Abstract
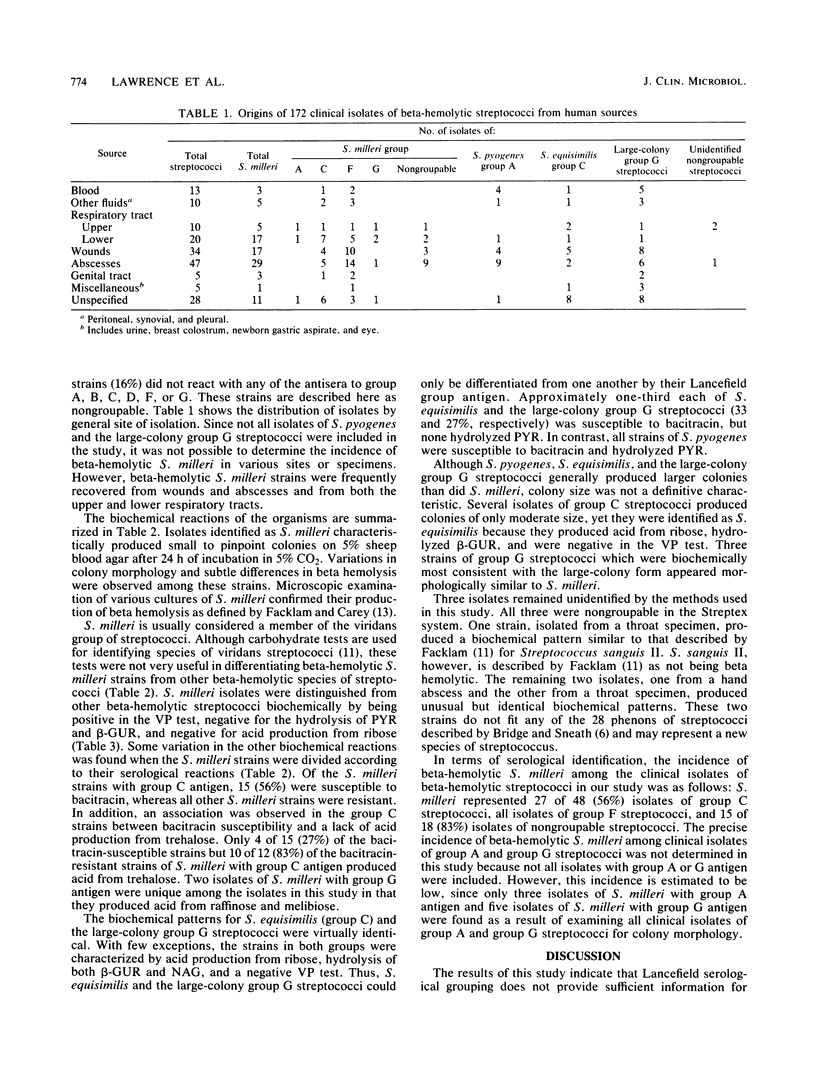
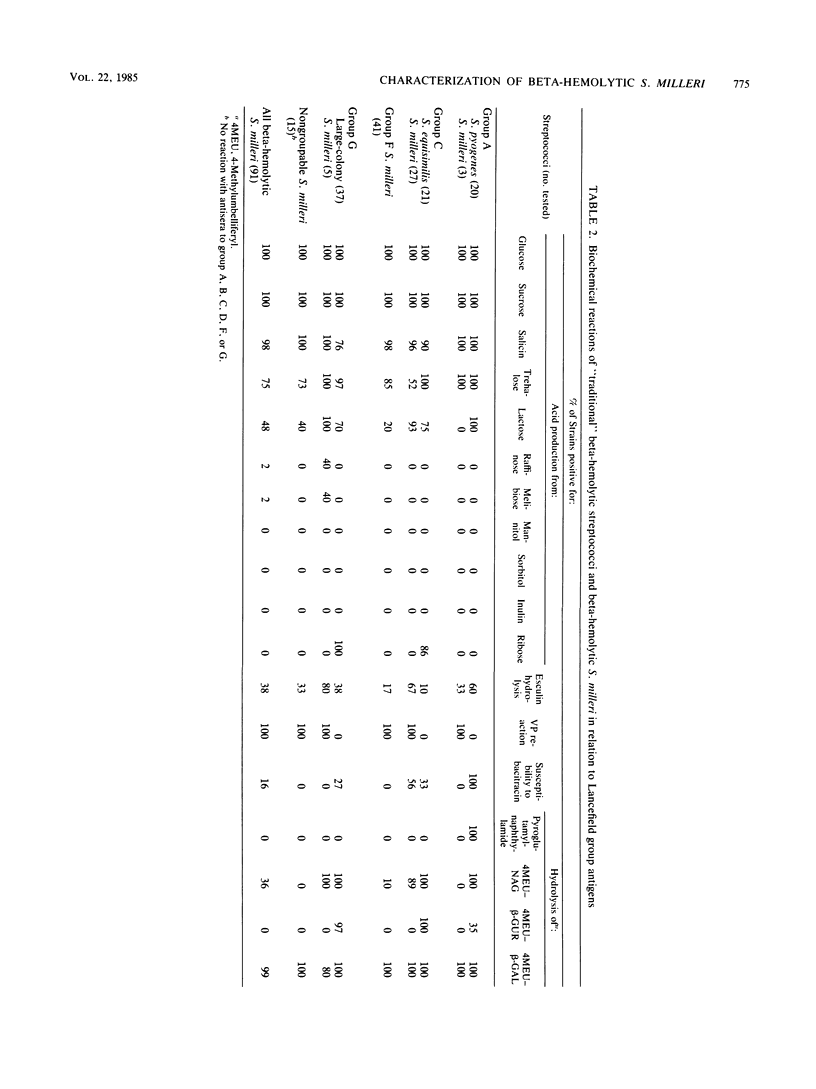
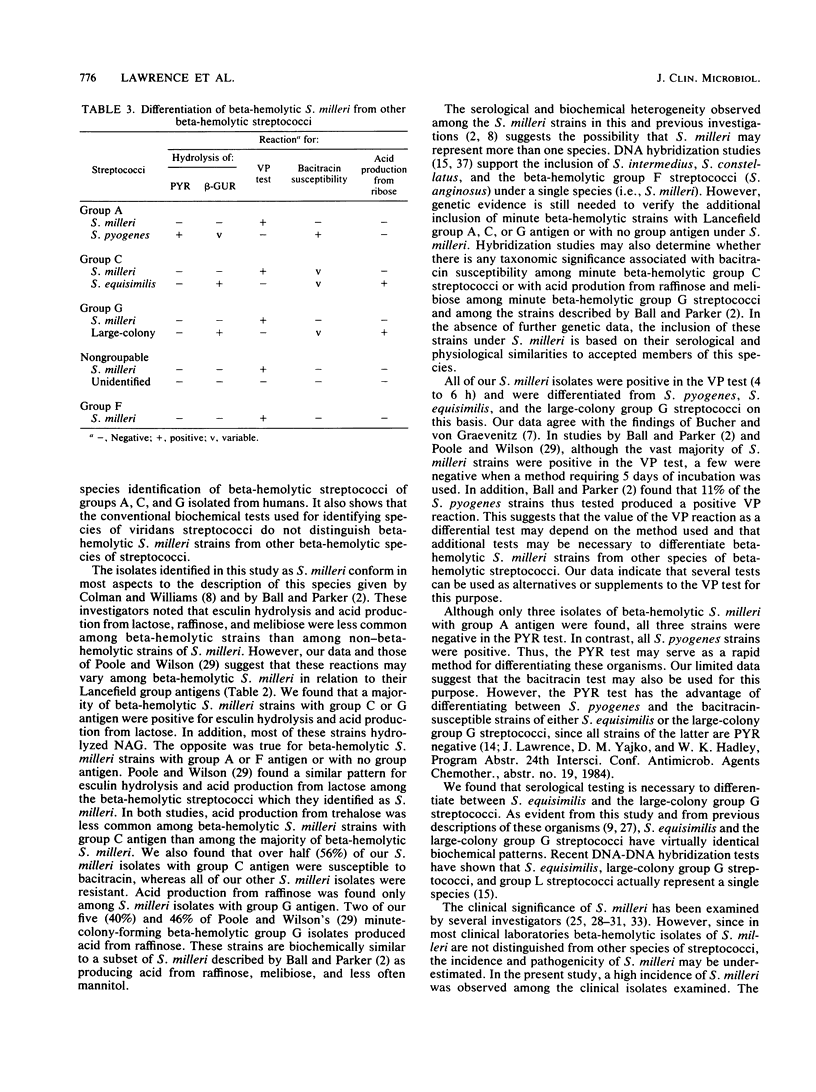
The biochemical characteristics of 172 clinical isolates of group A, C, F, or G or "nongroupable" beta-hemolytic streptococci were examined. Among these isolates, 91 were identified as beta-hemolytic strains of Streptococcus milleri. The remaining isolates included 20 Streptococcus pyogenes, 21 Streptococcus equisimilis, 37 large-colony group G streptococci, and 3 unidentified nongroupable isolates. A majority (84%) of the S. milleri strains possessed Lancefield group antigen (3 A, 27 C, 41 F, and 5 G), whereas 15 S. milleri strains (16%) were nongroupable. Serological tests did not differentiate S. milleri isolates with group A, C, or G antigen from S. pyogenes (group A), S. equisimilis (group C), or large-colony group G streptococci. Biochemical tests which were found useful for differentiation included the Voges-Proskauer test, hydrolysis of pyroglutamic acid and beta-D-glucuronide, bacitracin susceptibility, and acid production from ribose. S. milleri represented 56% of the group C, 100% of the group F, and 83% of the nongroupable beta-hemolytic streptococci isolated in our clinical laboratory, whereas the incidence of S. milleri among group A and group G streptococci was estimated to be low. The role of beta-hemolytic S. milleri as a cause of human infection remains obscured by the failure to routinely differentiate S. milleri from other beta-hemolytic streptococci.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball L. C., Parker M. T. The cultural and biochemical characters of Streptococcus milleri strains isolated from human sources. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Feb;82(1):63–78. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002547x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Feeney K. L. Two quick methods for Voges-Proskauer test. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1138–1141. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1138-1141.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss E. A. Studies upon Minute Hemolytic Streptococci: III. Serological Differentiation. J Bacteriol. 1937 Jun;33(6):625–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.33.6.625-642.