Abstract
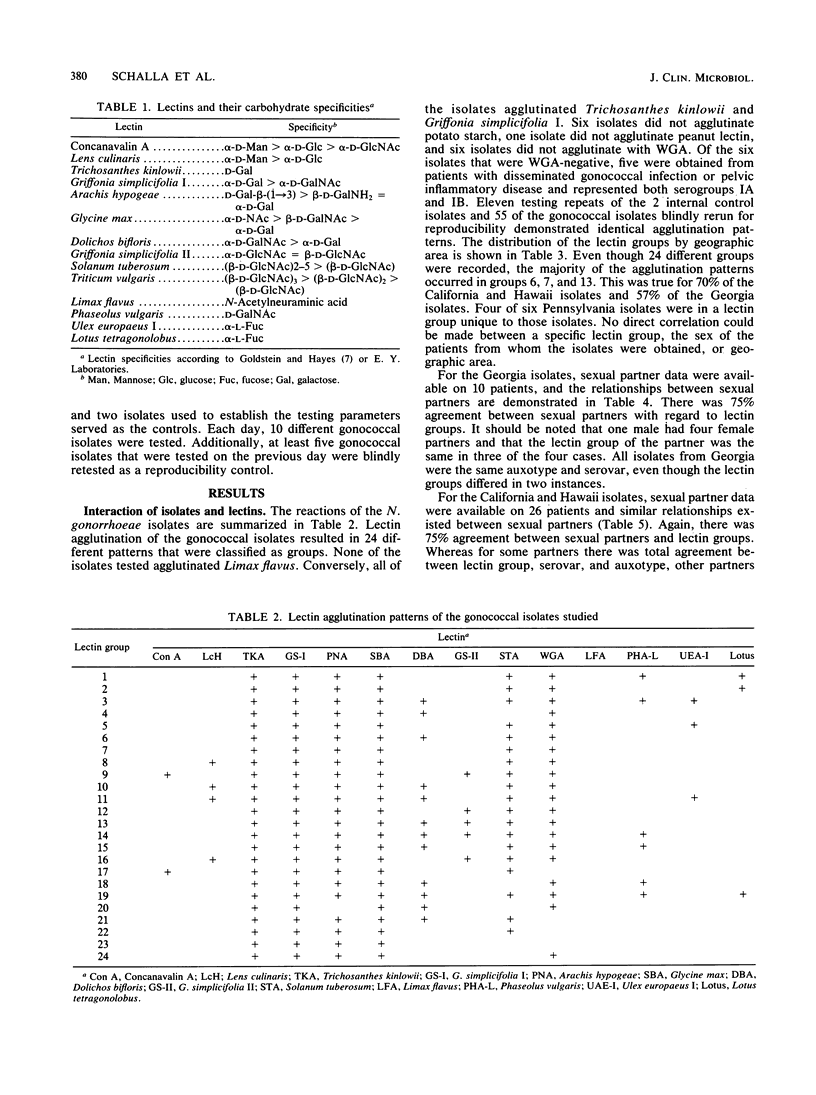
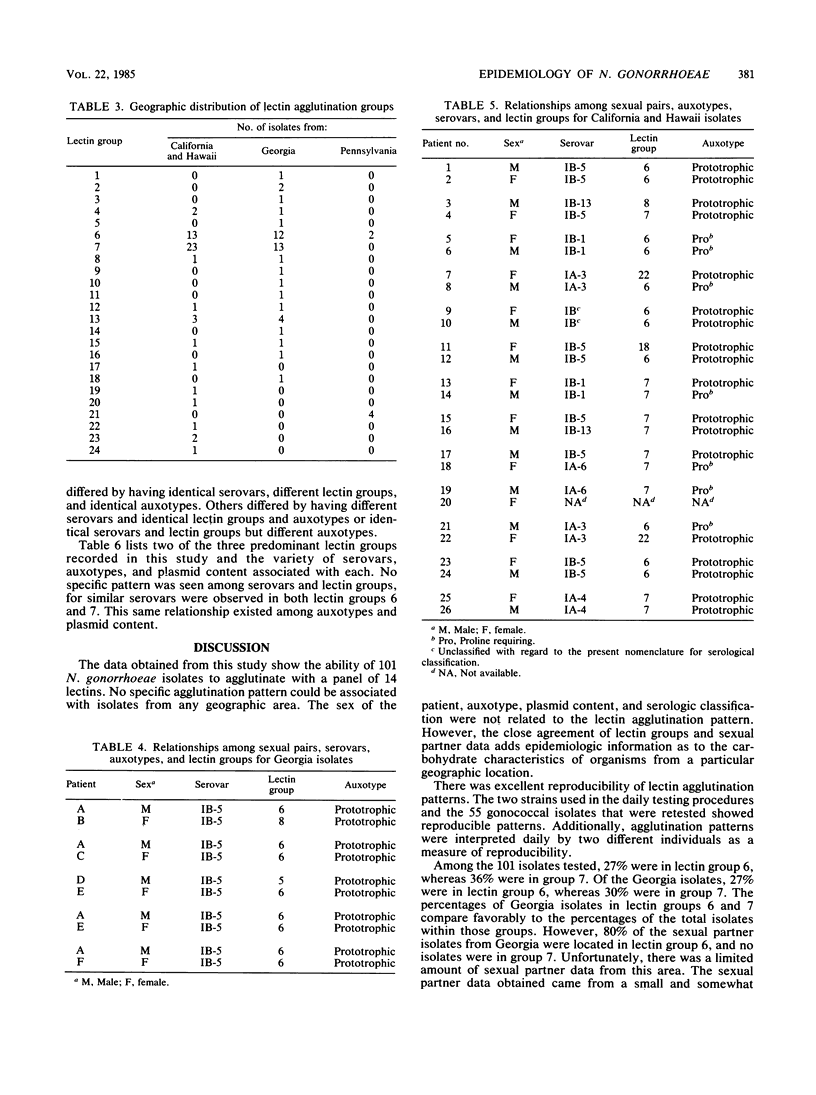
A total of 101 isolates of penicillinase-producing and non-penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae with known nutritional requirements, plasmid content, and serovars, were examined for lectin agglutination patterns. These isolates were from outbreaks in Georgia, California, Hawaii, and Pennsylvania. Cell suspensions made from 16- to 18-h cultures were mixed with 14 different lectins, and the resultant agglutination patterns were classified as agglutination groups. Among the 101 isolates tested, 24 different agglutination groups were demonstrated. Of the organisms tested, 55% were located in 3 of the 24 groups, and 86% of the isolates reacted with the lectins Trichosanthes kinlowii, Griffonia simplicifolia I, peanut agglutinin, soybean agglutinin, potato agglutinin, and wheat germ agglutinin. One isolate did not react with peanut or potato agglutinin, five isolates lacked reactivity with potato agglutinin, and six isolates did not react with wheat germ agglutinin. Of the wheat germ-negative isolates, four were from Pennsylvania and were identical with regard to auxotype, plasmid content, serovar, and lectin group. The other two wheat germ-negative isolates were from California and were unrelated by the same criteria to the four Pennsylvania isolates and to each other. Among the isolates tested, there were no differences in lectin groups with regard to the sex of the patient. In the Georgia collection, agglutination with one lectin group was confined to isolates of serogroup IA. This association was not observed for the other geographic areas. Some isolates showing identical auxotype, plasmid content, and serovars could be differentiated based on lectin agglutination patterns, whereas other isolates were identical by all testing criteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. Z., Connelly M. C., Apicella M. A. Interaction of lectins with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Apr;26(4):468–474. doi: 10.1139/m80-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. B., Ezzell J. W., Jr, Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Differentiation of Bacillus anthracis and other Bacillus species by lectins. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):48–53. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.48-53.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis G. D., Slack M. P. Wheat-germ agglutination of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. A laboratory investigation. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Aug;57(4):253–255. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.4.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson S. K., Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Differentiation of coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative staphylococci by lectins and plant agglutinins. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):547–553. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.547-553.