Abstract
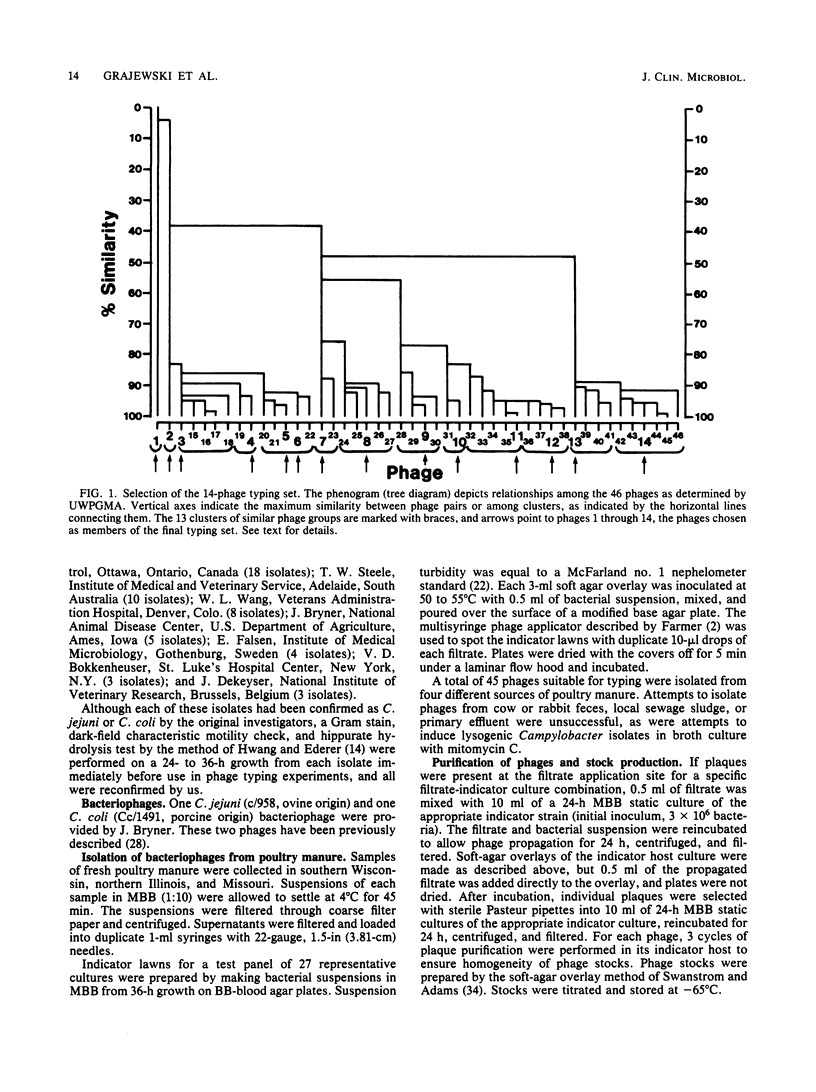
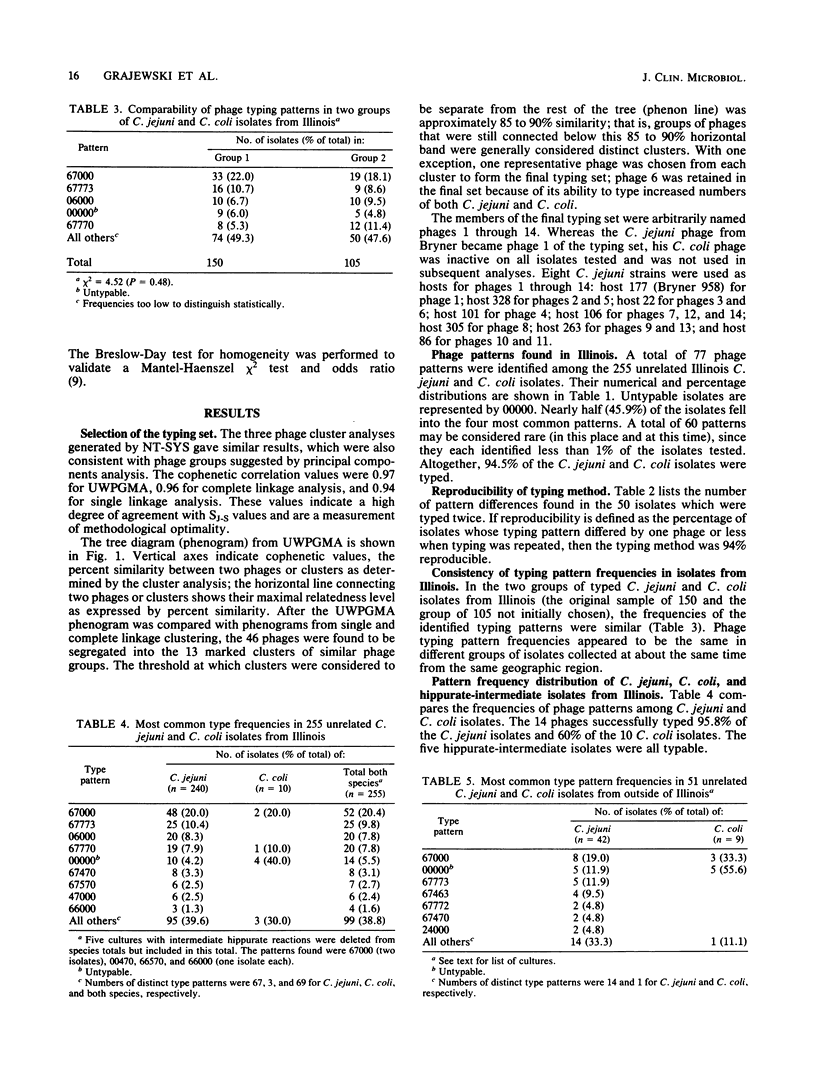
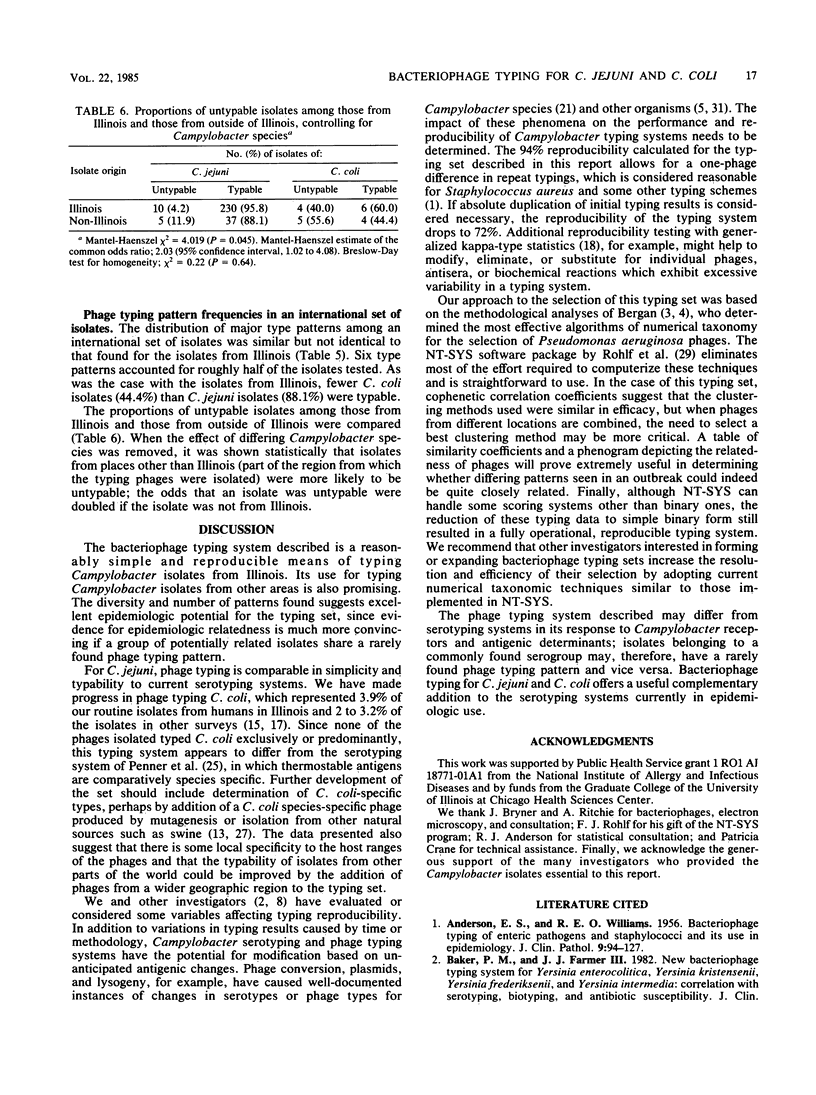
A bacteriophage typing system for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli was developed with phages isolated from poultry feces. Data for phage selection were generated from a set of isolates of C. jejuni and C. coli from humans in Illinois. Selection of 14 phages from the 47 phages available was assisted by determination of the Sneath-Jaccard similarity coefficients and subsequent unweighted pair-group arithmetic averaging cluster analysis. The typing set was reproducible and stable in the 255 isolates from Illinois. Of these isolates, 94.5% were typable, with 46% represented by the four most common phage patterns. In a set of 51 isolates from humans outside of Illinois, 88.1% of the C. jejuni isolates were typable. Phage typing for C. jejuni and C. coli has excellent epidemiologic potential and should serve as a useful adjunct or alternative to serotyping systems in current use.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON E. S., WILLIAMS R. E. Bacteriophage typing of enteric pathogens and staphylococci and its use in epidemiology. J Clin Pathol. 1956 May;9(2):94–127. doi: 10.1136/jcp.9.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T. Comparison of numerical procedures for grouping pseudomonas bacteriophages according to lytic spectra. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(1):55–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanson G., Khakhria R., Lacroix R. Involvement of plasmids in determining bacteriophage sensitivity in Salmonella typhimurium: genetic and physical analysis of phagovar 204. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Sep;28(9):993–1001. doi: 10.1139/m82-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokkenheuser V. D., Richardson N. J., Bryner J. H., Roux D. J., Schutte A. B., Koornhof H. J., Freiman I., Hartman E. Detection of enteric campylobacteriosis in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.227-232.