Abstract
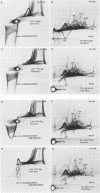
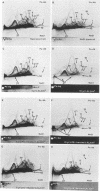
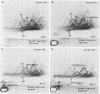
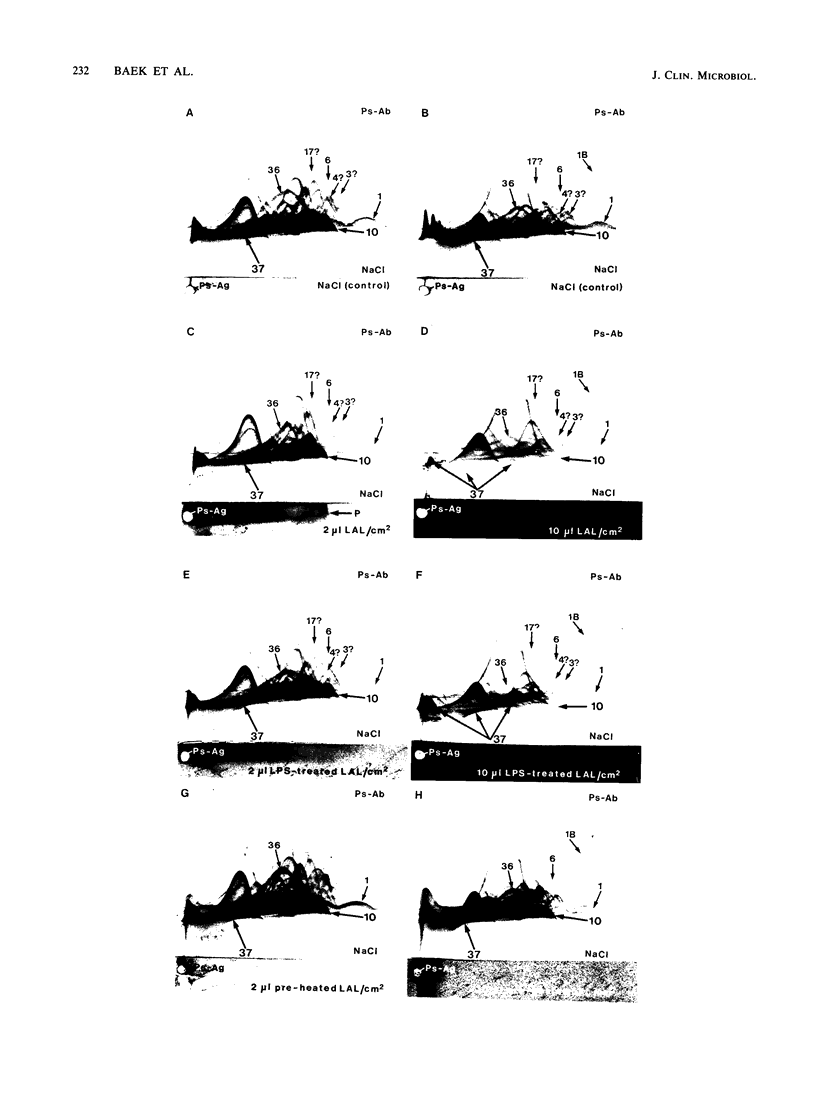
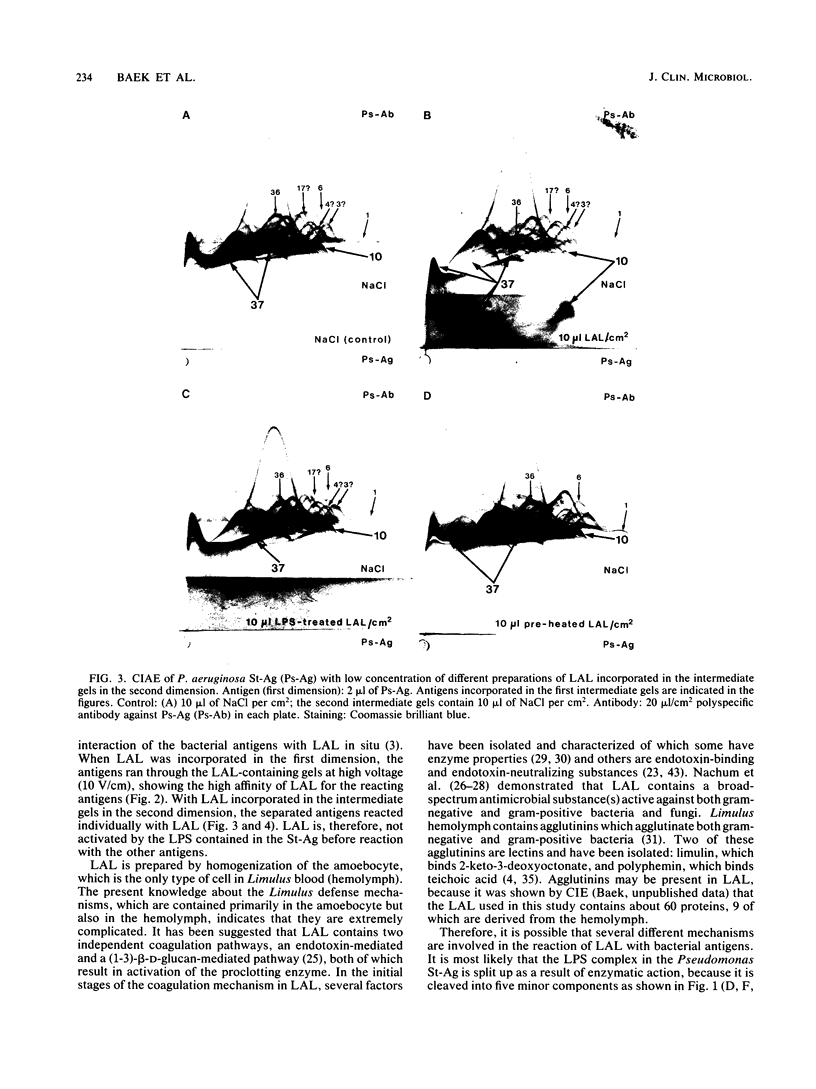
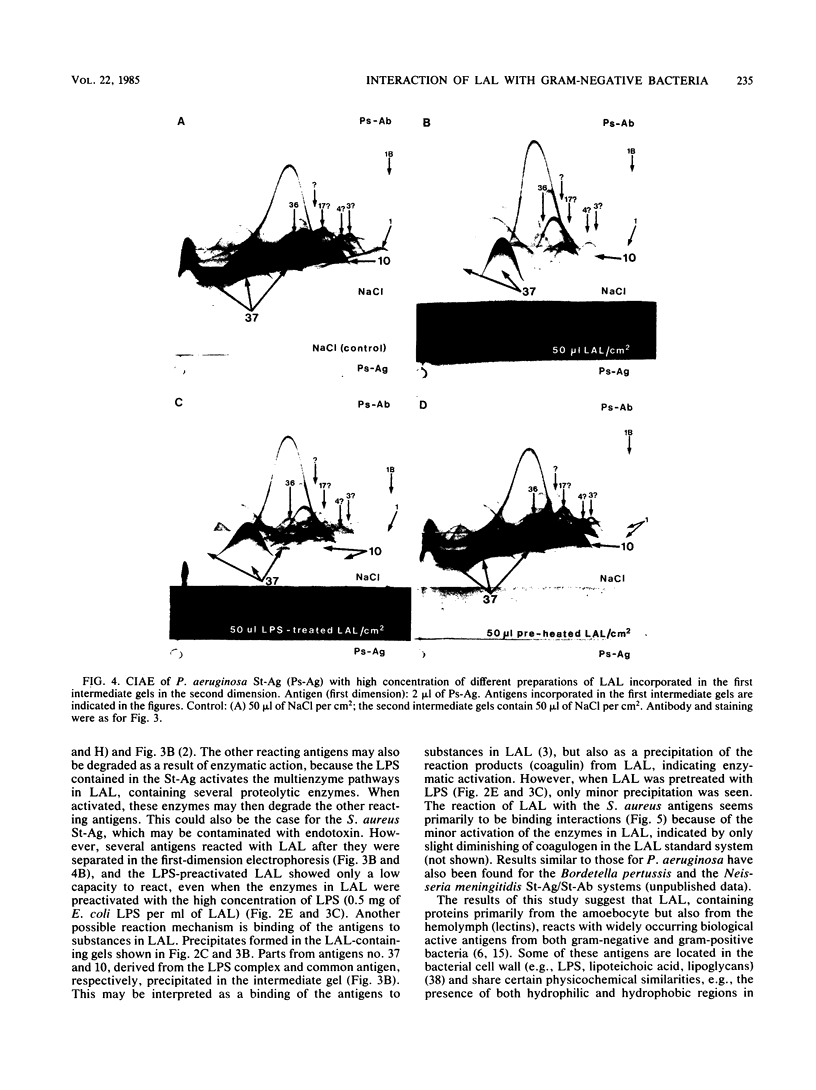
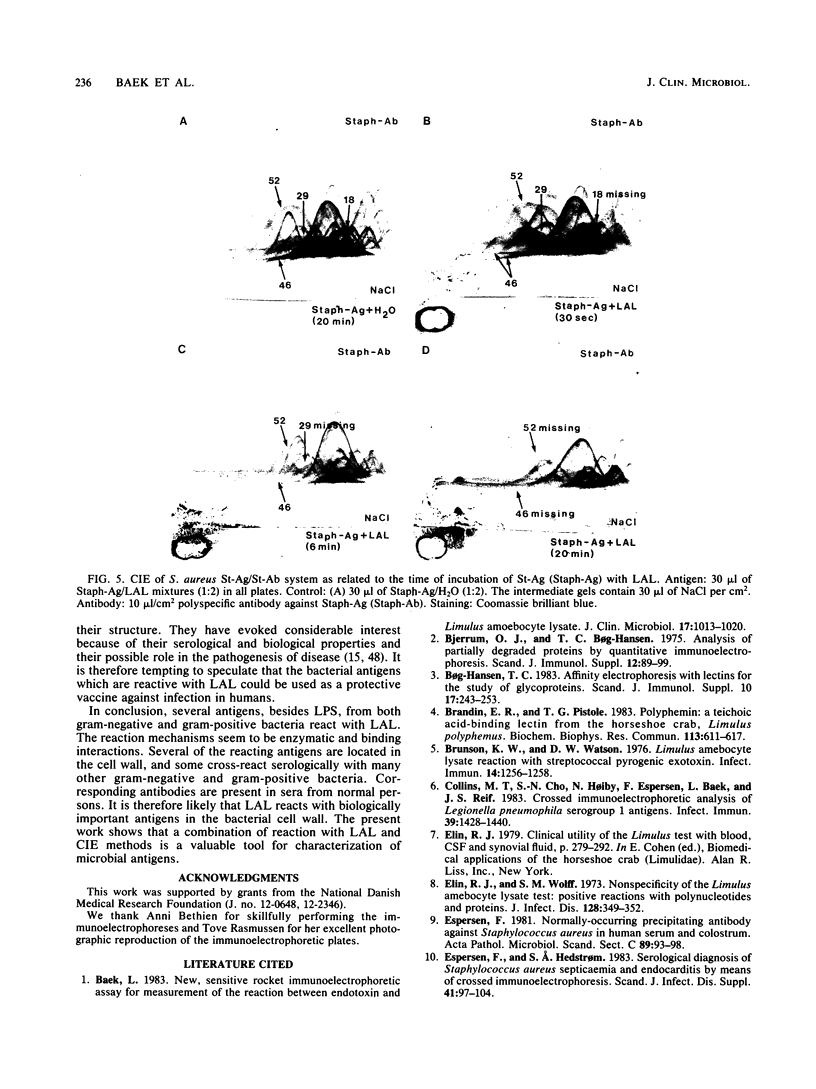
To investigate the interaction of Limulus amoebocyte lysate (LAL) with gram-negative bacteria, soluble antigens from sonicated Pseudomonas aeruginosa were studied by various crossed-immunoelectrophoresis methods before and after reaction with LAL. Of 64 possible, at least 7 antigens were affected, as indicated by precipitin pattern, after the reaction with LAL. The precipitates corresponding to lipopolysaccharide and Pseudomonas "common antigen" disappeared. This reaction was inhibited when LAL was pretreated with lipopolysaccharide or by heating. Several of the reacting antigens have been shown to cross-react with many other strains of both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Soluble antigens from a protein A-deficient strain of Staphylococcus aureus were also studied. LAL reacted with at least four of these antigens, including the teichoic acid complex. It is concluded that LAL is highly reactive with lipopolysaccharide, but it can react with other antigens from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria as well. It is suggested that LAL interacts with biologically important antigens from the bacterial membrane. It is proposed that the reactivity and specificity of LAL for various microbial antigens can be studied by immunoelectrophoretic techniques.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baek L. New, sensitive rocket immunoelectrophoretic assay for measurement of the reaction between endotoxin and Limulus amoebocyte lysate. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1013-1020.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandin E. R., Pistole T. G. Polyphemin: a teichoic acid-binding lectin from the horseshoe crab, Limulus Polyphemus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):611–617. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91770-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunson K. W., Watson D. W. Limulus amebocyte lysate reaction with streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1256–1258. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1256-1258.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Cho S. N., Høiby N., Espersen F., Baek L., Reif J. S. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1428–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1428-1440.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J. Clinical utility of the Limulus test with blood, CSF and synovial fluid. