Abstract
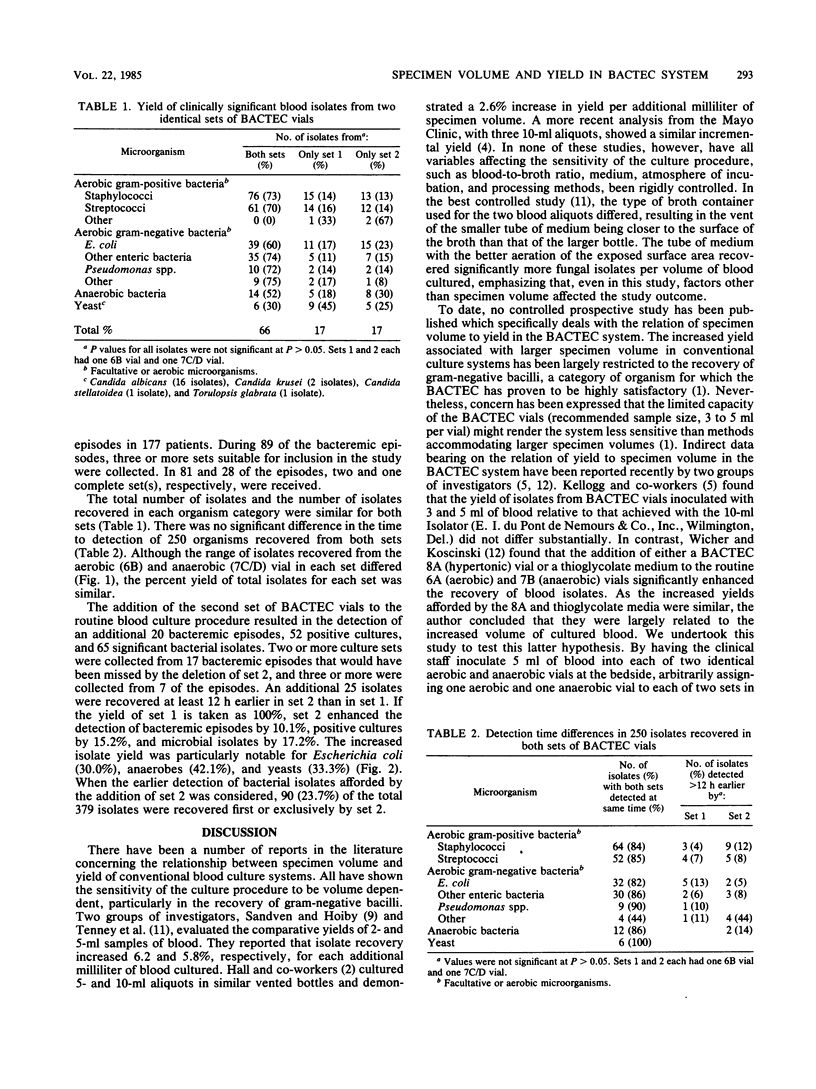
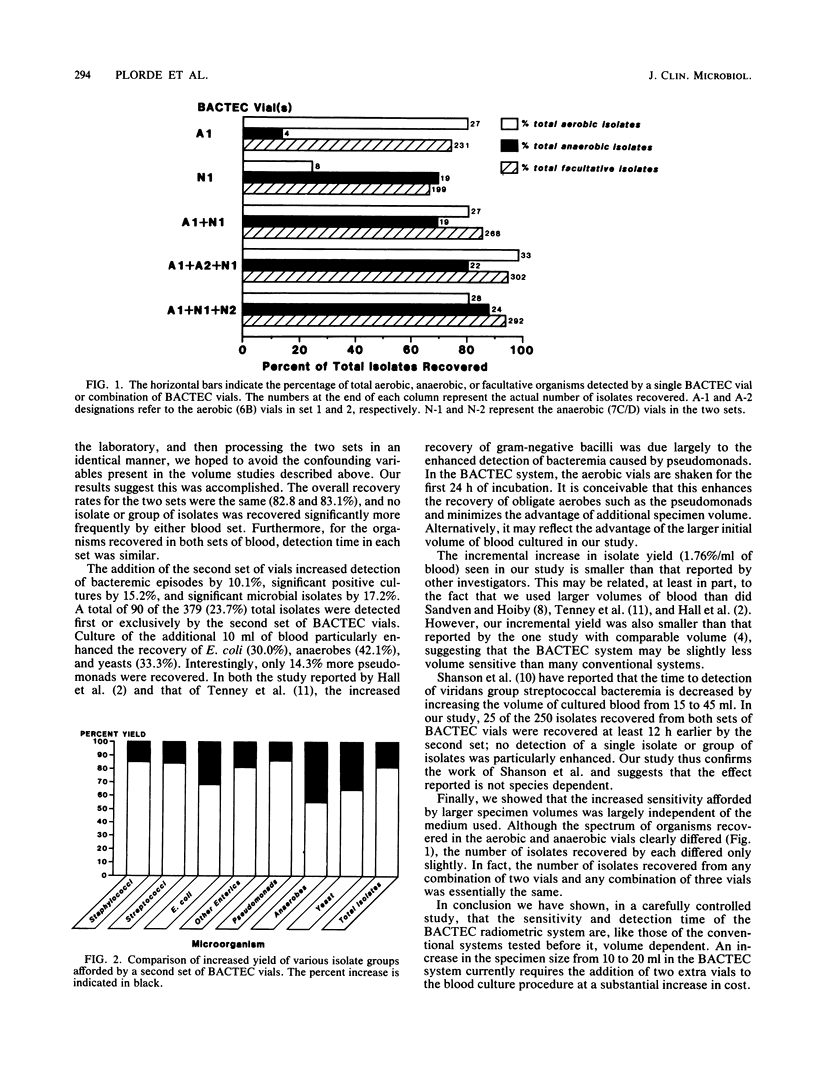
During a 24-month period, 5,625 blood culture specimens were collected at the Seattle Veterans Administration Medical Center in 20-ml volumes and divided into separate 10-ml aliquots. The two aliquots were processed as duplicate sets (set 1, set 2) by the BACTEC system (Johnston Laboratories, Inc., Towson, Md.). Specimens (5 ml) from each set were inoculated into aerobic (6B) and anaerobic (7C/7D) vials. A total of 434 significantly positive blood cultures were found. In 342 of these positive cultures, yielding 379 isolates (112 members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, 104 staphylococci, 87 streptococci, 27 anaerobes, 20 yeasts, 14 pseudomonads, and 15 miscellaneous organisms), there was adequate specimen volume to fill all four vials. The utilization of set 1 would have resulted only in the failure to detect 65 of 379 (17.2%) significant isolates, 52 of 342 (15.2%) positive cultures, and 20 of 198 (10.1%) bacteremic episodes. There were no significant differences in the recovery of individual species in sets 1 and 2. Although the range of isolates recovered by the aerobic and anaerobic vials of each set differed, the percent yield of total isolates was similar, indicating total isolate yield was predominantly a function of specimen volume. The addition of set 2 most dramatically increased the recovery of Escherichia coli (30%), yeasts (33%), and anaerobes (42%).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hall M. M., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Effect of volume of blood cultured on detection of bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):643–645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.643-645.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd The importance of volume of blood cultured in the detection of bacteremia and fungemia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;1(2):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg J. A., Manzella J. P., McConville J. H. Clinical laboratory comparison of the 10-ml isolator blood culture system with BACTEC radiometric blood culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.618-623.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salventi J. F., Davies T. A., Randall E. L., Whitaker S., Waters J. R. Effect of blood dilution on recovery of organisms from clinical blood cultures in medium containing sodium polyanethol sulfonate. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):248–252. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.248-252.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandven P., Høiby E. A. The importance of blood volume cultured on detection of bacteraemia. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Jun;89(3):149–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00168_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanson D. C., Thomas F., Wilson D. Effect of volume of blood cultured on detection of Streptococcus viridans bacteraemia. J Clin Pathol. 1984 May;37(5):568–570. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.5.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney J. H., Reller L. B., Mirrett S., Wang W. L., Weinstein M. P. Controlled evaluation of the volume of blood cultured in detection of bacteremia and fungemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):558–561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.558-561.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher K., Koscinski D. Laboratory experience with radiometric detection of bacteremia with three culture media. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.668-671.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



