Abstract
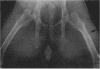
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to evaluate and compare the immunoglobulin G antibody response to Staphylococcus aureus cell walls of rabbits with either chronic staphylococcal osteomyelitis or subcutaneous abscesses. Osteomyelitis of the femur was produced by the intramedullary application of a sclerosing agent (3% sodium tetradecyl sulfate) and S. aureus. Radiographic evidence of osteomyelitis was observed in 10 of the 13 animals that survived the 10-week experimental period, and the diagnosis was confirmed by histopathology in 8 of the 10 instances. Abscess formation was initiated in a separate group of rabbits by the subcutaneous injection of S. aureus cells. All 10 of these rabbits subsequently developed abscesses, which usually resolved spontaneously within 3 to 5 weeks. Elevated levels of immunoglobulin G antibodies to the cell wall antigen were detected in 7 of 10 rabbits with osteomyelitis at 21 days postinfection, and these animals continued to display high antibody levels even at 59 days postinfection. In contrast, elevated levels of anti-cell-wall antibodies were only detected in 1 of 10 rabbits with subcutaneous abscesses. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was found to be a rapid and sensitive serological technique for the detection of cell wall antibodies in this experimental osteomyelitis model and may be useful for the diagnosis of staphylococcal bone infections in humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andriole V. T., Nagel D. A., Southwick W. O. Chronic staphylococcal osteomyelitis: an experimental model. Yale J Biol Med. 1974 Mar;47(1):33–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. Teichoic acids: antigenic determinants, chain separation, and their location in the cell wall. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):910–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eid A. M., Issa H., Deif A. I. Some immunological aspects of staphylococcal haematogenous osteomyelitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1980;96(3):221–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00457786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hedström S. A. Precipitating antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus in serum from patients with staphylococcal osteomyelitis, investigated by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Jun;90(3):205–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROST H. M., VILLANEUVA A. R., ROTH H. Pyogenic osteomyelitis: diffusion in live and dead bone with particular reference to the tetracycline antibiotics. Henry Ford Hosp Med Bull. 1960 Jun;8:255–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson L. J., Sottile M. I., Aguilar-Torres F. G., Dee T. H., Rytel M. W. Correlation of antistaphylococcal antibody titers with severity of staphylococcal disease. Am J Med. 1978 Apr;64(4):629–633. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90583-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski J. J., Tipper D. J., Berman D. T. Preparation of Cell Wall Antigens of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):54–59. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.54-59.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurek M., Pryjma K., Bartkowski S., Heczko P. B. Anti-staphylococcal gamma hemolysin antibodies in rabbits with staphylococcal osteomyelitis. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 May 18;163(1):61–65. doi: 10.1007/BF02126710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackowiak P. A., Smith J. W. Teichoic acid antibodies in chronic staphylococcal osteomyelitis. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):494–496. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson D. S., Kazmierowski J. A., Dossett J. H., Williams R. C., Jr, Quie P. G. Studies of immune and normal opsonins during experimental staphylococcal infection in rabbits. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1235–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Experimental osteomyelitis. I. A description of the model. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):410–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Fierer J., Bryant R. E. Chronic staphylococcal osteomyelitis: treatment with regimens containing rifampin. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5 (Suppl 3):S495–S501. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_3.s495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn D. W., Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Levine J. H., Hardin J. A. Evidence for Pseudomonas antigen in immune complexes in Pseudomonas osteomyelitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Dec;25(12):1403–1408. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. G., Cook J., Fincham W. J., Millard F. J. Serological tests in the differentiation of staphylococcal and tuberculous bone disease. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Apr;28(4):284–288. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.4.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Sheagren J. N. Teichoic acid antibodies in the diagnosis of serious infections with Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1976 May;84(5):543–546. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Rozenberg-Arska M., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Antibodies to cell wall peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with serious staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veys E. M., Gabriel P. A., Piret J. R., van der Jeught J. D., van Overschelde J. L., Mastelinck C. M. Humoral immunity in osteomyelitis and infectious arthritis. Acta Orthop Belg. 1975 Jan-Feb;41(1):84–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldvogel F. A., Medoff G., Swartz M. N. Osteomyelitis: a review of clinical features, therapeutic considerations and unusual aspects (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1970 Jan 29;282(5):260–266. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197001292820507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldvogel F. A., Papageorgiou P. S. Osteomyelitis: the past decade. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 14;303(7):360–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008143030703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., Kohler R. B., White A. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for immunoglobulin G Staphylococcus aureus antibody in serious staphylococcal infection. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):467–472. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., White A. C., Norden C. Serological diagnosis of Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):764–767. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.764-767.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Dossett J. H., Quie P. G. Comparative studies of immunoglobulin opsonins in osteomyelitis and other established infections. Immunology. 1969 Aug;17(2):249–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ekstedt R. D. Antibody response to Staphylococcus aureus in rabbits: sequence of immunoglobulin synthesis and its correlation with passive protection in mice. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1540–1545. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1540-1545.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]