Abstract
Small RNAs targeted to gene promoters in human cells can mediate transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) by directing silent state epigenetic modifications to targeted loci. Many mechanistic details of this process remain poorly defined, and the ability to stably modulate gene expression in this manner has not been explored. Here we describe the mechanisms of establishment and maintenance of long-term transcriptional silencing of the human ubiquitin C gene (UbC). Sustained targeting of the UbC promoter with a small RNA for a minimum of 3 days resulted in long-term silencing which correlated with an early increase in histone methylation and a later increase in DNA methylation at the targeted locus. Transcriptional silencing of UbC required the presence of a promoter-associated RNA. The establishment and maintenance of the TGS were shown to require distinct protein factors. Argonaute 1 (Ago1), DNA methyltransferase 3a (DNMT3a) and histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) were required for the initiation of silencing, and DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) was necessary for maintenance. Taken together the data presented here highlight the cellular pathway with which noncoding RNAs interact to epigenetically regulate gene expression in human cells.
INTRODUCTION
The study of gene regulation has greatly expanded over the past several years as numerous RNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms have been discovered (1). One such method is termed RNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing (TGS), by which promoter-targeted small RNAs can, in some cases, induce transcriptional silencing in a homology-dependent manner. As the body of literature on this subject grows and more genes are shown to be susceptible to this form of transcriptional regulation, a putative model of this mechanism in human cells has begun to take shape. In this model, the generation and activity of small RNA molecules requires Argonaute 1 (Ago1) (2,3). Target recognition occurs as the antisense strand of the promoter-targeted small RNA binds to a complementary promoter-associated RNA (pRNA) (4,5). Interestingly, several recent reports have shown that transcription of promoter regions is much more common that previously realized (6–8). Upon exposure to the small RNA, the targeted promoter exhibits higher levels of the silent state histone methyl marks H3 lysine-9 di-methylation (H3K9me2) and histone H3 lysine-27 tri-methylation (H3K27me3) (2,4,9,10). These silent state chromatin marks have been observed not only at the targeted locus, but also downstream, 3′ of the target site, providing a possible mechanism by which silent state histone methyl marks may extend to affect neighboring genes or intergenic regions (10,11). A role for DNA methylation in this process remains uncertain, as some targeted promoters have been observed to exhibit increased CpG methylation (12), while others have not (13).
Protein factors responsible for these enzymatic processes constitute a partially characterized transcriptional silencing complex (TSC). Recent work indicates that this putative TSC may contain DNMT3a (10), Ago-1 (2,9), HDAC-1 (14) and histone methyltransferases such as enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Ezh2) and/or G9a (4,15). In some instances Argonaute 2 (Ago2) has been shown to be required for TGS (9), and recently published work indicates that the varying incorporation of Ago1 and Ago2 may depend on the level of complementarity between the small RNA and its target (16).
Recently, several labs have begun to identify and describe endogenous examples of RNA-mediated TGS in human cells. One finding in this area is the discovery that RNA-mediated TGS appears to play an important role in early transcriptional silencing events which lead to human X-inactivation (17). In addition, two newly published reports have identified the first examples of endogenously expressed promoter targeted miRNAs which mediate TGS (16,18). It has also been shown that some noncoding, antisense transcripts may direct TGS to their respective sense promoters to possibly affect the local chromatin signature (19, 20), and that targeting these antisense transcripts can lead to activation of sense transcription (21,22). Recent genome-wide studies indicate that nonrandom antisense transcription is widespread in the human genome, and may represent a prevalent mechanism of transcriptional regulation (23).
While much is known regarding the temporal aspects of targeting coding regions with siRNAs and miRNAs in a post-transcriptional manner (PTGS), far less is known regarding the ability of small RNA molecules to direct long-term gene silencing. Additionally, specific cellular proteins which could mediate such a process remain uncharacterized. To address these questions we studied transcriptional gene silencing of the human ubiquitin C gene (UbC). Ubiquitin is directly involved in skeletal muscle atrophy, which is a serious complication of catabolic conditions (24), as well as Parkinson's disease (25) and space travel (26). Additionally, much is known about the transcriptional features of Ubiquitin, making it an ideal gene for further study (27).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
UbC dsRNAs transfections and mRNA knockdown
Two dsRNAs were generated to determine the target susceptibility of the UbC gene promoter and screened in 293Gt GripTight™, Ntera and 2102Ep cells (Invitrogen). 1.0 × 105 cells were transfected in quadruplicate (100 nM, Lipofectamine™ 2000 and/or RNAiMAX™, Invitrogen). Forty-eight hours later the cultures were collected, mRNA isolated (CellsDirect™ Invitrogen) and UbC expression determined relative to GAPDH expression by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) with UbC mRNAF and UbC mRNAR, and GAPDHF and GAPDHR primers (Table S1) as described in ref. (4).
TSA treatment
Roughly 5 × 105 293Trex-UBC167 cells were transfected in triplicate with pENTER™/H1/TO-167 or pENTER™/H1/TO-308 plasmids, containing an shRNA targeted to the 167 and 308 target sites of UbC cloned into the BlockIT system (Invitrogen™) (1 μg/1 × 106 cells), or UBC167 or UBC308 dsRNAs, targeted to the 167 and 308 sites, respectively (100 nM, Lipofectamine 2000™). Cultures were treated with or without 0.05 mM TSA. ShRNA samples were treated with or without Tet, and additional samples were transfected with a CCR5-targeted siRNA as a control for the dsRNA samples. Culture mRNA was isolated (Qiagen, RNeasy™) 48 h later. The resulting RNA was then DNase treated (Turbo DNA Free, Ambion™), reverse transcribed (Superscript III, Invitrogen™) and analyzed by qPCR (Sybr Green Invitrogen™) using GAPDH and the UbC mRNA-specific primers UBIC Fwd and Rev (Table S1). The qPCR results were standardized first to GAPDH, and subsequently to untreated control values.
Nuclear run-on
Cell cultures, ∼1.0 × 106 293GT, were transfected with either the UBC167 dsRNA or the CCR5 siRNA (control) siRNAs (100 nM, Lipofectamine 2000™). Nuclear run-on was performed as described in (28) although subsequent analysis was slightly modified to use biotin tagged transcripts (29). Biotinlyated RNA was pulled down using Dynabeads (Invitrogen™), after which cDNA copies of pulled down RNA were generated (Superscript III, Invitrogen™). QPCR was then performed using GAPDH and UBIC primers (Table S1). A dot blot of pulled down RNA was also performed using GAPDH and UBIC Rev primers and the Ambion BrightStar detection system per manufacturer's guidelines.
