Abstract
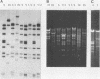
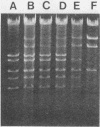
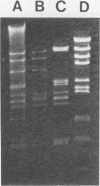
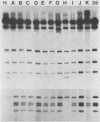
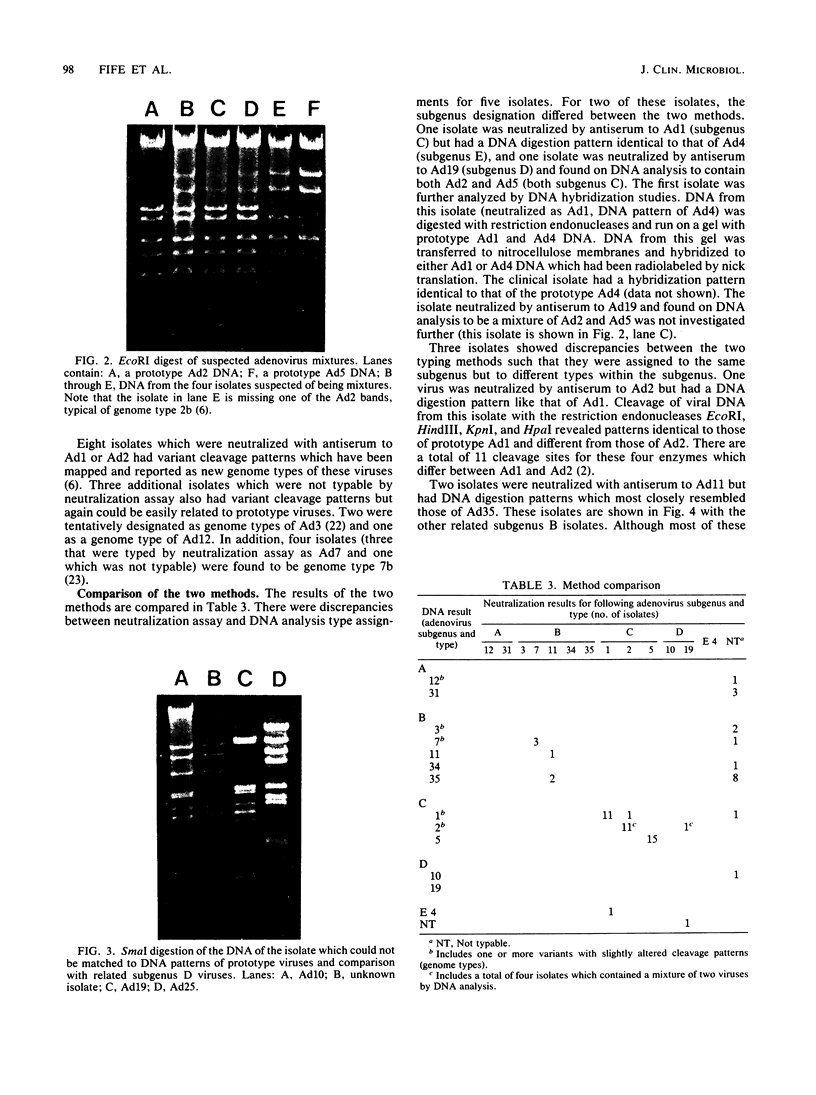
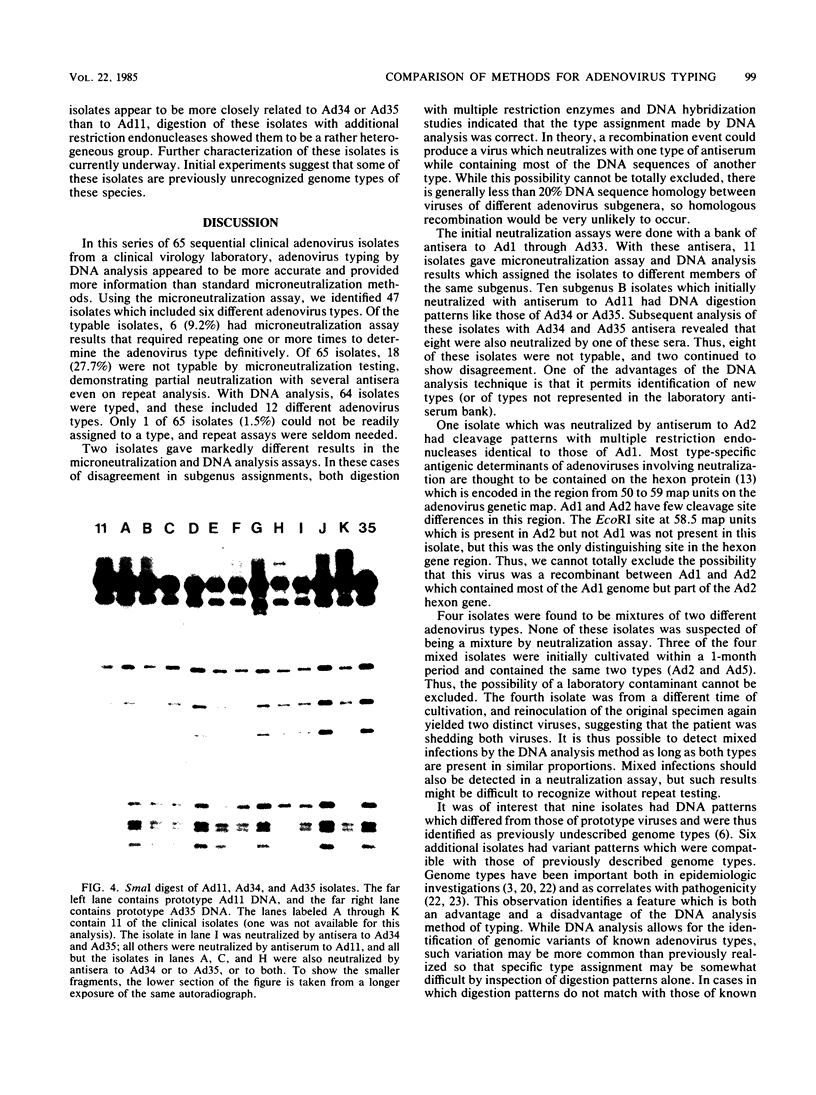
Sixty-five adenovirus isolates collected over a 3.5-year period were typed by both standard microneutralization techniques and restriction endonuclease digestion of viral DNA. Of the 65 isolates, 47 (72.3%) representing six adenovirus types could be typed by microneutralization. Eighteen isolates demonstrated partial neutralization with standard antisera to two or more adenovirus serotypes and thus could not be definitively typed. DNA analysis permitted typing of 64 of the 65 isolates (98.5%) (including four isolates which contained mixtures of two adenovirus types), and 12 different types were identified. Neutralization and DNA typing disagreed for five isolates, and in each case, digestion with multiple restriction endonucleases and DNA hybridization studies were consistent with the type assigned by DNA analysis. In addition, the DNA analysis method allowed the identification of genomic variants (genome types) of five adenovirus types. We conclude that typing clinical isolates of adenovirus by restriction endonuclease digestion of viral DNA can be done rapidly, provides additional epidemiological and typing information, and provides fewer ambiguous results than does typing by neutralization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berns K. I., Kort J., Fife K. H., Grogan E. W., Spear I. Study of the fine structure of adeno-associated virus DNA with bacterial restriction endonucleases. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):712–719. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.712-719.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brůcková M., Wadell G., Sundell G., Syrůcek L., Kunzová L. An outbreak of respiratory disease due to a type 5 adenovirus identified as genome type 5a. Acta Virol. 1980 May;24(3):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Whetstone C. A., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus hexon monoclonal antibody that is group specific and potentially useful as a diagnostic reagent. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):360–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.360-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fife K. H., Ashley R., Corey L. Isolation and characterization of six new genome types of human adenovirus types 1 and 2. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):20–23. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.20-23.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Hall C. E., Cooney M. K. The Seattle Virus Watch. VII. Observations of adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Apr;105(4):362–386. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Mackey J. K., Wold W. S., Rigden P. Thirty-one human adenovirus serotypes (Ad1-Ad31) form five groups (A-E) based upon DNA genome homologies. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett G. B., Newnham W. A. Isolation of adenovirus type 19 from the male and female genital tracts. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Feb;57(1):55–57. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M. C., Hierholzer J. C., Cabradilla C. P., Obijeski J. F. The changing etiology of epidemic keratoconjunctivitis: antigenic and restriction enzyme analyses of adenovirus types 19 and 37 isolated over a 10-year period. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):24–33. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner R. L., Kelly T. J., Jr The structure of replicating adenovirus 2 DNA molecules. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1007–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Wadell G. Immunological relationships between hexons of certain human adenoviruses. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):663–670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.663-670.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Wigand R., Heinrich W. Worldwide epidemiology of human adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Apr;117(4):455–466. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A. F., Hackman R. C., Fife K. H., Corey L., Meyers J. D. Adenovirus infections in patients undergoing bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 28;312(9):529–533. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502283120901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. E., Patch C. T., Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S. Simian virus 40 DNA replication, transcription, and antigen induction during infection with two adenovirus 2-SV40 hybrids that contain the entire SV40 genome. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):43–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.43-52.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straube R. C., Thompson M. A., Van Dyke R. B., Wadell G., Connor J. D., Wingard D., Spector S. A. Adenovirus type 7b in a children's hospital. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):814–819. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Ueno T., Yamashita T., Fujinaga K. Grouping of adenoviruses and identification of restriction endonuclease cleavage patterns of adenovirus DNAs using infected cell DNA: simple and practical methods. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(12):1291–1301. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., Hammarskjöld M. L., Winberg G., Varsanyi T. M., Sundell G. Genetic variability of adenoviruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:16–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G. Molecular epidemiology of human adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:191–220. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., de Jong J. C., Wolontis S. Molecular epidemiology of adenoviruses: alternating appearance of two different genome types of adenovirus 7 during epidemic outbreaks in Europe from 1958 to 1980. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):368–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.368-372.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigand R., Bartha A., Dreizin R. S., Esche H., Ginsberg H. S., Green M., Hierholzer J. C., Kalter S. S., McFerran J. B., Pettersson U. Adenoviridae: second report. Intervirology. 1982;18(4):169–176. doi: 10.1159/000149322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Bishop C. A., Townsend T. R., Bolyard E. A., Bartlett J., Santos G. W., Saral R. Infectious gastroenteritis in bone-marrow-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 29;306(17):1010–1012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204293061701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Lawrence F., Leister F., Takiff H. E., Strauss S. E. Gastroenteritis associated with enteric type adenovirus in hospitalized infants. J Pediatr. 1982 Jul;101(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong J. C., Wigand R., Kidd A. H., Wadell G., Kapsenberg J. G., Muzerie C. J., Wermenbol A. G., Firtzlaff R. G. Candidate adenoviruses 40 and 41: fastidious adenoviruses from human infant stool. J Med Virol. 1983;11(3):215–231. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890110305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]