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasitus T. A., Cleri D. J., Szabo K. Streptococcus MG-intermedius (S milleri) hepatic abscesses in two patients with regional enteritis. South Med J. 1983 Oct;76(10):1297–1298. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198310000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge P. D., Sneath P. H. Numerical taxonomy of Streptococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):565–597. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher C., von Graevenitz A. Differentiation in throat cultures of group C and G streptococci from Streptococcus milleri with identical antigens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;3(1):44–45. doi: 10.1007/BF02032818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Physiological differentiation of viridans streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):184–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.184-201.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Thacker L. G., Fox B., Eriquez L. Presumptive identification of streptococci with a new test system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):987–990. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.987-990.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHOF O. Ueber pathogene vergrünende Streptokokken; Streptokokken-Befunde bei dentogenen Abszessen und Infiltraten im Bereich der Mundhöhle. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1956 Sep;166(7-8):553–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo J. C., Raff M. J. Brain abscess due to Streptococcus MG-intermedius (Streptococcus milleri). J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):529–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.529-532.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Gross K. C., Masur H., Roberts R. B. Serious infections caused by Streptococcus milleri. Am J Med. 1978 May;64(5):759–764. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90514-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTTENS H., WINKLER K. C. Indifferent and haemolytic streptococci possessing group-antigen F. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:181–191. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T., Ball L. C. Streptococci and aerococci associated with systemic infection in man. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Aug;9(3):275–302. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole P. M., Wilson G. Infection with minute-colony-forming beta-haemolytic streptococci. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;29(8):740–745. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.8.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole P. M., Wilson G. Occurrence and cultural features of Streptococcus milleri in various body sites. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;32(8):764–768. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.8.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole P. M., Wilson G. Streptococcus milleri in the appendix. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Oct;30(10):937–942. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.10.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulliam L., Porschen R. K., Hadley W. K. Biochemical properties of CO2-dependent streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.27-31.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kunz L. J., Ferraro M. J. Occurrence of Streptococcus milleri among beta-hemolytic streptococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):149–151. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.149-151.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Lerner P. I., Wolinsky E., Gopalakrishna K. V. Infections due to Lancefield group F and related Streptococci (S. milleri, S. anginosus). Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):197–207. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198105000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifkin M., Gil G. M. Rapid biochemical tests for the identification of groups A, B, C, F, and G streptococci from throat cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):29–32. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.29-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Louvois J., Gortavai P., Hurley R. Bacteriology of abscesses of the central nervous system: a multicentre prospective study. Br Med J. 1977 Oct 15;2(6093):981–984. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6093.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