ChIP assay
Roughly 4 × 106 HEK 293GT cells (Invitrogen) plate were transfected in replicate with either UBC167, UBC308, or CCR5 (Control) (28) dsRNAs (100 nM, Lipofectamine 2000™) (Table S1). In the case of the ODN blocking ChIP assays, the cultures (4.0 × 106/10 cm plate) were first transfected with the respective antisense ODNs (100 nM, Lipofectamine 2000™) followed 4 h later by a transfection with the UBC167 dsRNA (100 nM, Lipofectamine 2000™). In the case of Figure 2D, 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with or without Tet for 7 days. Next, the cultures were collected and a ChIP assay performed as described in ref. (4). Antibodies used: anti-dimethyl-H3K9 (Upstate #07-441), anti-trimethyl-H3K27 (Upstate #07-449), anti-Ago1 (Upstate #07-599), anti-acetyl-Histone H3K14 (Upstate #07-353), anti-NF-kB (Zymed, #51-0500), anti-RNAPII CTD (AbCam #ab817) and anti-RNAPII phosphor-S2 (AbCam #ab5095). Immunopreciptated DNA was then recovered by phenol/chloroform extraction and assayed by qPCR using indicated primers overlapping the promoter (1 and 2), farther downstream (4 and 5) and upstream of the target site (7 and 8) (Table S1) (Sybr Green™, Invitrogen).
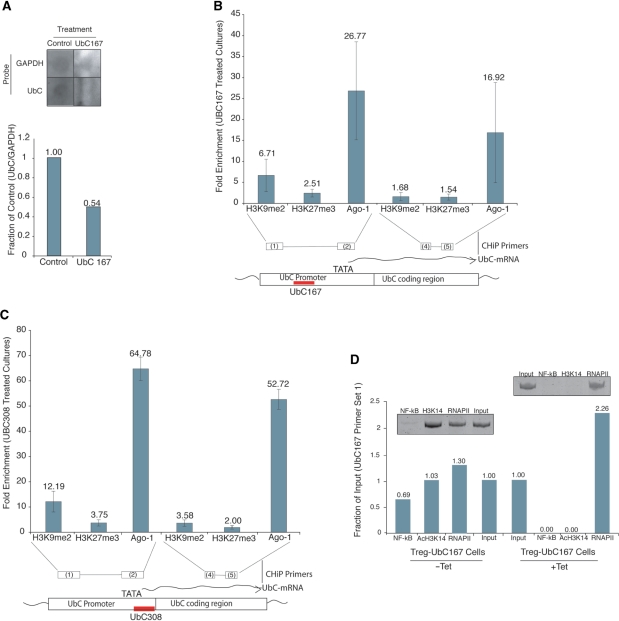
Figure 2.
Mechanism of UBC167 induced silencing. (A) UBC167-mediated suppression of UbC expression in 293Gt cells is operative via transcriptional gene silencing. Nuclear run-on assay was carried out on UBC167 or Control (CCR5) duplex RNA treated cultures 48 h post-transfection. Run-on RNA samples containing incorporated biotin UTP were immunopreciptated and analyzed by dot blot and qRT-PCR (29). (B, C) UBC167 and UBC308 direct silent state histone marks H3K9me2 and H3K27me3, and Ago-1 to the targeted locus. UBC167, UBC308 or CCR5 (control) dsRNA-treated 293Gt cells were assessed by ChIP for H3K9me2, H3K27me3 and Ago-1 at various regions of the UbC gene. Cultures were assessed 48 h post-dsRNA transfection with primers spanning the target site and downstream of the known TATAA site. Standard errors of the means are shown from quadruplicate duplex RNA treated cultures. (D) Activating chromatin marks are lost following UBC167 treatment, while RNAPII remains. ChIP analysis was performed using antibodies against NF-kB (p65), AcH3K14 and RNAPII, followed by PCR and qPCR with UbC promoter-specific primers. Samples were isolated from stable Tet-inducible 293Trex-UBC167 cells treated with Tet for 3 days.
UbC promoter RNA detection
To determine the expression of the UbC promoter-associated RNA by RT-PCR, total 293Gt cellular mRNA was DNase treated (Turbo DNA Free, Ambion™) and reverse transcribed (Superscript III, Invitrogen™). CDNA samples were then PCR amplified (Platinum PCR Supermix, Invitrogen™) with primers 1 and 2 (Table S1) and analyzed on a 6% polyacrylamide gel.
ODN blocking experiments
To determine the role of promoter-associated RNAs in small RNA-mediated TGS of the UbC gene, phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) (30) were generated (IDT, Coralville, Iowa) to target the UBC167 target site (Table S1). Next, 293GT cells (5.5 × 105/well or 4.0 × 106/10 cm plate for RT PCR and ChIP assays respectively) were plated and 24 h later transfected with the respective ODNs (100 nM (30), Lipofectamine 2000™). Four hours later the ODN transfected cultures were transfected with the UbC targeted dsRNAs (100 nM, Lipofectamine 2000™). Forty-eight hours following the dsRNA transfection the dually transfected cultures were collected and cellular RNA isolated, converted to cDNA and used in qRT-PCR for UbC mRNA expression with the UbC mRNA-specific UBICFwd and UBICRev primers (Table S1) (described above).
Analysis of promoter-associated RNA levels upon UBC167 targeting
Six samples of ∼1 × 106 293Trex cells were transfected with pENTER™/H1/TO-167 plasmid, containing an shRNA targeted to the 167 target site of UbC cloned into the BlockIT system (Invitrogen™) (1 μg/1 × 106 cells, Lipofectamine 2000™). Triplicate samples were treated with or without Tet for 48 h. RNA was isolated (Rneasy™, Qiagen), DNase treated (Turbo DNA Free, Ambion™) and reverse transribed (Superscript III, Invitrogen ™). Samples were then pooled, amplified (Platinum PCR Supermix, Invitrogen ™) with primers 1 and 2 (Table S1), and analyzed by 6% polyacrylamide electrophoresis, or analyzed by qPCR using primers 1 and 2 (Table S1) (Sybr Green Mastermix Invitrogen™).
