Abstract
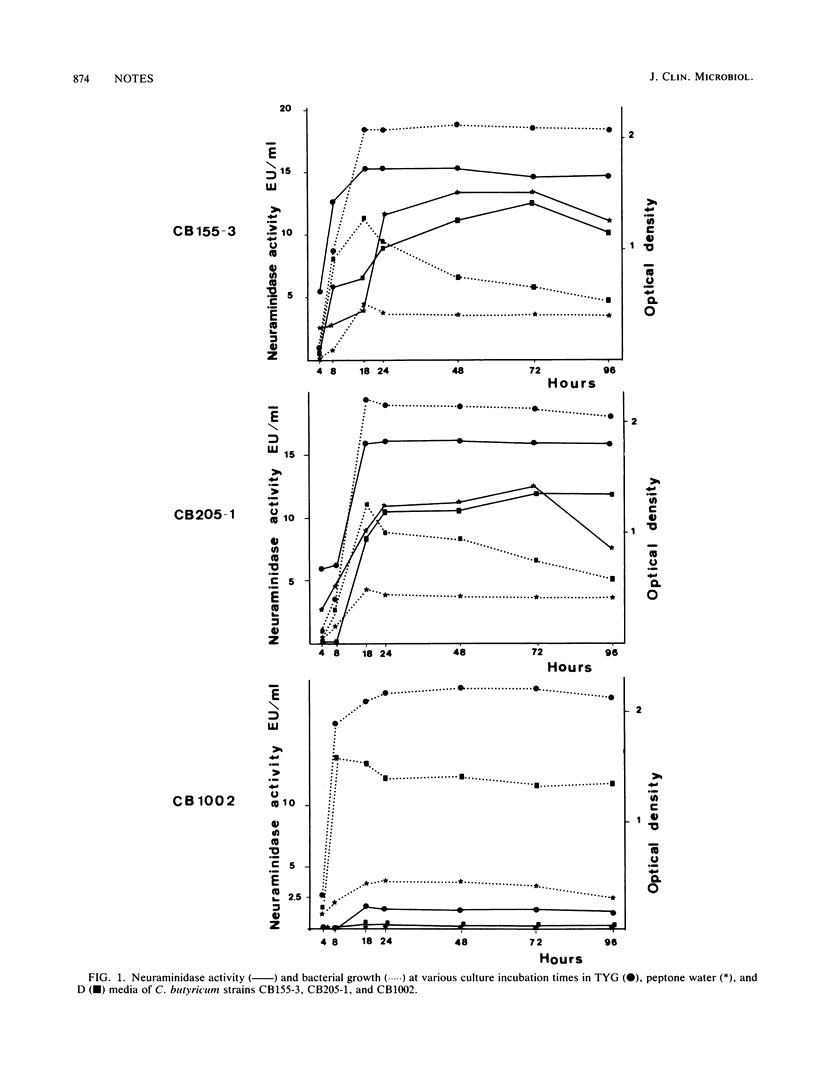
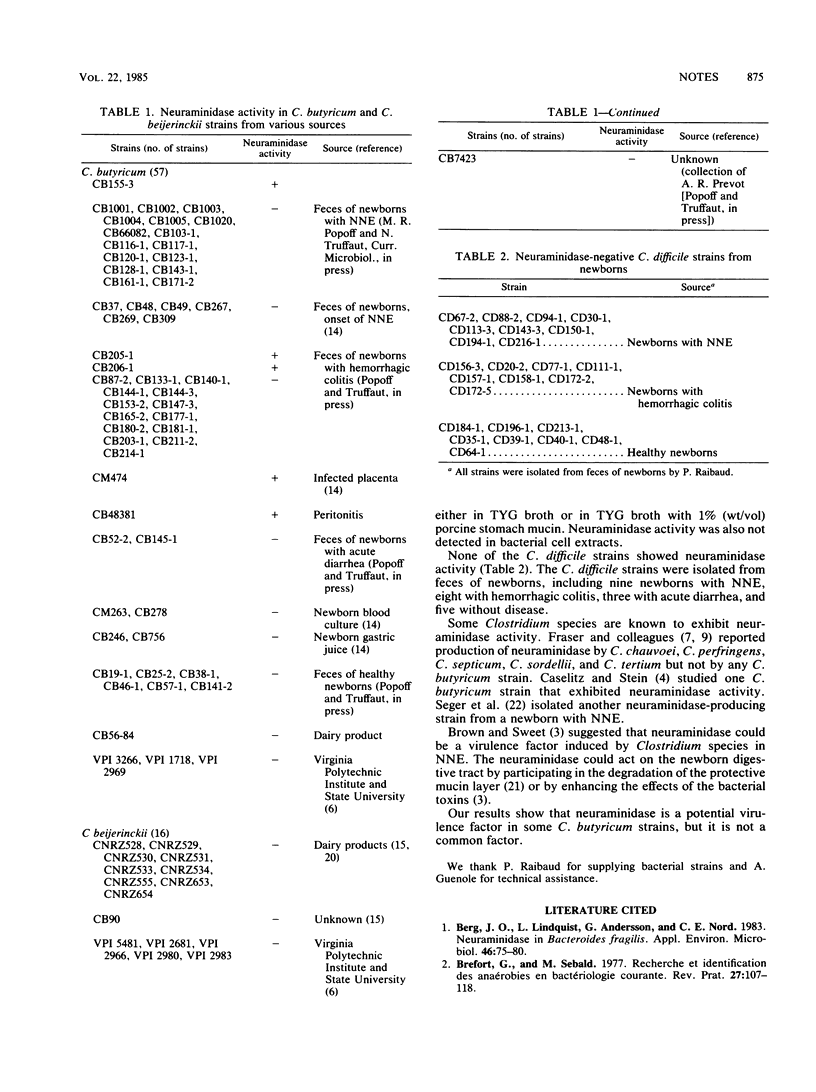
Neuraminidase production was investigated in 57 Clostridium butyricum strains, 16 Clostridium beijerinckii strains, and 25 Clostridium difficile strains. Neuraminidase activity was found only in C. butyricum strains originating from one human newborn with neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis, two newborns with hemorrhagic colitis, one infected placenta, and one adult with peritonitis, It was concluded that neuraminidase was not a major virulence factor in C. butyricum strains.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. O., Lindqvist L., Andersson G., Nord C. E. Neuraminidase in Bacteroides fragilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.75-80.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. G., Sweet A. Y. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1982 Oct;29(5):1149–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashore W. J., Peter G., Lauermann M., Stonestreet B. S., Oh W. Clostridia colonization and clostridial toxin in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):308–311. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser A. G., Brown R. Neuraminidase production by Bacteroidaceae. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):63–76. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser A. G., Collee J. G. The production of neuraminidase by food poisoning strains of Clostridium welchii (C. perfringens). J Med Microbiol. 1975 May;8(2):251–263. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser Neuraminidase production by clostridia. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Aug;11(3):269–280. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-3-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., Sayed H., Chance G. W., Brabyn D. G., Shaheed W. A. An outbreak of Clostridium difficile necrotizing enterocolitis: a case for oral vancomycin therapy? Pediatrics. 1983 Jun;71(6):935–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard F. M., Flynn D. M., Bradley J. M., Noone P., Szawatkowski M. Outbreak of necrotising enterocolitis caused by Clostridium butyricum. Lancet. 1977 Nov 26;2(8048):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M., Fanaroff A. A. Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 26;310(17):1093–1103. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404263101707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe R. G. Enterotoxin formation by Clostridium perfringens type A in a defined medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):315–317. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.315-317.