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Nedjat-Haiem F., Keller K. F., Frasch C. E. Diagnostic value of interactions between members of the family Neisseriaceae and lectins. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):383–387. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.383-387.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E. Role of lipopolysaccharide in wheat germ agglutinin-mediated agglutination of Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):498–501. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.498-501.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Hayes C. E. The lectins: carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1978;35:127–340. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Turner E. M. Rapid fermentation confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):550–552. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.550-552.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Tam M. R., Nowinski R. C., Holmes K. K., Sandström E. G. Serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with use of monoclonal antibodies to gonococcal outer membrane protein I. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):44–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. S., Martin J. E., Jr Evaluation of the phadebact gonococcus test, a coagglutination procedure for confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):153–156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.153-156.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Interaction of wheat-germ agglutinin with bacterial cells and cell-wall polymers. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perine P. L., Thornsberry C., Schalla W., Biddle J., Siegel M. S., Wong K. H., Thompson S. E. Evidence for two distinct types of penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Lancet. 1977 Nov 12;2(8046):993–995. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92891-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistole T. G. Interaction of bacteria and fungi with lectins and lectin-like substances. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:85–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer R. L., Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Lectins in diagnostic microbiology: use of wheat germ agglutinin for laboratory identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):669–672. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.669-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short H. B., Ploscowe V. B., Weiss J. A., Young F. E. Rapid method for auxotyping multiple strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):244–248. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.244-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam M. R., Buchanan T. M., Sandström E. G., Holmes K. K., Knapp J. S., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1042–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1042-1053.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


