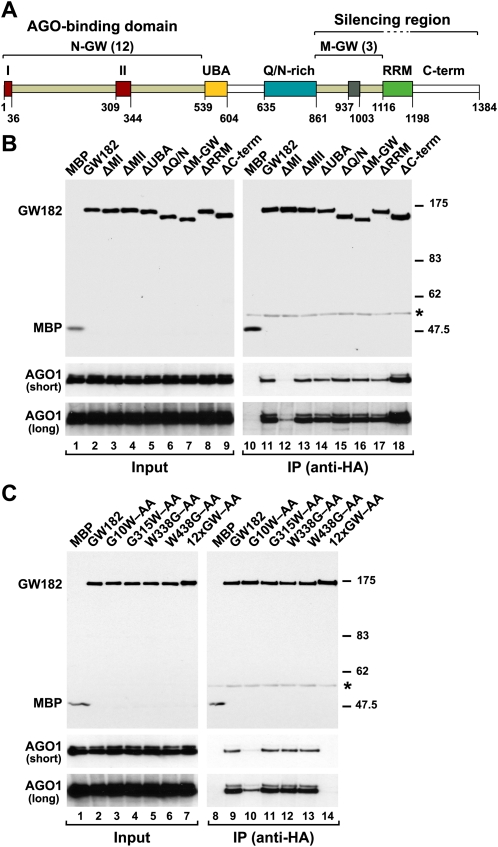
FIGURE 1.
A GW-repeat in motif I of D. melanogaster GW182 provides a major binding site for AGO1. (A) Domain organization of GW182. N-GW and M-GW: N-terminal and middle GW-repeat-containing regions, respectively, with the number of repeats indicated in brackets; (UBA) ubiquitin associated-like domain; (Q/N-rich) region rich in glutamine (16.7%) and asparagine (14.5%); (RRM) RNA recognition motif; (C-term) C-terminal region. Red boxes I and II: two conserved motifs within the N-terminal GW-repeats. Gray box: conserved motif III in the middle region. The bipartite silencing region includes the M-GW and C-terminal regions but not the RRM, which is dispensable for silencing (Eulalio et al. 2009a). Amino acid positions at domain boundaries are indicated. (B,C) Lysates from S2 cells expressing HA-tagged versions of MBP, wild-type GW182, or GW182 mutants were immunoprecipitated using a monoclonal anti-HA antibody. Inputs (1.5%) and immunoprecipitates (30%) were analyzed by Western blotting using a polyclonal anti-HA antibody. Endogenous AGO1 was detected by Western blotting using anti-AGO1 antibodies (two different exposures are shown, short and long). (Asterisks) Indicate cross-reactivity with the immunoglobulin heavy chain by the secondary antibody (IP panels).