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magot M., Carlier J. P., Popoff M. R. Identification of Clostridium butyricum and Clostridium beijerinckii by gas-liquid chromatography and sugar fermentation: correlation with DNA homologies and electrophoretic patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2837–2845. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magot M. Résistance aux pénicillines due à la production d'une béta-lactamase chez les Clostridium du groupe butyricum. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1981 Jan 19;292(3):285–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak R. W. Bacterial-induced RBC alterations complicating necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Feb;138(2):183–185. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140400065016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. R., Sebald M. Mise en évidence chez Clostridium butyricum d'un facteur thermostable responsable du pouvoir pathogène experimental. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1981 Mar 23;292(12):763–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. R., Szylit O., Ravisse P., Dabard J., Ohayon H. Experimental cecitis in gnotoxenic chickens monoassociated with Clostridium butyricum strains isolated from patients with neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):697–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.697-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau M., Hermier J., Bergere J. L. Structure de certains Clostridium du groupe butyrique. I. Sporulation de Clostridium butyricum et Clostridium saccharobutyricum. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Jan;120(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebald M., Bréfort G. Recherche et identification des anaérobies en bactériologie courante. Rev Prat. 1977 Jan 11;27(3):107–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Joller P., Bird G. W., Wingham J., Wuest J., Kenny A., Rapp A., Garzoni D., Hitzig W. H., Duc G. Necrotising enterocolitis and neuraminidase-producing bacteria. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1980 May;35(2):121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. F., Borriello S. P., Clayden G. S., Casewell M. W. Clinical and bacteriological findings in necrotising enterocolitis: a controlled study. J Infect. 1980 Mar;2(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(80)91727-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Staneck J. L., Stauffer L. R., Neblett W. W., 3rd Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis associated with penicillin-resistant, toxigenic Clostridium butyricum. Pediatrics. 1980 Dec;66(6):928–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