Time-course expression assays
Roughly 5 × 105 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with or without 1 μg/ml Tet for the amount of time indicated. RNA was isolated, DNAse treated, converted to cDNA and analyzed by qRT-PCR with the UBIC and GAPDH primers (Table S1) (described above).
Quantification of UBC167 shRNA expression in stable cells
Small RNAs were collected (miRVana™, Ambion) on Days 0, 7 and 12 from time-course experiment (see above) and DNase treated (Turbo DNA free™, Ambion). Poly(A) tails were added to samples (NCode™, Invitrogen™), which were analyzed by qPCR using universal qPCR primer (NCode™, Invitrogen) and 167S/AS primer (Table S1).
Suppression of Ago1, DNMT3a, HDAC1, Ezh2 and G9a
293Trex-UBC167 Tet-inducible BlockIt cells were generated (according to manufacture's instructions, Invitrogen™). Roughly 5 × 105 293Trex-UBC167 cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting Ago-1, DNMT3a, HDAC-1, Ezh2 or G9a in triplicate, and treated with 1 µg/ml Tet daily. For controls, CCR5 was used. Culture mRNA was isolated (Quiagen, RNeasy™) 72 h after transfection. The resulting mRNAs were then DNase treated (Turbo DNA Free, Ambion™), converted to cDNA (Superscript III, Invitrogen™) and analyzed by Sybr Green qPCR using GAPDH and UBIC primers (Table S1). The qPCR results were standardized first to GAPDH, and subsequently to control values. The same isolated RNA samples were also analyzed by qPCR with target gene primers (Table S1) to confirm suppression, and results were standardized first to GAPDH, and then to control samples.
Reactivation of UbC expression
Roughly 4 × 106 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with 1 μg/ml Tet for 7 days. Tet was removed from the samples which were cultured for an additional 5 days. The cells were then split into five separate plates of roughly 4 × 105 cells each. These samples were then transfected with siRNAs targeting CCR5 (control), Ago1, HDAC1, DNMT3a, DNTM1 at 100 nM, or DNTM3a and DNTM1 at 50 nM each (Lipofectamine 2000™). Additional samples were treated with 5′AzaC (4 μM). Forty-eight hours later cellular RNA was isolated from these samples (Rneasy™, Qiagen), DNase treated (Ambion turbo DNA free), copied to cDNA (Superscript III, Invitrogen™), and analyzed by qPCR using UBIC and GAPDH primer sets (Table S1) (Sybr Green Mastermix Invitrogen™). The same isolated RNA samples were also analyzed by qPCR with target gene primers (Table S1) to confirm suppression, and results were standardized first to GAPDH, and then to control samples.
DNA methylation-specific digestion
293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with Tet for 10 days. Duplicate samples of ∼5 × 105 cells were isolated prior to Tet treatment and after indicated days of treatment. DNA was extracted (Dneasy™, Qiagen), pooled and digested with the methylation-sensitive enzymes HhaI and HpaII (NEB), the methylation-dependent enzyme McrBC (NEB), or both. RT-PCR was performed on samples using primers specific for the UbC promoter region (1 and 2) (Table S1). RT-PCR was optimized to account for presence of enzyme buffer using the Epicentre real time PCR optimization kit. The proportions of densely, intermediately and unmethylated DNA were calculated using the method described by Ordway et al. (31,32).
DNA methylation-specific PCR
DNA samples isolated by trimethyl-H3K27 pull down from the ChIP in Figure S3 were bisulfite treated (Zymo-ResearchTM). After conversion, methylation-dependent and methylation-sensitive PCRs were performed using the respective UbC target site primers (Table S1). PCR products were analyzed on a 6% polyacrylamide gel.
RESULTS
Susceptibility of human UbC to promoter targeting
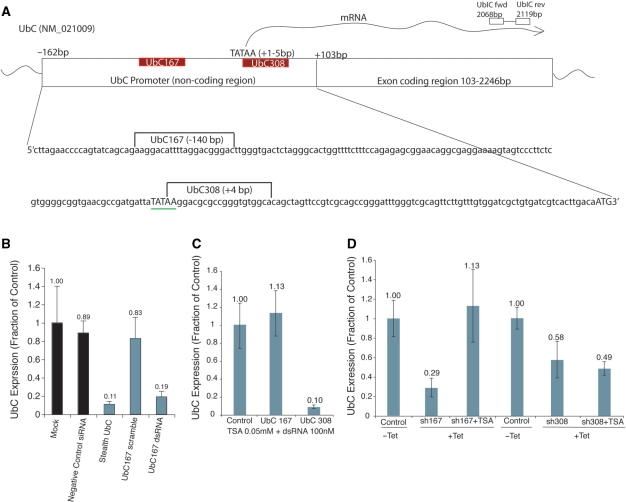
To determine the susceptibility of human UbC to RNA-mediated TGS, we transiently transfected promoter-targeted duplex RNAs spanning various regions of the UbC promoter (27,33) (Figure 1A), and monitored UbC expression in three different cell types by qRT-PCR. UbC expression was significantly reduced in all cell types targeted with the UBC308 duplex RNA. In contrast, variation in target susceptibility at the UBC167 locus was observed in a cell-line-specific manner (Figure S1). To confirm the results of the initial screen regarding the UbC167 duplex RNA in 293Gt cells, and to address the efficacy and specificity of the silencing activity of the UBC167 dsRNA, we compared its silencing activity with those of a scrambled UBC167 RNA duplex and a PTGS inducing, mRNA targeting stealth RNA. As measured by qRT-PCR, knock down achieved using the UBC167 duplex RNA was comparable to that achieved by mRNA targeting, and the scrambled UBC167 RNA did not induce silencing of UbC (Figure 1B).
Figure 1.
