Abstract
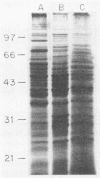
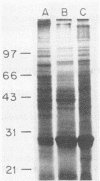
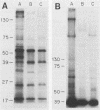
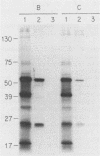
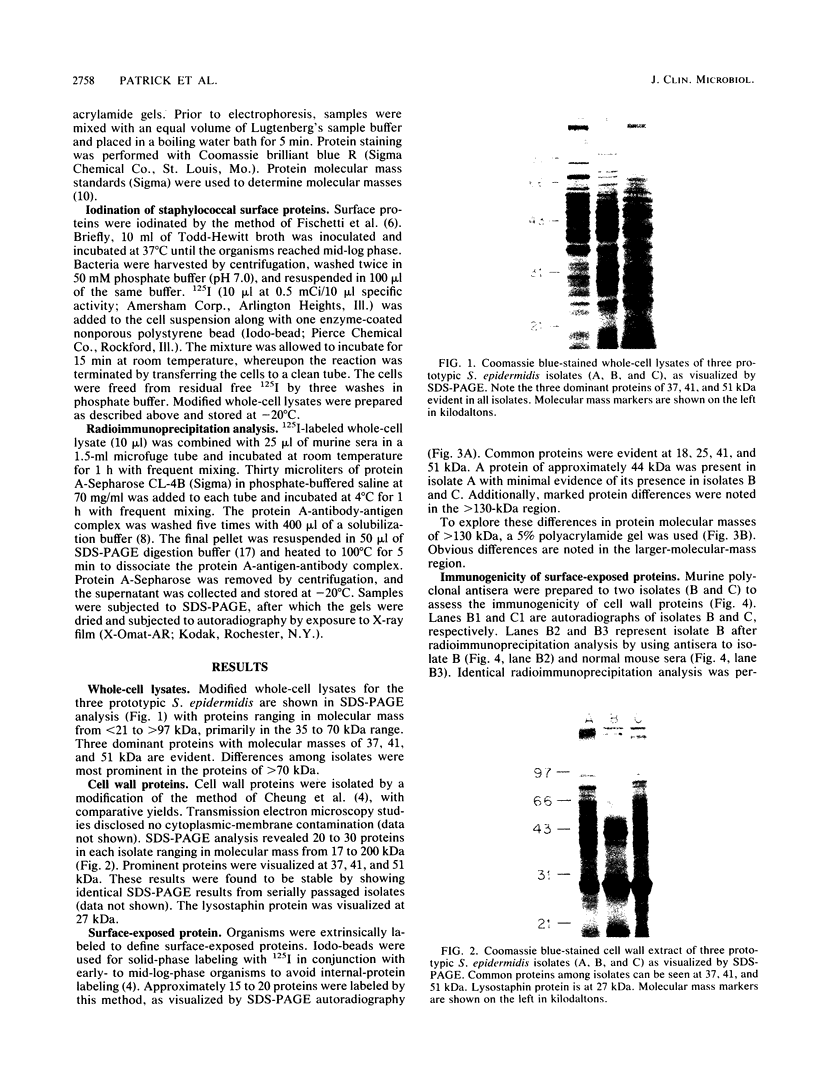
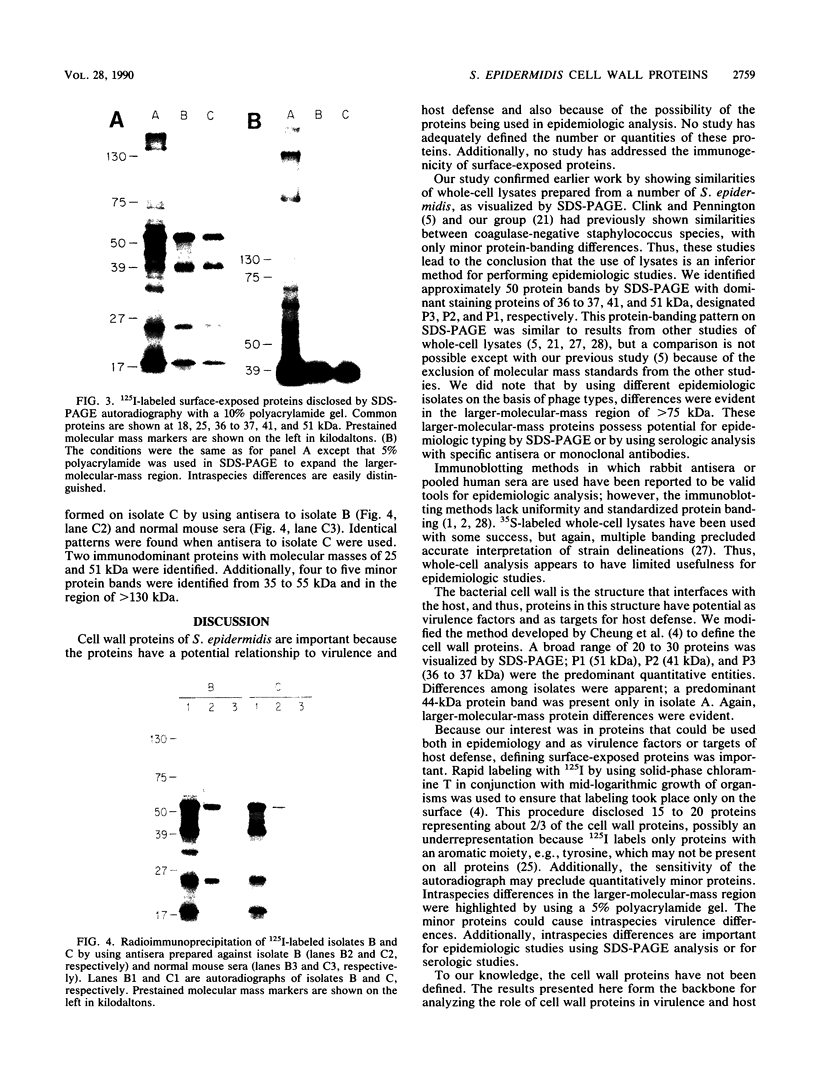
Three Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates of differing bacteriophage types were studied to define proteins confined to the cell wall, which were surface exposed and thus available to interact with the host. Three major proteins of 37, 41, and 51 kDa were identified in all whole-cell lysates and cell wall extracts by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis. Two additional proteins of 18 and 25 kDa became evident by using 125I labeling to delineate surface-exposed proteins. A classification scheme using P1 to P5 to delineate the 51-, 41-, 37-, 25- and 18-kDa proteins is proposed. Additionally, murine immune sera were used to identify two immunodominant proteins of 51 and 25 kDa (P1 and P4, respectively).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. A., Pennington T. H., Petrie D. T. Western blot analysis of staphylococcal antibodies present in human sera during health and disease. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):95–99. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Lee W., Matthews R. C., Bayston R. Immunoblot fingerprinting of coagulase negative staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jan;41(1):103–107. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Bayer A. S., Peter J., Ward J. I. Surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S351–S355. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clink J., Pennington T. H. Staphylococcal whole-cell polypeptide analysis: evaluation as a taxonomic and typing tool. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Feb;23(1):41–44. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Scott J. R. Size variation of the M protein in group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1384–1401. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., McCracken G. H., Jr, Frisch C. F., Johnston K. H., Hansen E. J. Antibody response of infants to cell surface-exposed outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b after systemic Haemophilus disease. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.82-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. T., Hall S. L., Barnes W. G., Izuegbu J., Rogolsky M., Zorbas I. Characteristics of coagulase-negative staphylococci from infants with bacteremia. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Apr;6(4):377–383. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198704000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslett T. M., Isenberg H. D., Hilton E., Tucci V., Kay B. G., Vellozzi E. M. Microbiology of indwelling central intravascular catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):696–701. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.696-701.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. M., Lee D. A., Regelmann W. E., Gray E. D., Peters G., Quie P. G. Interference with granulocyte function by Staphylococcus epidermidis slime. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.13-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H. Antigenic diversity of the serotype antigen complex of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: analysis by an indirect enzyme-linked immunoassay. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):101–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.101-110.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristinsson K. G., Hastings J. G., Spencer R. C. The role of extracellular slime in opsonophagocytosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Nov;27(3):207–213. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-3-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J., Gold R. Sepsis in febrile neutropenic children with cancer. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Jan;7(1):34–37. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198801000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirro J., Jr, Rao B. N., Stokes D. C., Austin B. A., Kumar M., Dahl G. V., Colten M., Balas L., Rafferty M., Hancock M. A prospective study of Hickman/Broviac catheters and implantable ports in pediatric oncology patients. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Feb;7(2):214–222. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel G. J., Edelson P. J. Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteremia in neonates: further observations and the occurrence of focal infection. Pediatrics. 1984 Nov;74(5):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. C. Coagulase-negative staphylococci: pathogens with increasing clinical significance. J Pediatr. 1990 Apr;116(4):497–507. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81593-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. C., Kaplan S. L., Baker C. J., Parisi J. T., Mason E. O., Jr Persistent bacteremia due to coagulase-negative staphylococci in low birth weight neonates. Pediatrics. 1989 Dec;84(6):977–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press O. W., Ramsey P. G., Larson E. B., Fefer A., Hickman R. O. Hickman catheter infections in patients with malignancies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Jul;63(4):189–200. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198407000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt B. K., Kirpalani H. M., Corey M., Low D. E., Philip A. G., Ford-Jones E. L. Coagulase-negative staphylococci as true pathogens in newborn infants: a cohort study. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Nov;6(11):1026–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum S. C., Gardner P., Shillito J. Infections of cerebrospinal fluid shunts: epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):543–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skahan J. M., Parisi J. T. Development of a bacteriophage-typing set for Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):16–18. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.16-18.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Tabaqchali S. New method for typing coagulase negative staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;39(11):1271–1275. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.11.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson-Carter F. M., Pennington T. H. Characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analyses. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2199–2203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2199-2203.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscoli C., Garaventa A., Boni L., Melodia A., Dini G., Cuneo R., Rizzo A., Moroni C., Rogers D., De Bernardi B. Role of Broviac catheters in infections in children with cancer. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Aug;7(8):556–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Schimpff S. C., Newman K. A., Wiernik P. H. Staphylococcus epidermidis: an increasing cause of infection in patients with granulocytopenia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):503–508. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Dudnick D. V., Chapin M., Ho W. G., Gale R. P., Martin W. J. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Jan;143(1):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bronswijk H., Verbrugh H. A., Heezius H. C., Renders N. H., Fleer A., van der Meulen J., Oe P. L., Verhoef J. Heterogeneity in opsonic requirements of Staphylococcus epidermidis: relative importance of surface hydrophobicity, capsules and slime. Immunology. 1989 May;67(1):81–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]