Abstract
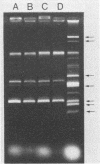
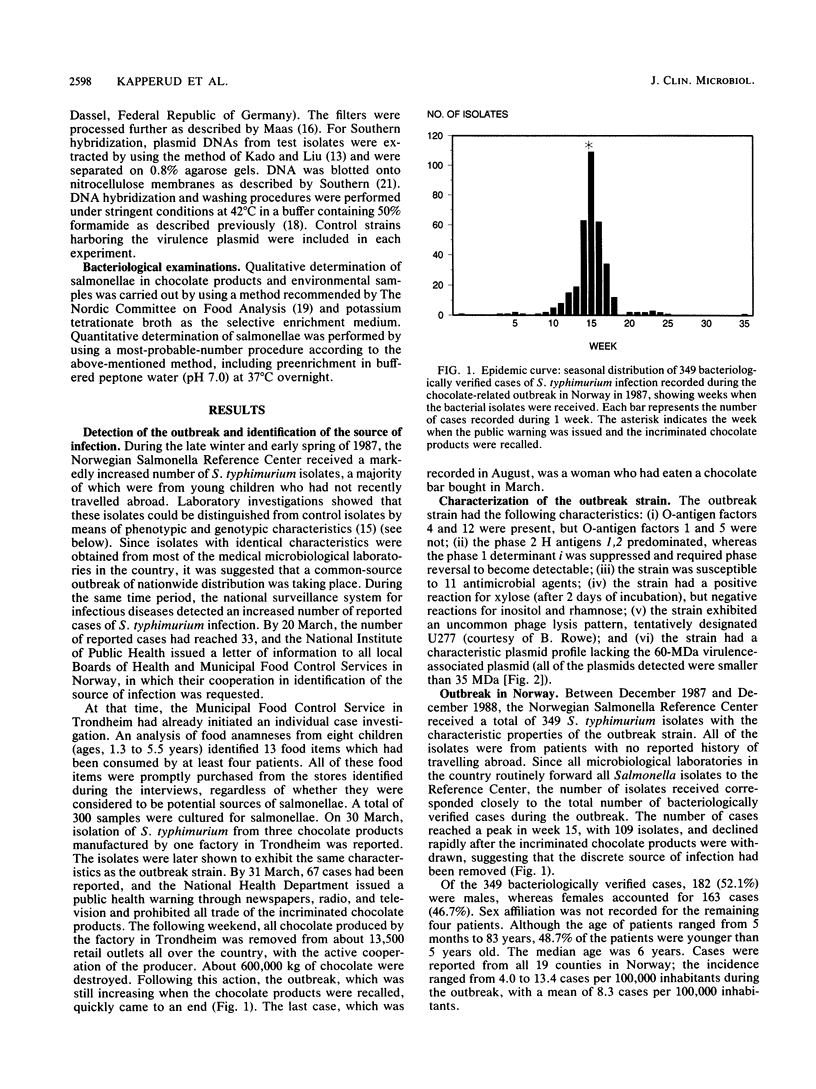
We describe an outbreak of Salmonella typhimurium infection, caused by contaminated chocolate produced by one Norwegian company, which occurred in Norway and Finland in 1987. A total of 349 bacteriologically verified cases were recorded in Norway, and 12 cases were recorded in Finland. There was a predominance of young children among the patients (median age, 6 years), many of whom developed acute hemorrhagic diarrhea. The outbreak strain exhibited a rare phage lysis pattern and a characteristic plasmid profile lacking the 60-MDa virulence-associated plasmid. DNA hybridization failed to demonstrate any DNA sequence homology between the outbreak strain and the virulence plasmid. The outbreak strain was nonlethal for orally infected mice. The finding of only less than or equal to 10 S. typhimurium cells per 100 g of chocolate in about 90% of the positive samples obtained from retail outlets suggested that an inoculum of fewer than 10 organisms may have been sufficient to cause symptomatic disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong R. W., Fodor T., Curlin G. T., Cohen A. B., Morris G. K., Martin W. T., Feldman J. Epidemic Salmonella gastroenteritis due to contaminated imitation ice cream. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Mar;91(3):300–307. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. C., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B., Barker W. H., Gangarosa E. J. International outbreak of Salmonella Eastbourne infection traced to contaminated chocolate. Lancet. 1975 Apr 5;1(7910):788–792. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92446-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine R. E., Cohen M. L., Martin W. T., Vernon T. M. Epidemic salmonellosis from cheddar cheese: surveillance and prevention. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Feb;111(2):247–253. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill O. N., Sockett P. N., Bartlett C. L., Vaile M. S., Rowe B., Gilbert R. J., Dulake C., Murrell H. C., Salmaso S. Outbreak of Salmonella napoli infection caused by contaminated chocolate bars. Lancet. 1983 Mar 12;1(8324):574–577. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92822-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood M. H., Hooper W. L. Chocolate bars contaminated with Salmonella napoli: an infectivity study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Apr 30;286(6375):1394–1394. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6375.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2891–2901. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2891-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsen S., Breen O. Investigation of an outbreak of Salmonella oranienburg infections in Norway, caused by contaminated black pepper. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 May;119(5):806–812. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Lassen J., Aasen S., Gustavsen S., Hellesnes I. Sjokoladeepidemien i 1987. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1989 Jun 30;109(19-21):1982–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Lassen J., Dommarsnes K., Kristiansen B. E., Caugant D. A., Ask E., Jahkola M. Comparison of epidemiological marker methods for identification of Salmonella typhimurium isolates from an outbreak caused by contaminated chocolate. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2019–2024. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2019-2024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R. An improved colony hybridization method with significantly increased sensitivity for detection of single genes. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCULLOUGH N. B., EISELE C. W. Experimental human salmonellosis. I. Pathogenicity of strains of Salmonella meleagridis and Salmonella anatum obtained from spray-dried whole egg. J Infect Dis. 1951 May-Jun;88(3):278–289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/88.3.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon P., Popoff M. Y., Coynault C., Marly J., Miras I. Virulence-associated plasmids of Salmonella serotype Typhimurium in experimental murine infection. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Jul-Aug;137B(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmonella nima in British Columbia. CMAJ. 1986 Dec 1;135(11):1286–1286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]