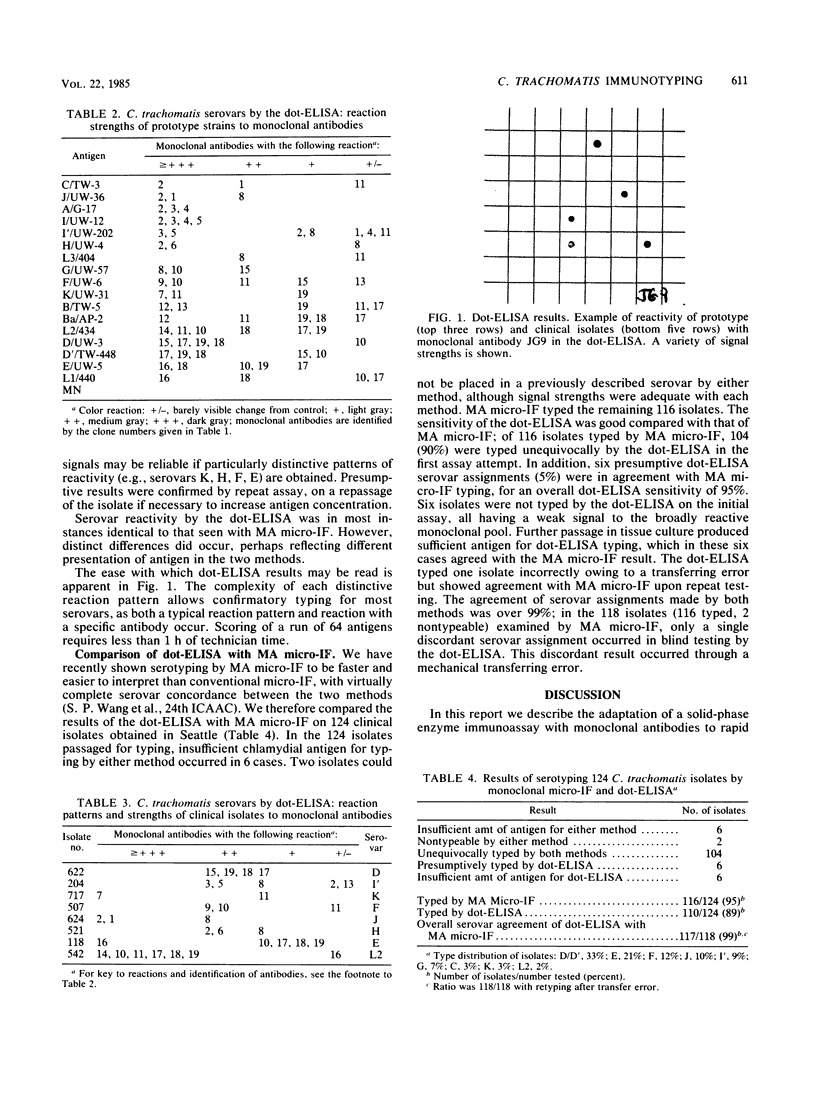
Abstract
The technical complexity of determining the serovar of Chlamydia trachomatis strains has limited the use of serotyping in clinical and epidemiologic studies. We developed a simple method for rapidly serotyping isolates of C. trachomatis by using monoclonal antibodies in a dot-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system. Isolates were passaged three to six times in shell vial cultures to greater than 50% monolayer infection, and chlamydial elementary bodies were isolated by sonication and microcentrifugation. Chlamydial antigen was spotted onto a series of replicate nitrocellulose membrane patches and reacted with C. trachomatis-specific monoclonal antibodies. Bound antibody was detected visually by a color reaction by using peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulins. This method can be routinely applied to 60 or more specimens concurrently. We compared dot-ELISA serotyping with monoclonal antibody microimmunofluorescence serotyping of 124 clinical C. trachomatis isolates and found that dot-ELISA has sensitivity and serotyping accuracy comparable to that of monoclonal antibody microimmunofluorescence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander E. R., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Further classification of TRIC agents from ocular trachoma and other sources by the mouse toxicity prevention test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5 Suppl):1469–1478. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)94133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL S. D., Jr, SNYDER J. C., MURRAY E. S. Immunization of mice against toxic doses of homologous elementary bodies of trachoma. Science. 1959 Sep 11;130(3376):626–627. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3376.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beem M. O., Saxon E. M. Respiratory-tract colonization and a distinctive pneumonia syndrome in infants infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 10;296(6):306–310. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702102960604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger R. E., Alexander E. R., Monda G. D., Ansell J., McCormick G., Holmes K. K. Chlamydia trachomatis as a cause of acute "idiopathic" epididymitis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 9;298(6):301–304. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802092980603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. W., Angel J. M., Bowen J. M. A quantitative immunobinding radioimmunoassay for antigens attached to nitrocellulose paper. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90467-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Weber K. Erythroid spectrin, brain fodrin, and intestinal brush border proteins (TW-260/240) are related molecules containing a common calmodulin-binding subunit bound to a variant cell type-specific subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4002–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon F. B., Harper I. A., Quan A. L., Treharne J. D., Dwyer R. S., Garland J. A. Detection of Chlamydia (Bedsonia) in certain infections of man. I. Laboratory procedures: comparison of yolk sac and cell culture for detection and isolation. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):451–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L., Orenstein N. S., King N. W. Purification on renografin density gradients of Chlamydia trachomatis grown in the yolk sac of eggs. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.102-106.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T., Alexander E. R. TRIC type K, a new immunologic type of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):591–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Holmes K. K., Grayston J. T. Immunotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis isolates in Seattle, Washington. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.865-868.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Ripa T., Svensson L., Weström L. Chilamydia trachomatis infection in patients with acute salpingitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 16;296(24):1377–1379. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706162962403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Goodell S. E., Mkrtichian E., Schuffler M. D., Wang S. P., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K. Chlamydia trachomatis proctitis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 23;305(4):195–200. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107233050404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. Chlamydial infections (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 2;298(9):490–495. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803022980905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Kuo C. C., Tam M. R. Sensitivity of immunofluorescence with monoclonal antibodies for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis inclusions in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):4–7. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.4-7.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Tam M. R., Kuo C. C., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis: antibody specificities and antigen characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG S. P., GRAYSTON J. T. CLASSIFICATION OF TRACHOMA VIRUS STRAINS BY PROTECTION OF MICE FROM TOXIC DEATH. J Immunol. 1963 Jun;90:849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T., Gale J. L. Three new immunologic types of trachoma-inclusion conjunctivitis organisms. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):873–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. A simplified method for immunological typing of trachoma-inclusion conjunctivitis-lymphogranuloma venereum organisms. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):356–360. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.356-360.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Grayston J. T. Chlamydia trachomatis immunotype J. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1711–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder B. L., Stamm W. E., Koester C. M., Alexander E. R. Microtest procedure for isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1036-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]