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;29:279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Nonspecificity of the limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):349–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hedström S. A. Serological diagnosis of Staphylococcus aureus septicaemia and endocarditis by means of crossed immuno-electrophoresis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1983;41:97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Schiøtz P. O. Normally-occurring precipitating antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus in human serum and colostrum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Apr;89(2):93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton S. C., Prior R. B., Spagna V. A., Kreier J. P. Evaluation of Plasmodium berghei for endotoxin by the Limulus lysate assay. J Parasitol. 1980 Oct;66(5):846–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. H., Kessler R. E., Tabak L. A., Shockman G. D. Limulus lysate activity of lipoteichoic acids. J Dent Res. 1977 Dec;56(12):1500–1500. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560121501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway R. E., Levin J., Butler T., Naff G. B., Goldsmith G. H., Saito H., Awoke S., Wallace C. K. Activation of protein mediators of inflammation and evidence for endotoxemia in Borrelia recurrentis infection. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):933–938. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H. Detection of endotoxin in urine: rapid diagnosis of gram negative bacteriuria by the Limulus assay. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;29:255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., Mutharia L. M., Hancock R. E., Høiby N., Lam K., Baek L., Costerton J. W. Immunogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane antigens examined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):88–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.88-98.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. The Limulus test: a status report. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;29:235–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. J., Thacker W. L., Mitchell S. H. Demonstration of chlamydial endotoxin-like activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):215–216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang S. M., Liang C. M., Liu T. Y. Studies on Limulus amoebocyte. Isolation and identification of a membrane-bound protein activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from Limulus amoebocyte. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4968–4972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami T., Nagase T., Matsumoto, Suzuki S., Suzuki M. Gelatin of Limulus amoebocyte lysate by simple polysaccharides. