Abstract
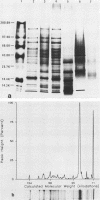
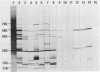
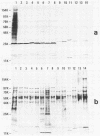
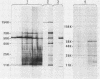
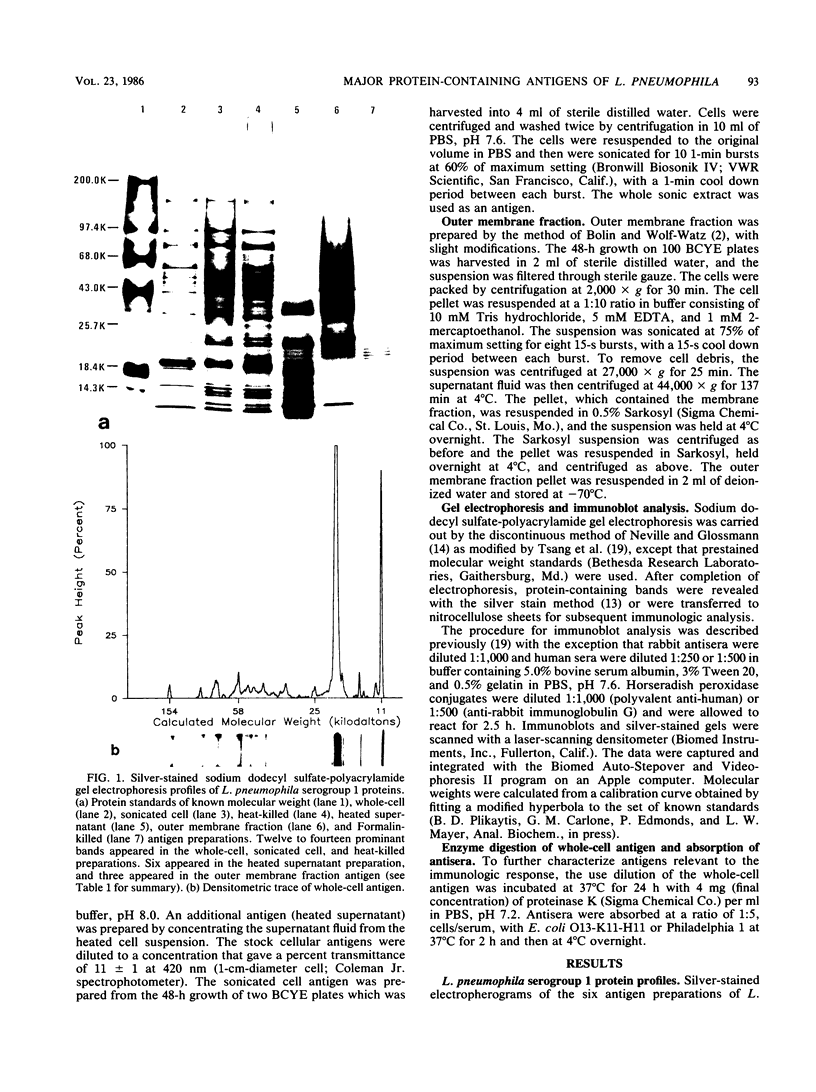
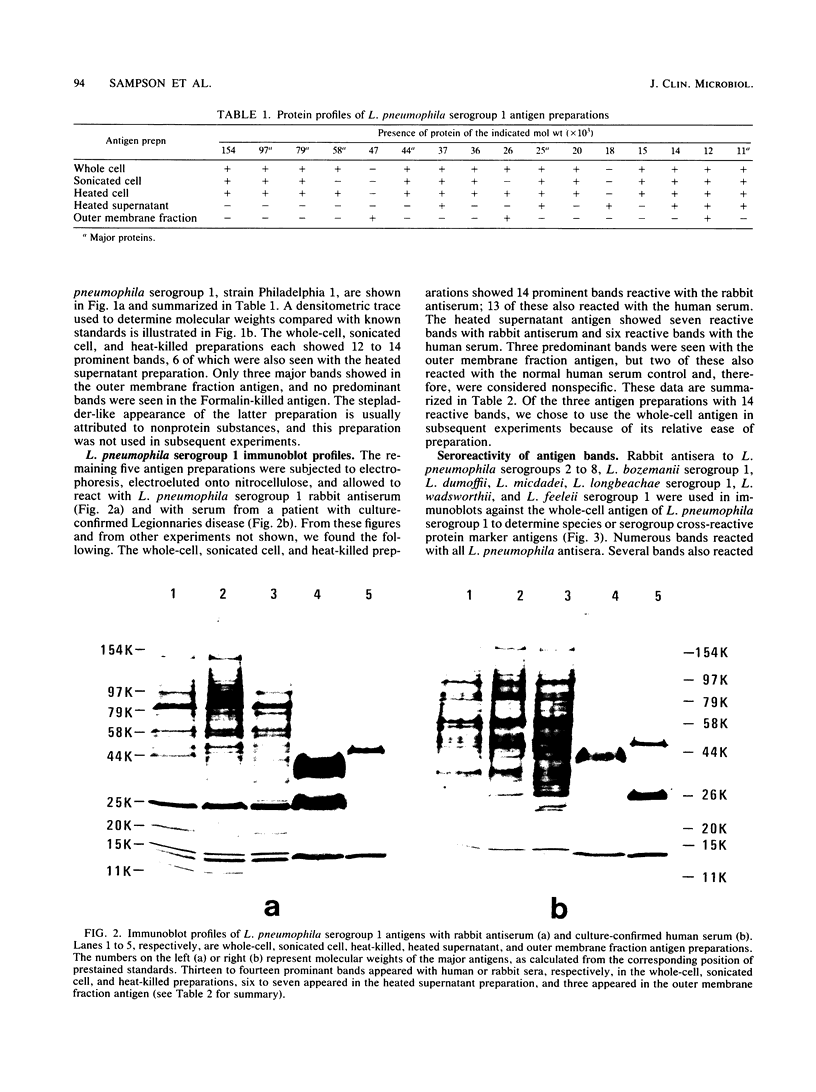
