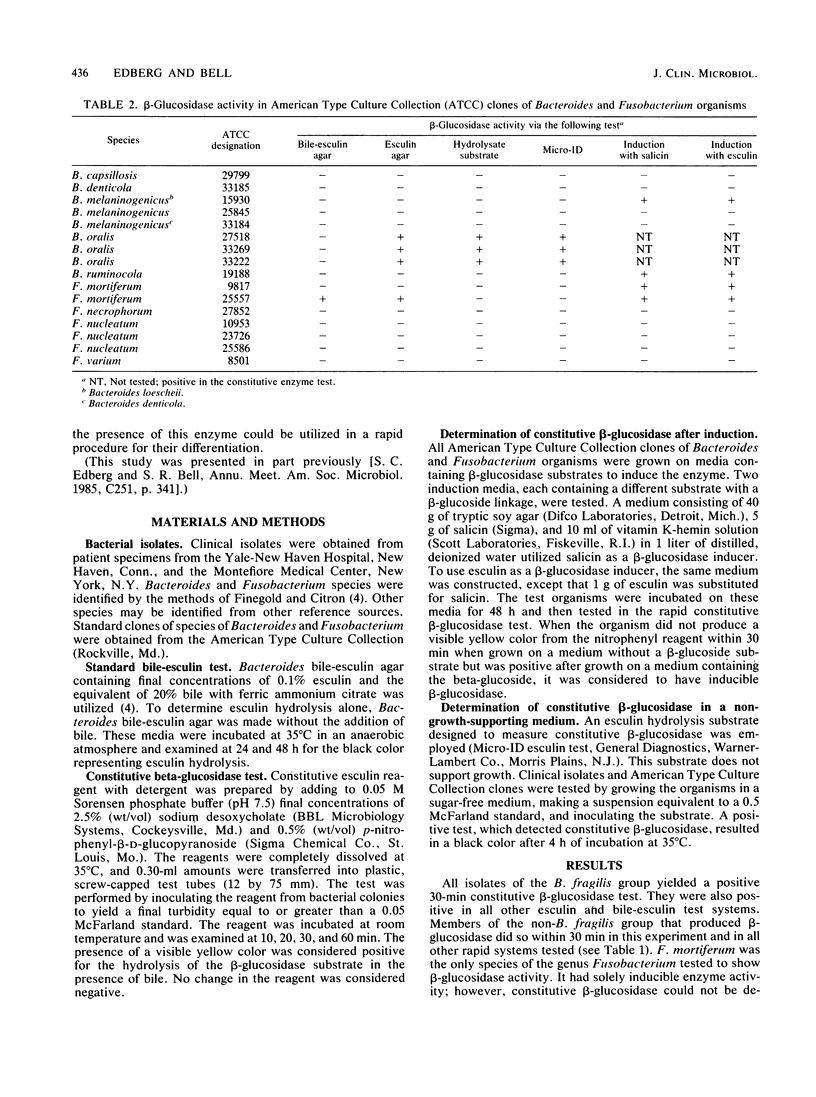
Abstract
Esculin has been incorporated into both a medium and test with 20% bile for many years to differentiate Bacteroides from Fusobacterium organisms. After 24 to 48 h, all members of the Bacteroides fragilis group grow in 20% bile and hydrolyze esculin. Fusobacterium mortiferum can both grow in bile and hydrolyze esculin, thus limiting the use of the bile-esculin medium and test. The hypothesis that constitutive esculinase (beta-glucosidase) could differentiate Bacteroides from Fusobacterium organisms was investigated. Clinical isolates and American Type Culture Collection clones of the B. fragilis group and other species of Bacteroides and Fusobacterium were tested. All B. fragilis were positive within 30 min. In no case was a Fusobacterium organism positive for constitutive enzyme in a hydrolyzable substrate-based test. The percentage of positive results for other species of Bacteroides agreed with those published in the literature for the esculin test. The genus Fusobacterium can be separated from Bacteroides organisms based on a lack of constitutive beta-glucosidase in the former in a 30-min one-tube test.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edberg S. C., Pittman S., Singer J. M. Esculin hydrolysis by Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):111–116. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.111-116.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Trepeta R. W., Kontnick C. M., Torres A. R. Measurement of active constitutive beta-D-glucosidase (esculinase) in the presence of sodium desoxycholate. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):363–365. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.363-365.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston S. J., Kominos S. D., Yee R. B. New medium for selection and presumptive identification of the Bacteroides fragilis group. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):448–453. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.448-453.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin A., Edberg S. C. Esculin hydrolysis reaction by Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):251–254. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.251-254.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


