 1 and 2. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):633–636. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.633-636.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch C. J., Heath R. L., Gust I. D. Use of serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies to study the epidemiology of rotavirus infection. J Med Virol. 1988 Jan;24(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Saif L. J., Cross R. F., Agnes A. G., Theil K. W. Rotavirus as a cause of diarrhea in pigs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):458–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J. Isolation and serotyping of porcine rotaviruses and antigenic comparison with other rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.105-111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Fowler K. J., Bishop R. F., Cotton R. G. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to human rotavirus and indications of antigenic drift among strains from neonates. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):14–20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.14-20.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Unicomb L. E., Pitson G. A., Bishop R. F. Simple and specific enzyme immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies for serotyping human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):509–515. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.509-515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Detection of rotaviruses by nucleic acid hybridization with cloned DNA of simian rotavirus SA11 genes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):293–300. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J. J., Firoozmand F., Sato S., Vonderfecht S. L., Yin F. Z., Yolken R. H. Detection of group B rotavirus in fecal specimens by dot hybridization with a cloned cDNA probe. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.422-426.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J., Sato S., Yolken R. Specificity of dot hybridization assay in the presence of rRNA for detection of rotaviruses in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1809–1811. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1809-1811.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J., Vonderfecht S., Theil K., Torres-Medina A., Yolken R. H. Genetic and antigenic relatedness of human and animal strains of antigenically distinct rotaviruses. J Infect Dis. 1986 Dec;154(6):972–982. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.6.972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Boeggeman E., Purcell R. H., Sereno M., Perez I., White L., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. A dot hybridisation assay for detection of rotavirus. Lancet. 1983 Mar 12;1(8324):555–558. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92811-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Green K. Y., Garcia D., Sears J., Perez-Schael I., Avendaño L. F., Rodriguez W. B., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z. Dot hybridization assay for distinction of rotavirus serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.29-34.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn W. T., Saif L. J., Moorhead P. D. Pathogenesis of porcine enteric calicivirus-like virus in four-day-old gnotobiotic pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jun;49(6):819–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Passarani N., Sarasini A., Battaglia M. Characterization of serotypes of human rotavirus strains by solid-phase immune electron microscopy. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1143–1151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Aguirre Y., Hoshino Y., Esparza J., Blumentals I., Askaa J., Thompson M., Glass R. I., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. VP7 serotype-specific glycoprotein of OSU porcine rotavirus: coding assignment and gene sequence. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2445–2454. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Nishikawa K., Green K., Taniguchi K. Gene sequence of the VP7 serotype specific glycoprotein of Gottfried porcine rotavirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):775–775. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Flores J. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the major neutralization protein of four human rotavirus serotypes. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Analysis by plaque reduction neutralization assay of intertypic rotaviruses suggests that gene reassortment occurs in vivo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):290–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.290-294.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z. Detection of differences among human and animal rotaviruses, using analysis of viral RNA. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassuba A., Saif L. J., Greenberg H. B. Subgroup classification of porcine group-A rotaviruses, using monoclonal antibodies in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Jun;51(6):938–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., King M. W., Mock R. Reovirus-like agent associated with fatal diarrhea in neonatal pigs. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):816–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.816-825.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Imai M., Bellamy A. R., Ikegami N., Furuichi Y., Summers D., Nuss D. L., Deibel R. Diagnosis of rotavirus infection with cloned cDNA copies of viral genome segments. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):509–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.509-512.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Imai M., Ikegami N., Bellamy A. R., Summers D., Nuss D. L., Deibel R., Furuichi Y. cDNA probes of individual genes of human rotavirus distinguish viral subgroups and serotypes. J Virol Methods. 1987 Mar;15(4):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattion N. M., Bellinzoni R. C., Blackhall J. O., La Torre J. L., Scodeller E. A. Antigenic characterization of swine rotaviruses in Argentina. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):795–798. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.795-798.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Valdesuso J., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Analysis by RNA-RNA hybridization assay of intertypic rotaviruses suggests that gene reassortment occurs in vivo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):295–300. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.295-300.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagesha H. S., Holmes I. H. New porcine rotavirus serotype antigenically related to human rotavirus serotype 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):171–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.171-174.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Nakagomi O. RNA-RNA hybridization identifies a human rotavirus that is genetically related to feline rotavirus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1431–1434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1431-1434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Lyoo Y. S., Andrews J. J., Hill H. T. Isolation of two new serotypes of porcine rotavirus from pigs with diarrhea. Arch Virol. 1988;100(1-2):139–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01310917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., McCrae M. A. A rapid screening assay for detecting individual RNA species in field isolates of rotaviruses. J Virol Methods. 1984 Oct;9(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. A., Iwamoto A., Ikegami N., Nomoto A., Furuichi Y. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the serotype-specific antigen of human (Wa) rotavirus: comparison with the homologous genes from simian SA11 and UK bovine rotaviruses. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):860–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.860-862.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz A. M., López I. V., López S., Espejo R. T., Arias C. F. Molecular and antigenic characterization of porcine rotavirus YM, a possible new rotavirus serotype. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4331–4336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4331-4336.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H. Passive immunity in transmissible gastroenteritis of swine: immunoglobulin classes of milk antibodies after oral-intranasal inoculation of sows with a live low cell culture-passaged virus. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jan;40(1):115–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson L., Grahnquist L., Pettersson C. A., Grandien M., Stintzing G., Greenberg H. B. Detection of human rotaviruses which do not react with subgroup I- and II-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1238–1240. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1238-1240.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Morita Y., Greenberg H. B., Urasawa S. Direct serotyping of human rotavirus in stools by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using serotype 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-specific monoclonal antibodies to VP7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Kohler E. M. Physicochemical characterization of porcine pararotavirus and detection of virus and viral antibodies using cell culture immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):268–272. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.268-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Moorhead P. D., Whitmoyer R. E. Porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus): characterization and pathogenicity for gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.340-345.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J., Hall G. A., Jones J. M., Jackson G. The isolation of reovirus-like agents (rota-viruses) from acute gastroenteritis of piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):203–209. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Kelso N. E., Simpson T. F., Gaul S. K., Evans L. E., Babiuk L. Antigenic relationships among some bovine rotaviruses: serum neutralization and cross-protection in gnotobiotic calves. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):358–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.358-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Zheng S. L., Rosen B. I., Knight N., Gourley N. E., Ramig R. F. Protection between different serotypes of bovine rotavirus in gnotobiotic calves: specificity of serum antibody and coproantibody responses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1052–1058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1052-1058.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James H. D., Jr, Pittman A. L., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Direct isolation in cell culture of human rotaviruses and their characterization into four serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.310-317.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B. J., Lam W. P., Yan Y. K., Lo S. K., Lung M. L., Ng M. H. Direct identification of serotypes of natural human rotavirus isolates by hybridization using cDNA probes derived from segment 9 of the rotavirus genome. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):552–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.552-557.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]