Abstract
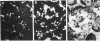
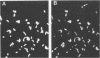
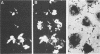
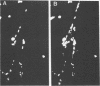
A double immunofluorescence staining technique is described for differentiation between cell-attached (extracellular) and ingested (intracellular) bacteria by HEp-2 cells in cell culture monolayers. This method is based upon the observation that membranes of viable mammalian cells are impermeable for antibodies but are rendered permeable by treatment with fixatives. Consequently, extracellular bacteria can be stained by specific rhodamine-labeled antibodies before fixation, and intracellular bacteria can be visualized by treatment with specific fluorescein-labeled antibodies after fixation. The accuracy and simplicity of this method is demonstrated with HEp-2 cell culture monolayers as target cells and an isogenic pair of Yersinia enterocolitica, one of which is phagocytosis resistant and the other of which is phagocytosis sensitive. Furthermore, it is shown that this staining technique is also applicable for studying the interaction of bacteria with macrophages and fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bukholm G., Johansen B. V., Namork E., Lassen J. Bacterial adhesiveness and invasiveness in cell culture monolayer. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Dec;90(6):403–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukholm G., Lassen J. Bacterial adhesiveness and invasiveness in cell culture monolayer. 2. In vitro invasiveness of 45 strains belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Dec;90(6):409–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth J. A., Hendley J. O., Mandell G. L. Attachment and ingestion of gonococci human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):512–516. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.512-516.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Hugdahl M. B., Chang M. T., Beery J. T. Serological relatedness of mouse-virulent Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1234–1240. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1234-1240.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Keller C., Morawa R., Schmidt N., Siemens H. J., Laufs R. Plasmids of human strains of Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular relatedness and possible importance for pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):107–115. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E. Infection of HeLa cells with Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR10 bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.290-295.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Maza O., Fehniger T. E., Ashman R. F. Antibody-secreting cell precursor frequencies among the sheep-erythrocyte-binding cells after immunization. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Apr;17(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlman I. J., Romero A., Atkinson J. C., Aulisio C., Sanders A. C., Campbell W., Cholenski J., Ferreira J., Forney E., O'Brian K. Detection of invasiveness of mammalian cells by Escherichia coli: collaborative study. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1982 May;65(3):602–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raevuori M., Harvey S. M., Pickett M. J., Martin W. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):888–890. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Sundqvist C., Mäki M. Adherence and toxicity of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3 and 0:9 containing virulence-associated plasmids for various cultured cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. J. The fate of gonococci in polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):501–509. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Effects of cytochalasin B on polymorphonuclear leucocyte locomotion, phagocytosis and glycolysis. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Aug;73(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]