Transcriptional silencing of UbC. (A) The UbC promoter and exon 1 are shown schematically with the target sites UBC167 and UBC308, TATAA signal, transcriptional start site, and primary qPCR primers. (B) Promoter targeting with dsRNA is effective and specific. 293Gt cells were transfected with either an siRNA targeting the UbC coding region (Stealth UBC), a scrambled UBC167 promoter-targeted dsRNA (UBC167 scramble), or the original UBC167 dsRNA, and samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for UbC mRNA levels 48 h later. Results were standardized to GAPDH levels, and quadruplicate treated cultures were assessed with the standard errors of the means shown. (C) UbC suppression by 167 targeting synthetic duplex RNAs is sensitive to TSA, while 308 targeting is not. 293Gt cells were transfected with CCR5 (control), UBC167 or UBC308 dsRNAs in triplicate. Twenty-four hours later cultures were treated with TSA (0.05mM). Forty-eight hours following TSA treatment the cultures were assessed for UbC expression standardized to GAPDH. Average values from triplicate transfected cultures with standard errors of the means are shown. (D) UbC suppression by a Tet-inducible UBC167 shRNA is sensitive to TSA treatment, while silencing by a similar UBC308 shRNA is not. 293Trex cells were transfected with either UBC167 or UBC308 expressing Tet-inducible plasmids, and treated with or without Tet. Twenty-four hours later these cultures were treated with TSA (0.05 mM). Forty-eight hours following TSA treatment the cultures were assessed for UbC mRNA levels standardized to GAPDH. Average values with standard errors of the means are shown.
Previously, we and others have observed that RNA directed TGS in human cells is operative via directed epigenetic modifications at the targeted promoter (2,10,13,28,34). In order to differentiate between TGS and other types of gene silencing, and to determine if chromatin modifications were necessary for the observed silencing, we assessed the sensitivity of the silencing induced by UBC167 and UBC308 dsRNAs to the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA). In 293Gt cells, gene suppression achieved upon targeting the 167 site was sensitive to TSA treatment, while targeting the 308 site was not (Figure 1C). These data were recapitulated in an almost identical experiment in which we transiently transfected plasmids containing tetracycline (Tet)-inducible 167 and 308 shRNA constructs (Figure 1D). These results indicate that while UBC167 targeting may induce TGS, targeting the 308 site (which overlaps the TATA box and transcriptional start site) may cause silencing by a separate mechanism, such as post-transcriptional gene silencing.
Mechanism of UBC167-mediated silencing
To more clearly establish that the observed silencing of UbC was indeed occurring at the transcriptional level, nuclear run-on was performed on 293Gt cultures transfected with CCR5 (control) or UBC167 dsRNAs. Nuclear run-on samples were analyzed using a novel biotin pulldown-based assay previously described by Zhang and colleagues (29) in addition to a standard dot blot. In cells transfected with the UBC167 duplex RNA, transcription was significantly reduced in comparison with control samples, indicating that the observed silencing was occurring at the transcriptional level (Figure 2A).
To more clearly define the mechanism of this gene silencing, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation assays (ChIP) with antibodies directed against histone H3K9me2, H3K27me3 and Ago-1. Compared to CCR5 siRNA-treated control samples, a significant enrichment of H3K9me2, H3K27me3 and Ago-1 were observed at the promoter upon targeting with the UBC167 duplex RNA (Figure 2B). Interestingly, similar enrichments were also observed at the promoter after treatment with the UBC308 small RNA (Figure 2C), despite the earlier observation that histone methylation is not required for the silencing activity of UBC308. These data do not necessarily contradict the results from Figure 1B and C which showed that silencing mediated by ds308 is not affected by TSA treatment. This result may indicate that small RNAs targeted to various gene sequences, including mRNA targeting si- and miRNAs, may direct epigenetic changes to corresponding DNA loci, even if their mode of silencing does not require such modifications.
Previous reports have shown that silent state chromatin marks, specifically H3K9me2, can be found 3′ of the targeted promoter region (2,10). Consistent with these reports, we show that treatment of cells with either UBC167 or UBC308 small RNAs resulted in enhanced levels of H3K9me2, H3K27me3 and Ago-1 recruitment 3′ of the small RNA targeted loci (Figure 2B and C). Interestingly, we were unable to detect a noticeable enrichment of either H3K27me3 or Ago-1 when upstream sites were assessed by ChIP (Figure S2).
An additional ChIP assay was performed using antibodies against the activating mark AcH3K14, NF-kB and RNA polymerase II. For this ChIP, and subsequent long-term experiments discussed below, we developed a novel 293-Trex cell line which contains a tetracycline-inducible UBC167 shRNA construct (293Trex-UBC167 cells). Treating these cells with tetracycline (Tet) leads to expression of the 167 shRNA. Targeting the UbC promoter in this manner resulted in a loss of activating factors such as NF-kB and AcH3K14, with no decrease in overall levels of RNAPII at the targeted locus (Figure 2D). Interestingly, the retained RNAPII, found specifically at the small RNA target locus, was predominantly the inactive form of RNAPII (Figure S3). Collectively, these data show that the UbC promoter transitions from an active state towards a silent state when targeted with synthetic duplex or shRNAs. This demonstrated mechanism is similar to previously reported examples of small RNA-directed TGS in human cells (35).
A promoter-associated RNA is required for TGS
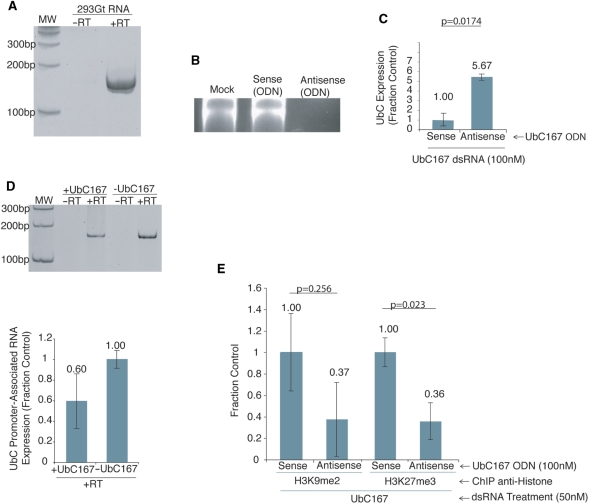
Recent work from our laboratory has shown that a sense-stranded promoter-associated RNA is required for RNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in human cells (4). To determine the extent of transcription across the UbC promoter, specifically at the UBC167-targeted locus, we performed RT-PCR with primers specific for this region. Similar to previous observations (4), a promoter-associated transcript was observed overlapping the UBC167-targeted region in the UbC promoter (Figure 3A). Previous observations have also shown that suppression of promoter-associated RNAs results in the abrogation of TGS (4). To ascertain whether a UbC promoter-associated RNA is required for TGS of UbC, a blocking experiment was performed. To block the UbC promoter-associated RNA, phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN) (30) were designed to recognize the cognate promoter-associated RNA for either the UBC167 sense or antisense directional transcript. Phosphorothioate ODNs hybridize to complementary genetic regions and induce RNA cleavage at the hetero-duplex by activation of the RNase H pathway (36). Results of treatment with the sense and antisense ODNs indicated that the promoter-associated RNA is sense-oriented, as the UbC antisense ODN was effective in reducing the promoter-associated RNA expression (Figure 3B). To determine the ability of the UBC167 dsRNA to modulate TGS in the absence of the UbC promoter-associated RNA, cells were treated with either the sense- or antisense-targeted ODN, and then four hours later with the UbC targeting dsRNAs. Blocking of the UbC promoter-associated RNA by ODN treatment resulted in a loss of UBC167-directed TGS (Figure 3C).