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Holt A. V., Hutchinson D. N. Campylobacter biotyping scheme of epidemiological value. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):677–681. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryner J. H., Ritchie A. E., Booth G. D., Foley J. W. Lytic activity of vibrio phages on strains of Vibrio fetus isolated from man and animals. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):404–409. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.404-409.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryner J. H., Ritchie A. E., Foley J. W., Berman D. T. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriophage for Vibrio fetus. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):94–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.94-99.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Abbott J. D., Painter M. J., Sutcliffe E. M. A comparison of biotypes and serotypes of Campylobacter sp. isolated from patients with enteritis and from animal and environmental sources. J Infect. 1984 Jul;9(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)94498-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakoyiannis C. K., Winter P. J., Marshall R. B. Identification of Campylobacter coli isolates from animals and humans by bacterial restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):545–549. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.545-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Penner J. L., Fleming P. C., Williams A., Hennessy J. N. The serotype and biotype distribution of clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli over a three-year period. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):243–246. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis J. R., Koch G. G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977 Mar;33(1):159–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg J. E., Chang W. Phage conversion of serotypes in Vibrio fetus. Am J Vet Res. 1972 May;33(5):1023–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N., Congi R. V. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli on the basis of thermostable antigens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;2(4):378–383. doi: 10.1007/BF02019474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruneda R. C., Farmer J. J., 3rd Bacteriophage typing of Shigella sonnei. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.66-74.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. E., Bryner J. H., Foley J. W. Role of DNA and bacteriophage in Campylobacter auto-agglutination. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Aug;16(3):333–340. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-3-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Smibert R. M., Krieg N. R. Improved biotyping schemes for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):990–992. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.990-992.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. The application of computers to taxonomy. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):201–226. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWANSTROM M., ADAMS M. H. Agar layer method for production of high titer phage stocks. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Nov;78(2):372–375. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui K. A., Bhattacharyya F. K. Role of temperate phage in determining lytic phage sensitivity and serotype of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):847–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.847-851.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Williams S., Gordon K. P., Harris N., Nolan C., Plorde J. J. Utility of plasmid fingerprinting for epidemiological studies of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):279–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


