Abstract
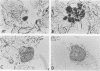
A comparison of two commercially available kits for rapid herpes simplex virus (HSV) detection directly in patient specimens was performed. The immunofluorescence assay (IFA) utilized monoclonal antibodies to HSV, and the DNA probe assay utilized three HSV sequences cloned into pBR322. A sample of 243 specimens received in viral transport medium were inoculated into MRC-5 tissue cultures. The remainder of the specimen was centrifuged, and the cellular pellet was examined by IFA and DNA probes. One hundred and sixty-two (66.7%) specimens were considered satisfactory for IFA and DNA probe testing, based on a criterion of observing greater than or equal to 2 intact cells per high-power field. Of the 162 specimens, 35 (21.6%) yielded HSV by culture. By IFA, the sensitivity of detecting HSV culture-positive specimens was 77.1%; specificity was 100%, positive predictive value was 100%, and negative predictive value was 93.3%. DNA probe sensitivity was 71.4%; specificity was 90.6%; positive predictive value was 67.6%; and negative predictive value was 92%. Forty-four (27.2%) of the 162 specimens exhibited nonspecific cytoplasmic staining with the DNA probe. IFA and DNA probe assays can be completed in 2 to 3 h, whereas the average time to culture positivity in this series was 2.2 days. Rapid HSV diagnosis can aid in timely and appropriate patient management.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binkin N. J., Koplan J. P., Cates W., Jr Preventing neonatal herpes. The value of weekly viral cultures in pregnant women with recurrent genital herpes. JAMA. 1984 Jun 1;251(21):2816–2821. doi: 10.1001/jama.251.21.2816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Betlach M. C., Boyer H. W. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. I. Ampicillin-resistant derivatives of the plasmid pMB9. Gene. 1977;2(2):75–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. T., Jaffe H. W., Zaidi A., Filker R., Herrmann K. L., Lylerla H. C., Jove D. F., Budell J. W. Sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic tests for genital infection with herpesvirus hominis. Sex Transm Dis. 1979 Jan-Mar;6(1):10–13. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197901000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Adams H. G., Brown Z. A., Holmes K. K. Genital herpes simplex virus infections: clinical manifestations, course, and complications. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jun;98(6):958–972. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-6-958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Descamps J., Verhelst G., Walker R. T., Jones A. S., Torrence P. F., Shugar D. Comparative efficacy of antiherpes drugs against different strains of herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):563–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker H., Frenkel N. BamI, KpnI, and SalI restriction enzyme maps of the DNAs of herpes simplex virus strains Justin and F: occurrence of heterogeneities in defined regions of the viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):429–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.429-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley R. C., Corey L., Benjamin D., Winter C., Remington M. L. Comparison of viral isolation, direct immunofluorescence, and indirect immunoperoxidase techniques for detection of genital herpes simplex virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):913–918. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.913-918.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerurkar L. S., Namba M., Sever J. L. Comparison of standard tissue culture, tissue culture plus staining, and direct staining for detection of genital herpes simplex virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):631–633. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.631-633.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Schmidt N., Plotkin S., Yolken R., Cherensky M., McIntosh K., Mattheis M. Summary of a workshop on new and useful methods in rapid viral diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):941–951. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Dennis J., Devlin V., Gallo D., Mills J. Comparison of direct immunofluorescence and direct immunoperoxidase procedures for detection of herpes simplex virus antigen in lesion specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):445–448. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.445-448.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D., Emmons R. W. Direct immunofluorescence staining for detection of herpes simplex and varicella-zoster virus antigens in vesicular lesions and certain tissue specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):651–655. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.651-655.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruance S. L., Overall J. C., Jr, Kern E. R., Krueger G. G., Pliam V., Miller W. The natural history of recurrent herpes simplex labialis: implications for antiviral therapy. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jul 14;297(2):69–75. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197707142970201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. A., Galloway D. A. Nucleotide sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 2 thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1045-1050.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]