Figure 3.
The requirement of the UbC promoter-associated RNA in TGS. (A) Detection of a promoter-associated RNA spanning the UbC promoter by RT-PCR of total RNA from 293Gt cells, using primers specifically spanning the UBC167 targeted locus. (B) Antisense ODN treatment results in loss of UbC promoter-associated RNA. 293Gt cells were left untreated (mock), transfected with UBC167-specific ODNs, either sense (Sense ODN) or antisense (Antisense ODN), and promoter-associated RNA expression determined by RT-PCR 48 h later. (C) Antisense ODN suppresses small RNA-mediated TGS. 293Gt cells were transfected with either UBC167 sense or antisense ODNs in quadruplicate followed 4 h later by transfection with UBC167 dsRNA. Forty-eight hours later the samples were collected and analyzed by qRT-PCR to assess affect of ODN treatment on TGS. Results were standardized to GAPDH expression, and triplicate treated cultures were assessed with the standard errors of the means shown. The respective P-values for paired T-tests from each treatment relative to the control are also shown. (D) Promoter-associated RNA levels are modestly decreased upon targeting. 293Trex cells were transfected with a Tet-inducible 167 shRNA plasmid and treated with or without Tet in triplicate. RNA was isolated from these samples 48 h later and converted to cDNA. These cDNA samples were then pooled, amplified by PCR and analyzed on a 6% polyacrylamide gel, or analyzed independently by qRT-PCR using UbC promoter primers 1 and 2. The standard errors of the mean from three independent samples are shown. (E) Suppression of UbC promoter-associated RNA inhibits UBC167-mediated histone methylation. 293Gt cells were transfected with UBC167-specific ODNs, either sense or antisense, followed 4 h later by transfection with UBC167 dsRNA. Forty-eight hours later a ChIP assay was performed for H3K9me2 or H3K27me3 with primers specific for the UBC167 target site. Quadruplicate treated cultures were assessed and the standard errors of the means are shown along with P values for paired T-tests from each treatment relative to the control.
We next investigated the abundance of the promoter-associated RNA upon targeting the UBC167 site. This was done by performing RT-PCR and qRT-PCR on RNA isolated from samples which we transiently transfected with plasmids containing a Tet-inducible 167 shRNA construct in the presence and absence of Tet. These results show that promoter-associated RNA levels are decreased but not completely suppressed (Figure 3D). This decrease in promoter-associated RNA levels may be the result of a blockage of RNAPII transcription by the assembled TSC, which transcription most likely originates from an upstream location.
To determine the requirement of the promoter-associated RNA for the induction of epigenetic modifications at the targeted UbC promoter, we suppressed the UbC promoter-associated RNA by ODN treatment, and then analyzed the epigenetic marks at the targeted locus by ChIP assay. The suppression of the UbC promoter-associated RNA expression by antisense ODN treatment resulted in a reduction of RNA-directed H3K9me2 and H3K27me3 at the UBC167 targeted locus compared to sense ODN treated controls (Figure 3E). Furthermore, there were no observable changes in H3K9me2 and H3K27me3 enrichment upstream of the targeted locus (Figure S4). Taken together, these data recapitulate previous observations (4), and suggest that a promoter-associated RNA is necessary for promoter-targeted small RNAs to direct silent state epigenetic modifications to gene promoters.
Promoter-targeted small RNAs induce long-term TGS
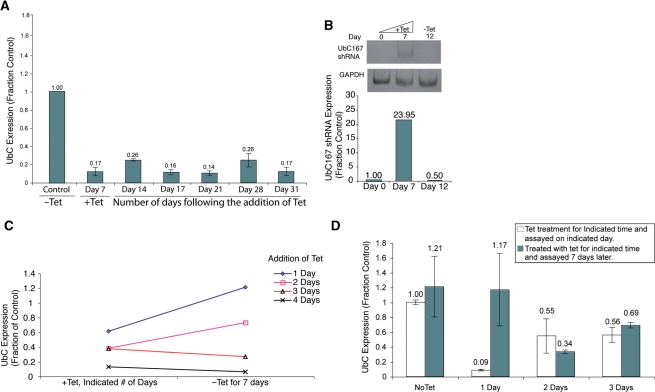
The observation that epigenetic modifications such as histone methylation occur at the UbC promoter upon small RNA treatment suggests that long-term gene silencing can be induced. To determine the effects of persistent targeting of the UBC167 site on chromatin composition and gene expression, we again used our UBC167 shRNA Tet-inducible cell line. The maintenance of long-term suppression of UbC, following a 7-day induction, could be observed for over a month (Figure 4A). Importantly, significant increases in UBC167 shRNA were detectable after 7 days of sustained Tet treatment, but were found to return to pre-induction levels of detection 5 days later, after removal of Tet (Figure 4B), indicating that a significant increase in shRNA expression is required to establish but not maintain the observed silencing. Upon further investigation, approximately 3 days of sustained shRNA exposure was required in dividing cells (Figure 4C), and only 2 days of shRNA exposure in serum starved nondividing cells (Figure 4D) to establish long-term silencing of UbC. These data suggest that long-term silencing of gene expression can be achieved when promoter regions are targeted with small RNAs for a relatively short period of time. It was also noted that upon long-term down-regulation of UbC, cell-growth rates slowed and adherence was weakened. These observations can most likely be attributed to the significant, sustained down-regulation of a necessary cellular protein.
Figure 4.