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(5):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachum R., Siegel S. E., Sullivan J. D., Jr, Watson S. W. Inactivation of endotoxin by Limulus amoebocyte lysate. J Invertebr Pathol. 1978 Jul;32(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(78)90173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachum R., Watson S. W., Sullivan J. D., Jr, Siegel S. E. Antimicrobial defense mechanisms in the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus: preliminary observations with heat-derived extracts of Limulus amoebocyte lysate. J Invertebr Pathol. 1979 May;33(3):290–299. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(79)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Levin J. Endotoxin-mediated Limulus proclotting enzyme activator and detection of a previously undescribed protease(Protease N). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1619–1623. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Levin J. Fractionation of Limulus amebocyte lysate. Characterization of activation of the proclotting enzyme by an endotoxin-mediated activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 5;707(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistole T. G. Bacterial agglutinins from Limulus polyphemus--an overview. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;29:547–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platica M., Harding W., Hollander V. P. Dithiols simulate endotoxin in the Limulus reaction. Experientia. 1978 Sep 15;34(9):1154–1155. doi: 10.1007/BF01922927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold R. B., Fine J. A technique for quantitative measurement of endotoxin in human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):334–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Corona R. R., Skarnes R., Tamakuma S., Fine J. The Limulus coagulation test for endotoxin. A comparison with other assay methods. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):599–601. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostam-Abadi H., Pistole T. G. Lipopolysaccharide-binding lectin from the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, with specificity for 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate (KDO). Dev Comp Immunol. 1982 Spring;6(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(82)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiøtz P. O., Høiby N., Hertz J. B. Cross-reactions between Staphylococcus aureus and fifteen other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seid R. C., Jr, Smith P. F., Guevarra G., Hochstein H. D., Barile M. F. Endotoxin-like activities of mycoplasmal lipopolysaccharides (lipoglycans). Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):990–994. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.990-994.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. E., Nachum R. Indications for the use of the Limulus lysate assay in bacterial meningitis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;29:245–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Hill J. O., Snyder I. S., Burrell R. Mitogenicity of cell wall fractions of Micropolyspora faeni. Ann Allergy. 1978 Jan;40(1):12–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Hertz J. B., Høiby N., Jensen K., Mansa B., Samra Z. An antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. I. The isolation of a 'common antigen' from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Mikami T., Matsumoto T., Suzuki S. Gelation of Limulus lysate by synthetic dextran derivatives. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(8):419–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Limulus anti-LPS factor: an anticoagulant which inhibits the endotoxin mediated activation of Limulus coagulation system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91493-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubbs H. Endotoxin in human and murine malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tvede M., Baek L. A rapid method to produce a sensitive Limulus amoebocyte lysate (LAL). I. Evaluation of inter and intra batch differences in LAL and hemolymph from Limulus polyphemus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Feb;91(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Smith P. F., Kahane I. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and mycoplasmal lipoglycans: a comparison between their abilities to induce macrophage-mediated tumor cell killing and Limulus amebocyte lysate clotting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H., Oppenheim J. D. Isolation, characterization, and biological properties of an endotoxin-like material from the gram-positive organism Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):845–857. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.845-857.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Bacterial cell surface amphiphiles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 27;604(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90583-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Heymer B., Schleifer K. H., Haferkamp O. Investigations on the specificity of the Limulus test for the detection of endotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):867–871. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.867-871.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]