Abstract
DNAs from 34 mycobactin-dependent isolates of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and 1 isolate of M. paratuberculosis 18 were digested with four restriction endonucleases. Southern hybridization experiments were performed with a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide DNA probe derived from the sequence of IS900, an insertion sequence present in 15 to 20 copies per M. paratuberculosis chromosome. The probe hybridized with DNA from each of the mycobactin-dependent isolates, and restriction fragment length polymorphisms were detected among the isolates with each restriction endonuclease used. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis may permit identification of various strains of M. paratuberculosis, which has not been possible with other techniques.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiodini R. J. Characterization of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and organisms of the Mycobacterium avium complex by restriction polymorphism of the rRNA gene region. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):489–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.489-494.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E. Benefits of recombinant DNA technology for the study of Mycobacterium leprae. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:61–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Gabric D. M., De Lisle G. W. Identification of a repetitive DNA sequence specific to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90503-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Gabric D. M., de Lisle G. W. Identification of two groups of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis strains by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1591–1596. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1591-1596.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., de Lisle G. W. Restriction endonuclease analysis of various strains of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis isolated from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Oct;47(10):2226–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Crawford J. T., Bates J. H. Repetitive DNA sequences as probes for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2240–2245. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2240-2245.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. P., Tizard M. L., Moss M. T., Thompson J., Winterbourne D. J., McFadden J. J., Hermon-Taylor J. Sequence and characteristics of IS900, an insertion element identified in a human Crohn's disease isolate of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9063–9073. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley S. S., Splitter G. A., Welch R. A. Development of a diagnostic test for Johne's disease using a DNA hybridization probe. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1582–1587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1582-1587.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy-Frébault V. V., Thorel M. F., Varnerot A., Gicquel B. DNA polymorphism in Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, "wood pigeon mycobacteria," and related mycobacteria analyzed by field inversion gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2823–2826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2823-2826.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. Crohn's disease-isolated mycobacteria are identical to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis, as determined by DNA probes that distinguish between mycobacterial species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):796–801. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.796-801.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Butcher P. D., Thompson J., Chiodini R., Hermon-Taylor J. The use of DNA probes identifying restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms to examine the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A., Moriarty K. M., Scott D. B. A cloned DNA probe for the detection of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. N Z Vet J. 1989 Jun;37(2):47–50. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1989.35556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Tsang A. Y., Yang H. L. Speciation of organisms within the Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare-Mycobacterium scrofulaceum (MAIS) complex based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Dec;2(4):289–304. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary P. H., Andersen P. R., Green E., Hermon-Taylor J., McFadden J. J. Use of highly specific DNA probes and the polymerase chain reaction to detect Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in Johne's disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.933-937.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple D. L., Kapke P. A., Andrews R. E., Jr Analysis of restriction endonuclease fragment patterns of DNA from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Feb;19(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
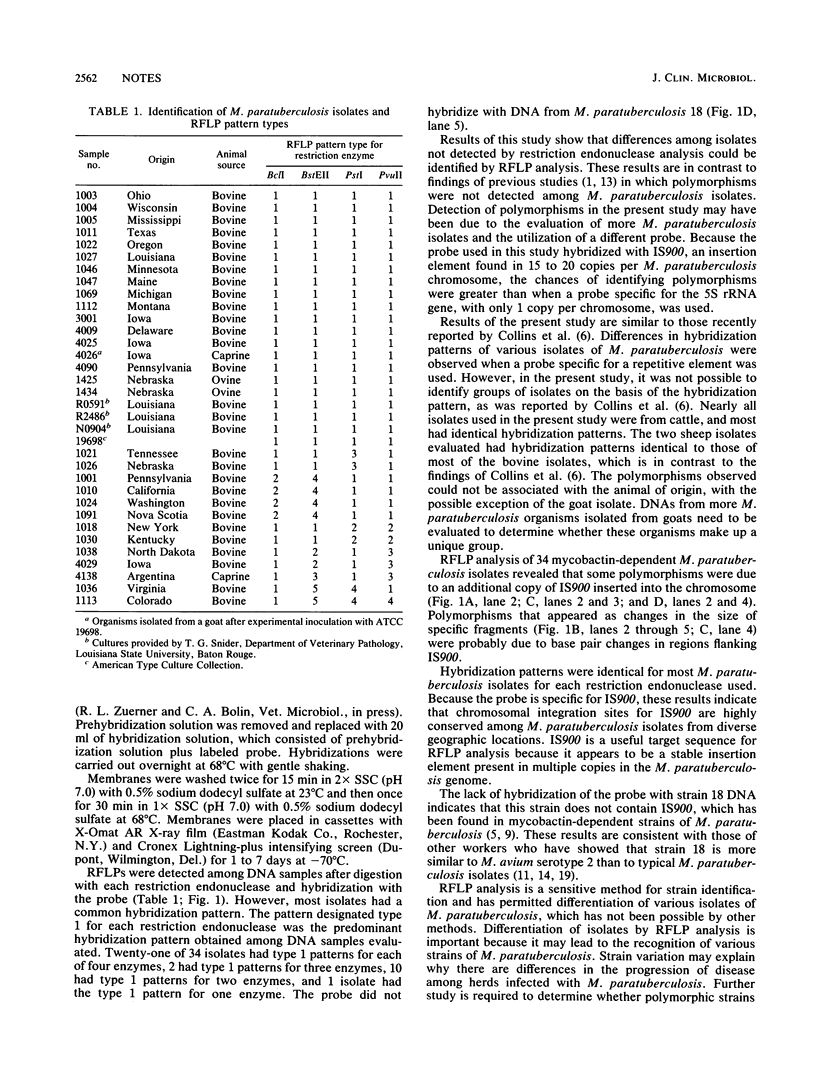
- Whipple D. L., Le Febvre R. B., Andrews R. E., Jr, Thiermann A. B. Isolation and analysis of restriction endonuclease digestive patterns of chromosomal DNA from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and other Mycobacterium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1511–1515. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1511-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]