Long-term gene silencing of UbC. (A) Long-term gene silencing. 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with Tet for 7 days, and then removed from Tet for 24 more days. Cellular mRNA was isolated from the treated cultures and UbC expression assessed at indicated times by qRT-PCR and standardized to GAPDH. The averages are shown with standard errors of the means. (B) UBC167 shRNA expression following 7 days of sustained Tet treatment. 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with Tet for 7 days, and then removed from Tet for five more. Small RNAs were isolated, polyadenlyated, converted to cDNA and analyzed by RT-PCR performed using primers specific for the UBC167 shRNA. The lower panel depicts the quantitative expression of UBC167 shRNA as determined by qPCR. (C) A minimum of 3 days of sustained UBC167 shRNA expression is required to establish long-term silencing. 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with Tet for either 1, 2, 3 or 4 days consecutively, and then cultured for another 7 days in the absence of Tet. UbC mRNA expression was determined after 7 days in the absence of Tet and standardized to GAPDH expression. (D) A minimum of 2 days of sustained UBC167 shRNA expression is required to establish long-term silencing under serum starved conditions. 293Trex-UBC167 cells were serum starved for 48 h and then treated with Tet for either 1, 2 or 3 days consecutively, and then cultured for another 7 days in the absence of Tet. UbC mRNA expression was determined after 7 days in the absence of Tet and standardized to GAPDH expression.
Establishment and maintenance of TGS require distinct subsets of protein factors
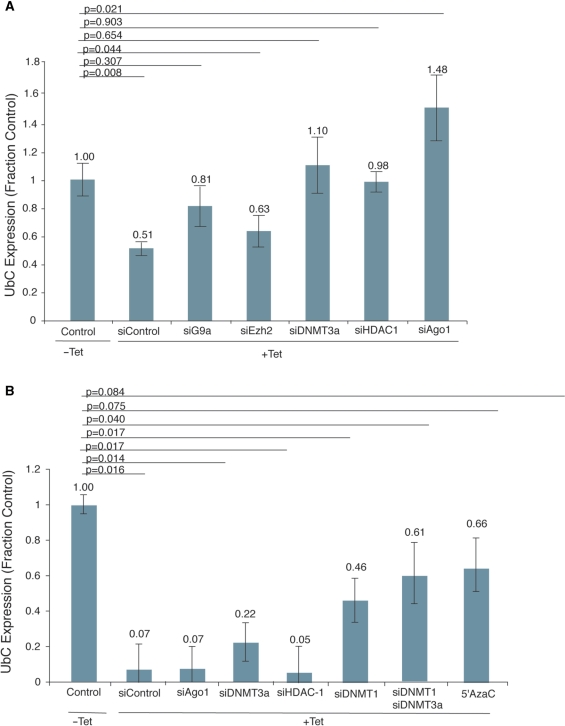
The observation that silent state histone methyl marks correlate with the observed small RNA-mediated transcriptional silencing of UbC implicates a central role of various epigenetic factors in this process. To first determine the involvement of several such factors in the establishment of transcriptional silencing of UbC, we used RNAi to knockdown these targets in the context of our Tet-inducible cell line, and assessed the effects of each knockdown on TGS after 72 h. Knockdown of each targeted gene was confirmed by qRT-PCR (Figure S5). Establishment of transcriptional silencing of UbC in this context required the activities of DNMT3a, Ago-1, HDAC1 and to some extent G9a, but not EZH2 (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Characterization of protein factors necessary for establishment and maintenance of TGS. (A) Defining components involved in the induction of small RNA-mediated TGS of UbC. 293Trex-UBC167 cells were transfected with various siRNAs targeted to CCR5 (Control), G9a, HDAC-1, DNMT3a, Ago-1 or Ezh2 and then treated with Tet for 3 days to induce UBC167 shRNA expression. On Day 3, cellular mRNA was isolated and UbC expression determined relative to GAPDH. The averages for three independent samples and the respective standard errors of the means are shown along with P-values for paired T-tests from each treatment relative to the control. (B) Defining components involved in maintaining small RNA-mediated TGS of UbC. 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with Tet for 7 days to induce UBC167 shRNA expression and establish long-term silencing. Samples were then removed from Tet. Five days after the removal from Tet the cultures were transfected with siRNAs targeted to CCR5 (Control), Ago-1, HDAC-1, DNMT3a, DNMT1 or DNTM3a and DNTM1, or treated with 5′AzaC. Forty-eight hours later the cellular mRNA was isolated and analyzed by qRT-PCR to determine UbC expression relative to GAPDH. The averages for three independent samples and the standard errors of the means are shown along with P-values for paired T-tests from each treatment relative to the control.
We next used a similar approach to determine necessary factors for the maintenance of TGS. We again used RNAi to knockdown several targets in our Tet-inducible cell line. The indicated targets were knocked down after 12 days, 7 days of Tet-induction followed by 5 days removed from Tet. Forty-eight hours after siRNA transfection, UbC transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR. We show that in this system, maintenance of TGS required DNMT1, but not Ago1 or HDAC1, and that UbC expression was also rescued by treatment with 5′AzaC (Figure 5B). A role for DNMT3a in the maintenance of gene silencing is not completely apparent from these results. While the statistical significance of the DNMT3a data is not particularly clear, modest increases in UbC expression in siDNTM3a, and siDNTM3a and siDNMT1-treated samples over control and siDNMT1 samples respectively may indicate that DNMT3a might play a role in maintaining transcriptional silencing.
Role of DNA methylation in long-term TGS
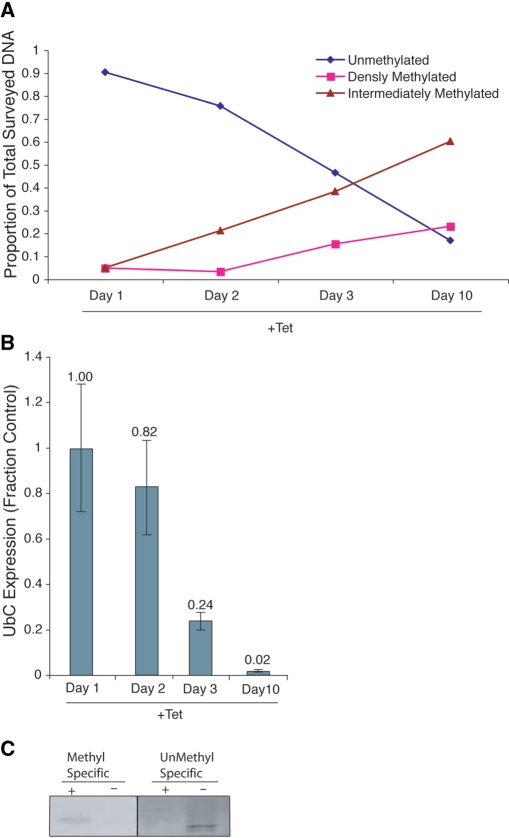
Another epigenetic mark frequently found in stably silenced genes is DNA methylation (38). To assess the methylation state of the UbC promoter upon small RNA targeting, we first compared methyl-specific digestion profiles of cells cultured with and without Tet over 10 days. Interestingly, DNA methylation was shown to increase upon prolonged treatment with Tet, as calculated using the method of methylation-specific restriction digest analysis described in refs (31,32,39) (Figure 6A). Notably, the increase in DNA methylation required several days, and correlated with a time when robust long-term gene silencing had already been established (Figure 6B), suggesting that DNA methylation functions primarily in maintaining long-term silencing of UbC.
