Abstract
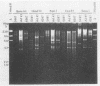
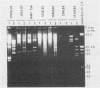
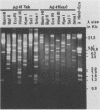
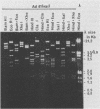
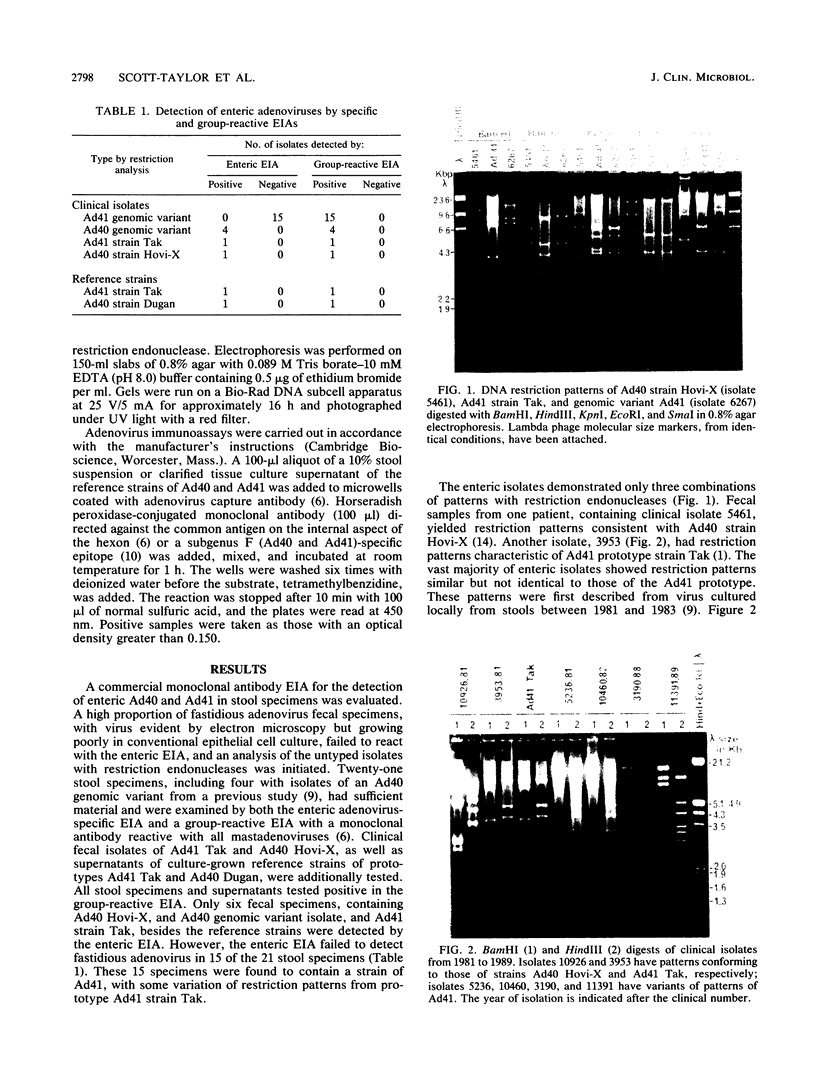
A commercial monoclonal antibody enzyme immunoassay for the detection of enteric adenovirus type 40 and 41 (Ad40 and Ad41) in stool specimens was evaluated. Twenty-one stool specimens from children with gastroenteritis, with adenovirus particles visible by electron microscopy, and reference strains Ad40 Dugan and Ad41 Tak were tested by Ad40- and Ad41-specific and adenovirus group-reactive immunoassays. All stool specimens tested positive in the group-reactive immunoassay. However, only six specimens, containing isolates of Ad40 strain Hovi-X, an Ad40 genomic variant, and Ad41 strain Tak, reacted with the specific immunoassay, besides the reference strains. Fifteen stool specimens determined by restriction analysis to contain a genomic variant of Ad41 were negative by specific immunoassay. The positions of restriction site differences from the prototype strain Ad41 Tak were analyzed, and four mutations were mapped within the hexon gene; two others may occur in the fiber gene. The Ad41 genomic variant not detected by the enteric test is presently the most frequent cause of local adenoviral gastroenteritis. Highly specific monoclonal antibodies can fail to detect genomic variants of enteric adenoviruses, probably because of alteration of external neutralizable epitopes under immunological pressure to vary.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T., Wadell G., Hierholzer J. C., Wigand R. DNA restriction analysis of adenovirus prototypes 1 to 41. Arch Virol. 1986;91(3-4):277–290. doi: 10.1007/BF01314287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt C. D., Kim H. W., Rodriguez W. J., Arrobio J. O., Jeffries B. C., Stallings E. P., Lewis C., Miles A. J., Gardner M. K., Parrott R. H. Adenoviruses and pediatric gastroenteritis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):437–443. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Petric M., Middleton P. J. Diagnosis of fastidious enteric adenoviruses 40 and 41 in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):334–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.334-338.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buitenwerf J., Louwerens J. J., De Jong J. C. A simple and rapid method for typing adenoviruses 40 and 41 without cultivation. J Virol Methods. 1985 Jan;10(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Whetstone C. A., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus hexon monoclonal antibody that is group specific and potentially useful as a diagnostic reagent. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):360–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.360-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Hazelton P. R., Chuang I., Klisko B. Improved detection of viruses by electron microscopy after direct ultracentrifuge preparation of specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):210–221. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.210-221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Mauthe G., Joshua J., Hannan C. K. Examination of uncommon clinical isolates of human adenoviruses by restriction endonuclease analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):611–616. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.611-616.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Perron-Henry D. M., Stobbs-Walro D., Blacklow N. R. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to enteric adenovirus types 40 and 41. Arch Virol. 1987;94(3-4):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01310718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson M. E., Uhnoo I., Svensson L., Pettersson C. A., Wadell G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of enteric adenovirus 41. J Med Virol. 1985 Sep;17(1):19–27. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H., Berkowitz F. E., Blaskovic P. J., Schoub B. D. Genome variants of human adenovirus 40 (subgroup F). J Med Virol. 1984;14(3):235–246. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H. Genome variants of adenovirus 41 (subgroup G) from children with diarrhoea in South Africa. J Med Virol. 1984;14(1):49–59. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd A. H., Madeley C. R. In vitro growth of some fastidious adenoviruses from stool specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Feb;34(2):213–216. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E. The structural and functional diversity of Adenovirus capsid components. J Gen Virol. 1969 Sep;5(2):221–236. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petric M., Krajden S., Dowbnia N., Middleton P. J. Enteric adenoviruses. Lancet. 1982 May 8;1(8280):1074–1075. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa M., Matsuda A., Ishiyama T., Goto H., Sato G. A rapid and simple method for preparation of adenovirus DNA from infected cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(9):817–822. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki T., Araki K., Kobayashi M., Fujita Y., Abe T., Ushijima H. Genome variants of human adenovirus types 40 and 41 (subgroup F) in Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2567–2571. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2567-2571.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh-Naz N., Naz R. K. Development and application of monoclonal antibodies for specific detection of human enteric adenoviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):840–842. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.840-842.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiff H. E., Straus S. E., Garon C. F. Propagation and in vitro studies of previously non-cultivable enteral adenoviruses in 293 cells. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):832–834. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toogood C. I., Hay R. T. DNA sequence of the adenovirus type 41 hexon gene and predicted structure of the protein. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2291–2301. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhnoo I., Wadell G., Svensson L., Johansson M. Two new serotypes of enteric adenovirus causing infantile diarrhoea. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., Cooney M. K., da Costa Linhares A., de Silva L., Kennett M. L., Kono R., Gui-Fang R., Lindman K., Nascimento J. P., Schoub B. D. Molecular epidemiology of adenoviruses: global distribution of adenovirus 7 genome types. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):403–408. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.403-408.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., de Jong J. C., Wolontis S. Molecular epidemiology of adenoviruses: alternating appearance of two different genome types of adenovirus 7 during epidemic outbreaks in Europe from 1958 to 1980. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):368–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.368-372.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcocks M. M., Carter M. J., Laidler F. R., Madeley C. R. Restriction enzyme analysis of faecal adenoviruses in Newcastle upon Tyne. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Oct;101(2):445–458. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800054406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong J. C., Wigand R., Kidd A. H., Wadell G., Kapsenberg J. G., Muzerie C. J., Wermenbol A. G., Firtzlaff R. G. Candidate adenoviruses 40 and 41: fastidious adenoviruses from human infant stool. J Med Virol. 1983;11(3):215–231. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890110305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. E., Rozijn T. H., de Jong J. C., Sussenbach J. S. Physicochemical properties of the DNAs of the fastidious adenovirus species 40 and 41. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90461-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Avoort H. G., Wermenbol A. G., Zomerdijk T. P., Kleijne J. A., van Asten J. A., Jensma P., Osterhaus A. D., Kidd A. H., de Jong J. C. Characterization of fastidious adenovirus types 40 and 41 by DNA restriction enzyme analysis and by neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Virus Res. 1989 Feb;12(2):139–157. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]