Abstract
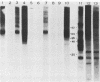
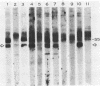
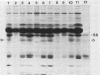
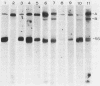
We tested 10 patient sera for the presence of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies to Candida albicans and for C. albicans antigens by immunoblot analysis (i.e., electrotransfer blot radioimmunoassay) (G. E. Smith and M. D. Summers, J. Virol. 39:125-137, 1981). We evaluated sera from two patients at risk for candidiasis, five patients with systemic candidiasis documented by culture, and two patients who had experienced transient candidemia. Both the specificity and the relative amount of IgG antibodies to C. albicans in each serum sample were readily visualized by this technique, as was the absence of antibody from serum of neonatal and immunocompromised patients. No antibody species appeared to be uniquely associated with candidiasis patients (i.e., each antibody species present in the candidiasis patient was also present in sera of normal individuals or "at-risk" patients). IgG from rabbits immunized with whole cells or with a cytoplasmic fraction of C. albicans was used to detect C. albicans antigens in patient sera. Although several antigens were detected in the sera from patients with candidiasis, the same antigens were also detected in sera from patients at risk and in normal human serum. No antigens were detected in human serum when preimmune rabbit sera were used. These results suggest that the antigens detected by the rabbit antisera were human serum proteins that cross-reacted with C. albicans antigens. These findings may have important implications in studies of both the pathobiology of C. albicans and the serodiagnosis of candidiasis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araj G. F., Hopfer R. L., Chesnut S., Fainstein V., Bodey G. P., Sr Diagnostic value of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Candida albicans cytoplasmic antigen in sera of cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou C. Structure and biosynthesis of the mannan component of the yeast cell envelope. Adv Microb Physiol. 1976;14(11):93–158. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb S. J., Parratt D. Determination of antibody levels to Candida albicans in healthy and hospitalised adults using a radioimmunoassay. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Dec;31(12):1161–1166. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.12.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dee T. H., Rytel M. W. Clinical application of counterimmunoelectrophoresis in detection of Candida serum precipitins. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jan;85(1):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines J. D., Remington J. S. Diagnosis of deep infection with Candida. A study of Candida precipitins. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Nov;132(5):699–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Wilkinson I. D., Lea A. S., Price M. F. Latex agglutination test for detection of Candida antigen in patients with disseminated disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):122–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02001577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Buckley H. R., Rosen H. M., Moellering R. C., Jr, Fischer J. E. Serologic tests in the diagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Enhanced diagnostic accuracy with crossed immunoelectrophoreses. Am J Med. 1978 Apr;64(4):586–591. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90577-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. W., Wong B., Bernard E. M., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Serum arabinitol concentrations and arabinitol/creatinine ratios in invasive candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):504–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield R. A., Jones J. M. Purification and characterization of a major cytoplasmic antigen of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):469–477. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.469-477.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinan M. E., Portas M. R., Hill H. R. The candida precipitin test in an immunosuppressed population. Cancer. 1979 Jan;43(1):299–302. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197901)43:1<299::aid-cncr2820430143>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer R. L., Gröschel D. Detection by counterimmunoelectrophoresis of anti-Candida precipitins in sera from cancer patients. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;72(2):215–218. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M. Quantitation of antibody against cell wall mannan and a major cytoplasmic antigen of Candida in rabbits, mice, and humans. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):78–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.78-89.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkering T. M., Espinel-Ingroff A., Shadomy S. Detection of candida antigenemia by counterimmunoelectrophoresis in patients with invasive candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):659–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R., Wheat L. J., White A. Detection of IgG candida antibodies by solid-phase radioimmunoassay and comparison with agar-gel diffusion. Am J Med Sci. 1979 Jul-Aug;278(1):49–55. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197907000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostiala A. A., Kostiala I. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for IgM, IgG and IgA class antibodies against Candida albicans antigens: development and comparison with other methods. Sabouraudia. 1981 Jun;19(2):123–134. doi: 10.1080/00362178185380191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar B. V., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Sieling W. L. Cross-reacting human and rabbit antibodies to antigens of Histoplasma capsulatum, Candida albicans, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):806–812. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.806-812.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald F., Odds F. C. Inducible proteinase of Candida albicans in diagnostic serology and in the pathogenesis of systemic candidosis. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Aug;13(3):423–435. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald F., Odds F. C. Purified Candida albicans proteinase in the serological diagnosis of systemic candidosis. JAMA. 1980 Jun 20;243(23):2409–2411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning M., Mitchell T. G. Analysis of cytoplasmic antigens of the yeast and mycelial phases of Candida albicans by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):484–495. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.484-495.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning M., Snoddy C. B., Fromtling R. A. Comparative pathogenicity of auxotrophic mutants of Candida albicans. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jan;30(1):31–35. doi: 10.1139/m84-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marier R., Andriole V. T. Usefulness of serial antibody determinations in diagnosis of candidiasis as measured by discontinuous counterimmunoelectrophoresis using HS antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):15–22. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.15-22.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Tabaqchali S. Immunoblot analysis of the serological response in systemic candidosis. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1415–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meckstroth K. L., Reiss E., Keller J. W., Kaufman L. Detection of antibodies and antigenemia in leukemic patients with candidiasis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):24–32. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. G., Witwer M. W., Braude A. I., Davis C. E. Rapid identification of Candida albicans septicemia in man by gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1235–1240. doi: 10.1172/JCI107867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson T. P., Wilkinson K. P. Mannose in body fluids as an indicator of invasive candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(5):557–562. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.5.557-562.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poor A. H., Cutler J. E. Partially purified antibodies used in a solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detecting candidal antigenemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):362–368. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.362-368.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Application of a novel radioimmunoassay to identify baculovirus structural proteins that share interspecies antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):125–137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.125-137.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Huang S., Young L. S., Berdischewsky M. Detection of candida antigenemia in human invasive candidiasis by a new solid phase radioimmunoassay. Infection. 1980;8 (Suppl 3):S–338. doi: 10.1007/BF01639607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Largen M. T., Zweibel S. M., Buckley H. R. Identification and molecular weight characterization of antigens from Candida albicans that are recognized by human sera. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):715–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.715-721.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syverson R. E., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. Cytoplasmic antigens unique to the mycelial or yeast phase of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1184-1188.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syverson R. E., Buckley H. R., Gibian J. R. Increasing the predictive value positive of the precipitin test for the diagnosis of deep-seated candidiasis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Nov;70(5):826–831. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.5.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. H., Coats-Stephen M. Immunodiagnosis of systemic candidiasis: mannan antigenemia detected by radioimmunoassay in experimental and human infections. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):989–993. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Weston H. D., Andersen O. F., Garber S. S., Hayes E. C. Immunity against infection with Trypanosoma cruzi in mice correlates with presence of antibodies against three trypomastigote polypeptides. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.826-830.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Reiss E. Current trends in immunodiagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):301–312. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]