Figure 6.
Role of DNA methylation in long-term transcriptional silencing. (A) Increased DNA methylation at the UbC promoter was observed several days post Tet induction of UBC167 shRNA. Genomic DNA was collected and pooled from duplicate samples of 293Trex-UBC167 cells treated without Tet (Day 0) and after 1, 2, 3 or 10 days of Tet treatment. Proportion of densely, intermediately and unmethylated DNA was calculated using method described (31). Methyl-sensitive restriction enzymes: HpaII and HhaI, methyl-dependent restriction enzyme: McrBC. qPCR was performed using promoter-specific primers. (B) Silencing of UbC is observed after Tet treatment. 293Trex-UBC167 cells were treated with Tet for 10 days. Cellular mRNA was isolated at various time points and UbC expression relative to GAPDH determined. The averages with the standard errors of the means are shown as determined by qRT-PCR along with P-values for paired T-tests from each treatment relative to the control. (C) DNA from H3K27me3 ChIP (Figureure S3) was treated with bisulfite and analyzed by methylation-specific PCR using primers specific for methylated or unmethylated DNA species overlapping the UBC167 target site.
To further investigate the methylation state of the targeted promoter we then used methyl-specific PCR. Both an enrichment of methylated DNA and a decrease of unmethylated DNA were detectable at the targeted promoter in H3K27me3 immunopreciptated DNA (from the experiment shown in figure S3) (Figure 6C).
DISCUSSION
The data presented here demonstrate that targeting promoters with small noncoding RNAs can induce long-term transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. We also show distinct mechanisms for the establishment and maintenance of this gene silencing. Similar to previous findings, the induction of the observed gene silencing was operative via site-specific histone methylation, which required the presence of a UbC promoter-associated RNA (4), HDAC-1 (14), DNMT3a (10) and Ago-1 (2). The observation that knockdown of Ezh2 results in an only moderate inhibition of the induction of TGS might indicate that H3K27me3 is not required for the silencing, but acts in an additive manner, or that various histone methylation enzymes are functional in a redundant manner. Maintenance of UbC silencing required a distinct subset of proteins, namely DNMT1 and possibly DNMT3a. This observation is particularly interesting as a synergistic interaction between DNMT1 and DNMT3a has also been observed in CpG methylation of LINE elements (40). In addition, significant DNA methylation was detected after several days of sustained small RNA targeting, at a time when robust histone methylation of the targeted locus had already taken place. This delay in the occurrence of DNA methylation may in part explain why DNA methylation has not been observed in all instances of RNA-mediated TGS (11).
It is noted that cells transfected with UBC308-targeted RNA were not sensitive to TSA treatment. Future experiments are aimed at determining whether sequence-specific gene silencing may be operative via additional mechanisms, such as obstructing the activity of RNAPII at the transcriptional start site (41). Such a hypothesis could in part explain why targeting the 308 site was not cell-line-specific, while targeting of the 167 site was. This might be understood by noting that targeting the 167 site is dependent on TGS, which requires cell-specific factors such as a promoter-associated RNA and the activity of various proteins. It is important to note, however, that while UBC308 targeting was not observed to induce TGS of UbC, chromatin modifications were nevertheless observed upon targeting. This may indicate that small RNAs can induce chromatin remodeling events, even if their primary mode of action is not at the transcriptional level, which may represent a novel mode of off-target effect which may result from classical RNAi experiments.
Overall, the data presented here provide the first evidence that promoter targeted small RNAs can induce long-term TGS in human cells. In addition, the mechanisms of induction and maintenance of this TGS are characterized and shown to be distinct. These results may be indicative of the ability of endogenous mechanisms, such as noncoding RNAs (42), to regulate transcription in a long-term manner, and may also prove a useful avenue for future gene therapy applications.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary Data are available at NAR Online.
FUNDING
National Institutes of Health [HL83473 to K.V.M.]; Stein Endowment Fund at The Scripps Research Institute. Funding for open access charge: National Institutes of Health [HL83473 to K.V.M.].
