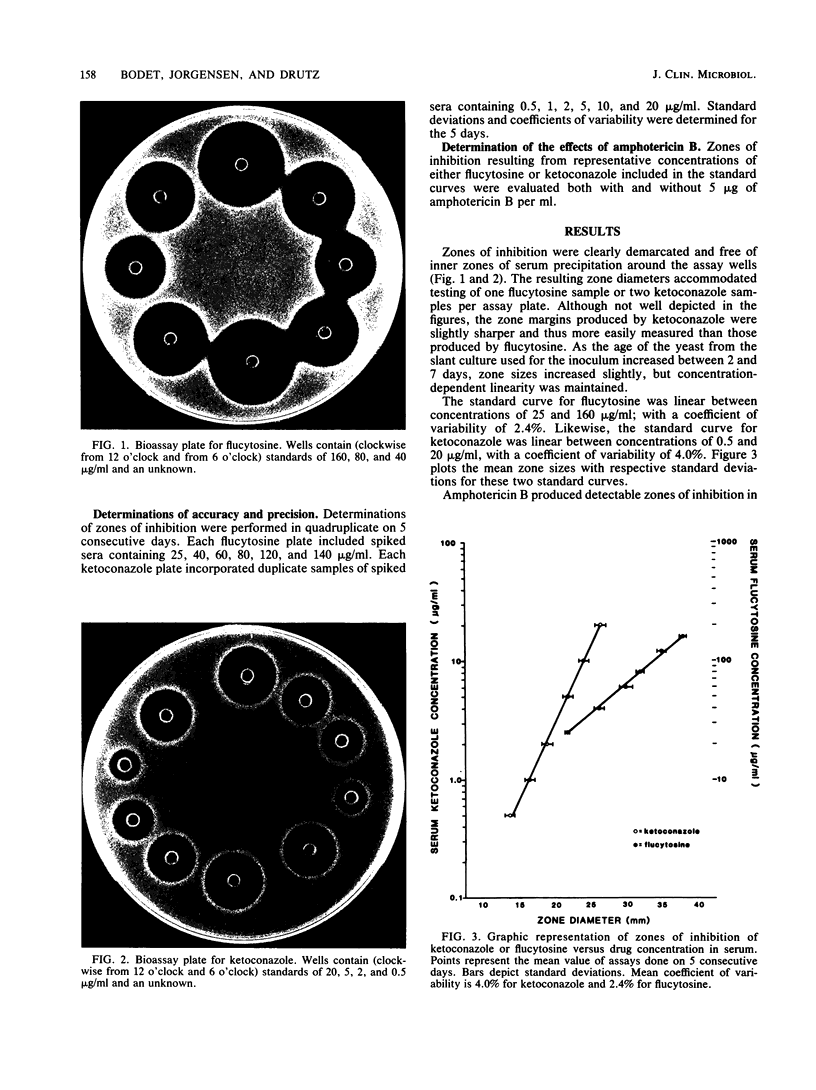
Abstract
A simple agar-well diffusion bioassay suitable for measurement of flucytosine or ketoconazole was developed by using Candida pseudotropicalis ATCC 46764 as the assay organism. A test medium composed of (per liter) 7 g of Trypticase peptone, 7 g of YNB (yeast-nitrogen base), 15 g of glucose, and 15 g of agar was seeded with an inoculum which had been grown to no. 2 McFarland turbidity after 4 to 6 h in YNB-glucose broth. Determinations of flucytosine or ketoconazole were performed without necessity of heating or diluting of serum samples to alleviate amphotericin B interference. A linear relationship between zone diameters and log10 concentration of the drugs was observed over the pharmacologically relevant ranges of 25 to 160 micrograms/ml for flucytosine and 0.5 to 20 micrograms/ml for ketoconazole. The mean coefficient of variability for samples measured on 5 separate days was 2.4% for flucytosin and 4.0% for ketoconazole. This assay represents a significant improvement over previous bioassay methods in that a single test system may be used for measurement of either flucytosine or ketoconazole, no serum dilution or pretreatment is required, inoculum preparation is accomplished entirely on the day of the assay, and sharp, clearly defined zones of inhibition are obtained with both drugs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews F. A., Peterson L. R., Beggs W. H., Crankshaw D., Sarosi G. A. Liquid chromatographic assay of ketoconazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):110–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E., Dismukes W. E., Duma R. J., Medoff G., Sande M. A., Gallis H., Leonard J., Fields B. T., Bradshaw M., Haywood H. A comparison of amphotericin B alone and combined with flucytosine in the treatment of cryptoccal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 19;301(3):126–131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907193010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block E. R., Bennett J. E. Pharmacological studies with 5-fluorocytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jun;1(6):476–482. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro A., Einstein H., Levine B., Ross J. B., Schillaci R., Fierer J., Friedman P. J. Ketoconazole for treatment of disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Apr;96(4):436–440. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-4-436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diasio R. B., Lakings D. E., Bennett J. E. Evidence for conversion of 5-fluorocytosine to 5-fluorouracil in humans: possible factor in 5-fluorocytosine clinical toxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Dec;14(6):903–908. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.6.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diasio R. B., Wilburn M. E., Shadomy S., Espinel-Ingroff A. Rapid determination of serum 5-fluorocytosine levels by high-performance liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):500–504. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes W. E., Stamm A. M., Graybill J. R., Craven P. C., Stevens D. A., Stiller R. L., Sarosi G. A., Medoff G., Gregg C. R., Gallis H. A. Treatment of systemic mycoses with ketoconazole: emphasis on toxicity and clinical response in 52 patients. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases collaborative antifungal study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jan;98(1):13–20. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Herndon J. H., Jr, Kniker W. T., Levine H. B. Ketoconazole treatment of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Arch Dermatol. 1980 Oct;116(10):1137–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann I. M., Prentice H. G., Corringham R., Blacklock H. A., Keaney M., Shannon M., Noone P., Gascoigne E., Fox J., Boesen E. Ketoconazole versus nystatin plus amphotericin B for fungal prophylaxis in severely immunocompromised patients. Lancet. 1982 Apr 10;1(8276):826–829. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91874-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Alexander G. A., Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Sensitive bioassay for ketoconazole in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):59–62. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar R. L., Drutz D. J. Rapid, simple bioassay for 5-fluorocytosine in the presence of amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):462–465. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman C. A., Carleton J. A., Frame P. T. Simple assay for 5-fluorocytosine in the presence of amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):381–383. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman C. A., Frame P. T. Bone marrow toxicity associated with 5-fluorocytosine therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):244–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Carpentier F. Treatment of mycoses in cancer patients. Am J Med. 1983 Jan 24;74(1B):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble M. A., Harper B., Grant A. G., Bernstein M. Rapid determination of 5-fluorocytosine levels in blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):996–997. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.996-997.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. H., Rich P., Parker F., Hanifin J. M. Ketoconazole in griseofulvin-resistant dermatophytosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982 Feb;6(2):224–229. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwertschlag U., Nakata L. M., Gal J. Improved procedure for determination of flucytosine in human blood plasma by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):303–305. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]