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Supplementary Material
REFERENCES
- 1.Mattick JS. A new paradigm for developmental biology. J. Exp. Biol. 2007;210:1526–1547. doi: 10.1242/jeb.005017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kim DH, Villeneuve LM, Morris KV, Rossi JJ. Argonaute-1 directs siRNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006;13:793–797. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Janowski BA, Younger ST, Hardy DB, Ram R, Huffman KE, Corey DR. Activating gene expression in mammalian cells with promoter-targeted duplex RNAs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007;3:166–173. doi: 10.1038/nchembio860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Han J, Kim D, Morris KV. Promoter-associated RNA is required for RNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:12422–12427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701635104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schwartz JC, Younger ST, Nguyen NB, Hardy DB, Monia BP, Corey DR, Janowski BA. Antisense transcripts are targets for activating small RNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008;15:842–848. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Core LJ, Waterfall JJ, Lis JT. Nascent RNA sequencing reveals widespread pausing and divergent initiation at human promoters. Science. 2008;322:1845–1848. doi: 10.1126/science.1162228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Seila AC, Calabrese JM, Levine SS, Yeo GW, Rahl PB, Flynn RA, Young RA, Sharp PA. Divergent transcription from active promoters. Science. 2008;322:1849–1851. doi: 10.1126/science.1162253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Preker P, Nielsen J, Kammler S, Lykke-Andersen S, Christensen MS, Mapendano CK, Schierup MH, Jensen TH. RNA exosome depletion reveals transcription upstream of active human promoters. Science. 2008;322:1851–1854. doi: 10.1126/science.1164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Janowski BA, Huffman KE, Schwartz JC, Ram R, Nordsell R, Shames DS, Minna JD, Corey DR. Involvement of AGO1 and AGO2 in mammalian transcriptional silencing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006;13:787–792. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Weinberg MS, Villeneuve LM, Ehsani A, Amarzguioui M, Aagaard L, Chen Z-X, Riggs AD, Rossi JJ, Morris KV. The antisense strand of small interfering RNAs directs histone methylation and transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. RNA. 2005;12:256–262. doi: 10.1261/rna.2235106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Morris KV. siRNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing: the potential mechanism and a possible role in the histone code. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005;62:3057–3066. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5182-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Morris KV. RNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008;320:211–224. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75157-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ting AH, Schuebel KE, Herman JG, Baylin SB. Short double-stranded RNA induces transcriptional gene silencing in human cancer cells in the absence of DNA methylation. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:906–910. doi: 10.1038/ng1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Suzuki K, Juelich T, Lim H, Ishida T, Watanebe T, Cooper DA, Rao S, Kelleher AD. Closed chromatin architecture is induced by an RNA duplex targeting the HIV-1 promoter region. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:23353–233630. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709651200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vire E, Brenner C, Deplus R, Blanchon L, Fraga M, Didelot C, Morey L, Van Eynde A, Bernard D, Vanderwinden JM, et al. The Polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature. 2005;439:871–874. doi: 10.1038/nature04431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gonzalez S, Pisano DG, Serrano M. Mechanistic principles of chromatin remodeling guided by siRNAs and miRNAs. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2601–2608. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.16.6541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ogawa Y, Sun BK, Lee JT. Intersection of the RNA interference and X-inactivation pathways. Science. 2008;320:1336–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.1157676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kim DH, Saetrom P, Snove O, Jr, Rossi JJ. MicroRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:16230–16235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808830105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yu W, Gius D, Onyango P, Muldoon-Jacobs K, Karp J, Feinberg AP, Cui H. Epigenetic silencing of tumour suppressor gene p15 by its antisense RNA. Nature. 2008;451:202–206. doi: 10.1038/nature06468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O, Carey BW, Cassady JP, et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature. 2009 doi: 10.1038/nature07672. [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Morris KV, Santoso S, Turner AM, Pastori C, Hawkins PG. Bidirectional transcription directs both transcriptional gene activation and suppression in human cells. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schwartz JC, Younger ST, Nguyen NB, Hardy DB, Monia BP, Corey DR, Janowski BA. Antisense transcripts are targets for activating small RNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008;15:842–848. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.He Y, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE, Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW. The antisense transcriptomes of human cells. Science. 2008;322:1855–1857. doi: 10.1126/science.1163853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Price SR. Increased transcription of ubiquitin-proteasome system components: molecular responses associated with muscle atrophy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003;35:617–628. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00385-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Martianov I, Ramadass A, Serra Barros A, Chow N, Akoulitchev A. Repression of the human dihydrofolate reductase gene by a non-coding interfering transcript. Nature. 2007;445:666–670. doi: 10.1038/nature05519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hawkey A. Physiological and biomechanical considerations for a human Mars mission. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 2005;58:117–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nenoi M, Cartwright IL, Mita K, Ichimura S. Comparison of the 5′ upstream region of the evolutionarily equivalent polyubiquitin gene of humans and Chinese hamsters. Gene. 1996;179:297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00380-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Morris KV, Chan SW, Jacobsen SE, Looney DJ. Small interfering RNA-induced transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Science. 2004;305:1289–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.1101372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang M, Ou H, Shen YH, Wang J, Coselli J, Wang XL. Regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by small RNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:16967–16972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503853102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yoo BH, Bochkareva E, Bochkarev A, Mou TC, Gray DM. 2′-O-methyl-modified phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides have reduced non-specific effects in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:2008–2016. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ordway JM, Bedell JA, Citek RW, Nunberg A, Garrido A, Kendall R, Stevens JR, Cao D, Doerge RW, Korshunova Y, et al. Comprehensive DNA methylation profiling in a human cancer genome identifies novel epigenetic targets. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:2409–2423. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ordway JM, Bedell JA, Citek RW, Nunberg AN, Jeddeloh JA. MethylMapper: a method for high-throughput, multilocus bisulfite sequence analysis and reporting. Biotechniques. 2005;39 doi: 10.2144/000112035. 464, 466, 468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nenoi M, Mita K, Ichimura S, Cartwright IL, Takahashi E, Yamauchi M, Tsuji H. Heterogeneous structure of the polyubiquitin gene UbC of HeLa S3 cells. Gene. 1996;175:179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(96)00145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Suzuki K, Shijuuku, T. Fukamachi T, Zaunders J, Guillemin G, Cooper D, Kelleher A. Prolonged transcriptional silencing and CpG methylation induced by siRNAs targeted to the HIV-1 promoter region. J. RNAi Gene Silencing. 2005;1:66–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hawkins PG, Morris KV. RNA and transcriptional modulation of gene expression. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:602–607. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.5.5522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Agrawal S, Kandimalla ER. Antisense and/or immunostimulatory oligonucleotide therapeutics. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2001;1:197–209. doi: 10.2174/1568009013334160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gromak N, West S, Proudfoot NJ. Pause sites promote transcriptional termination of mammalian RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;26:3986–3996. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.10.3986-3996.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Matzke MA, Birchler JA. RNAi-mediated pathways in the nucleus. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:24–35. doi: 10.1038/nrg1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Holemon H, Korshunova Y, Ordway JM, Bedell JA, Citek RW, Lakey N, Leon J, Finney M, McPherson JD, Jeddeloh JA. MethylScreen: DNA methylation density monitoring using quantitative PCR. BioTechniques. 2007;43:683–693. doi: 10.2144/000112597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liang G, Chan MF, Tomigahara Y, Tsai YC, Gonzales FA, Li E, Laird PW, Jones PA. Cooperativity between DNA methyltransferases in the maintenance methylation of repetitive elements. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;22:480–491. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.480-491.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Janowski BA, Huffman KE, Schwartz JC, Ram R, Hardy D, Shames DS, Minna JD, Corey DR. Inhibiting gene expression at transcription start sites in chromosomal DNA with antigene RNAs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005;1:210–215. doi: 10.1038/nchembio725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15(Spec No 1):R17–R29. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.