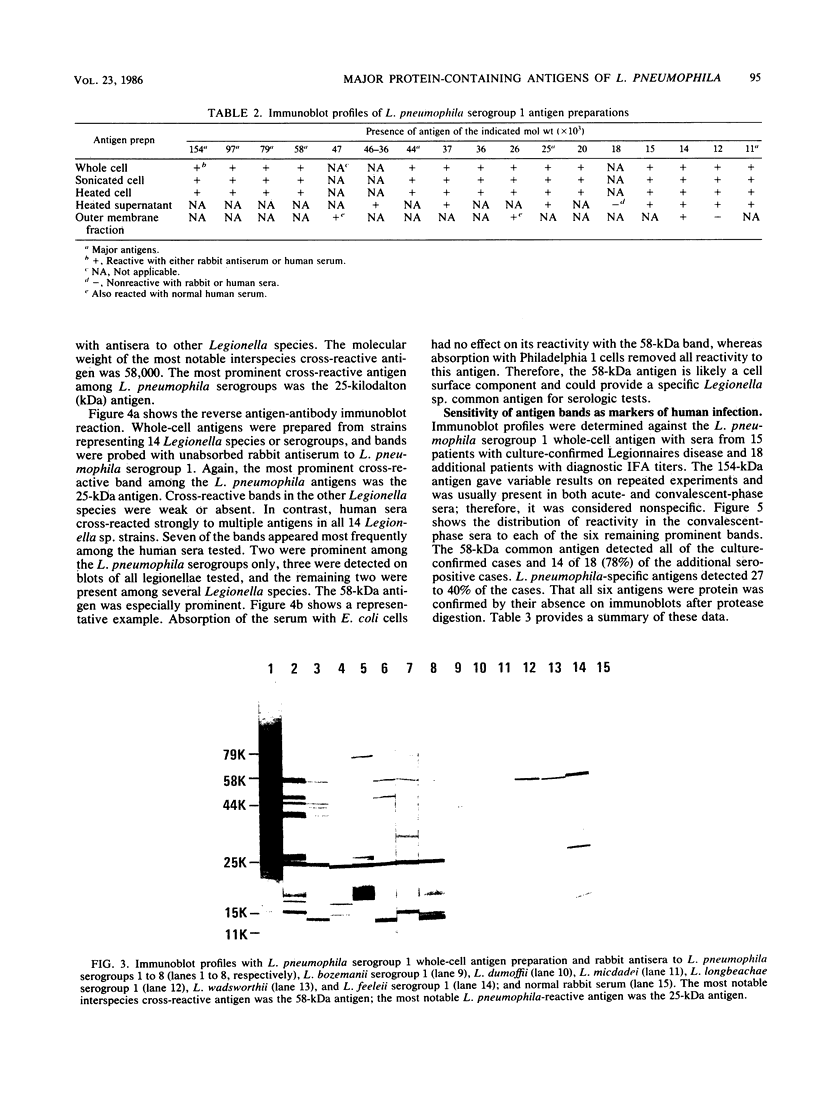
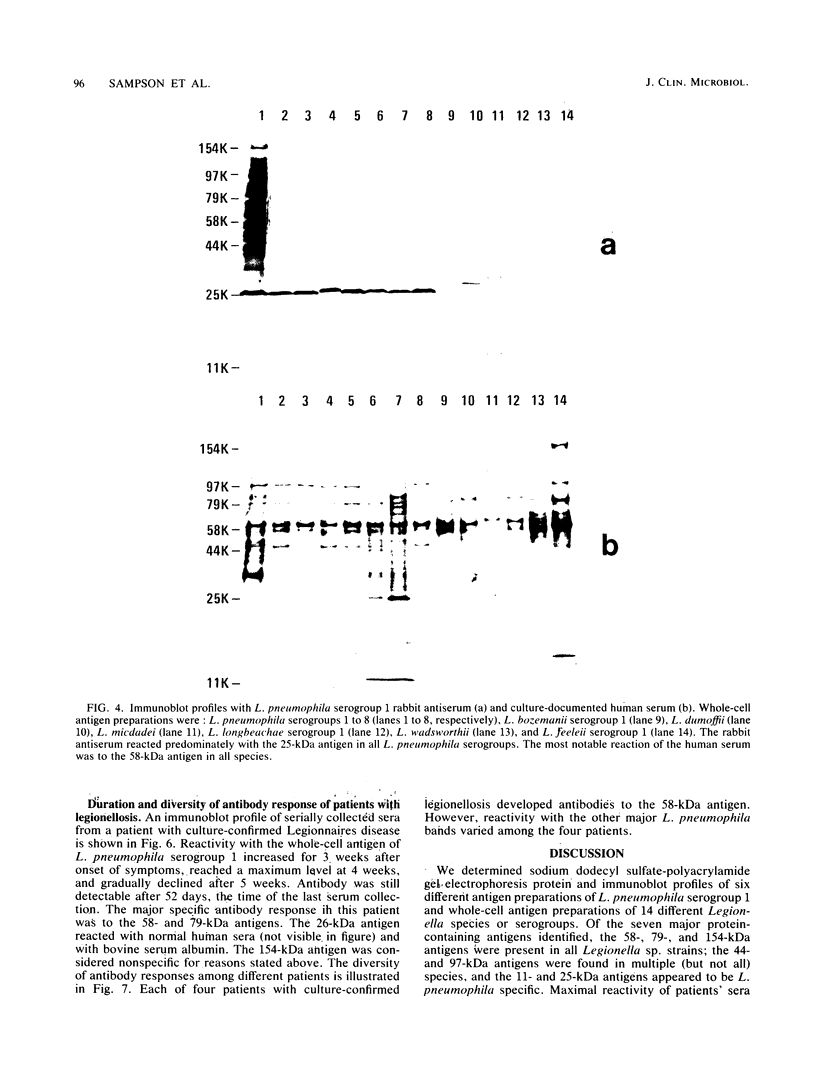
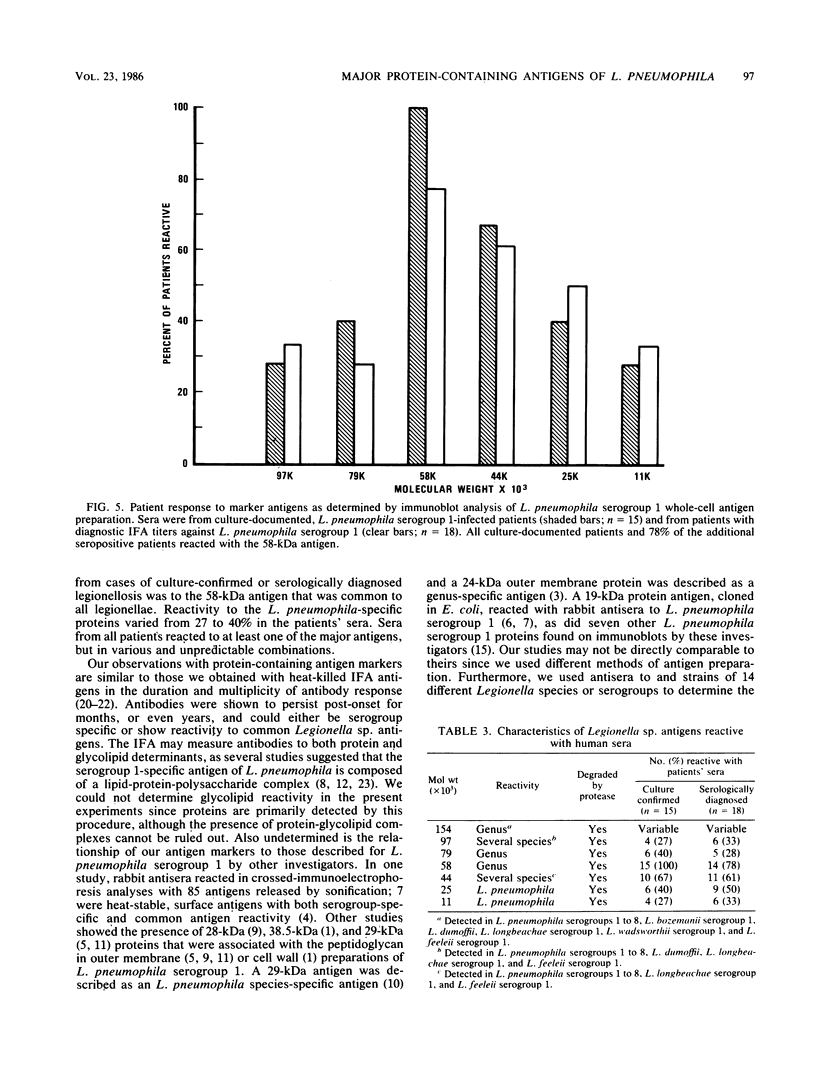
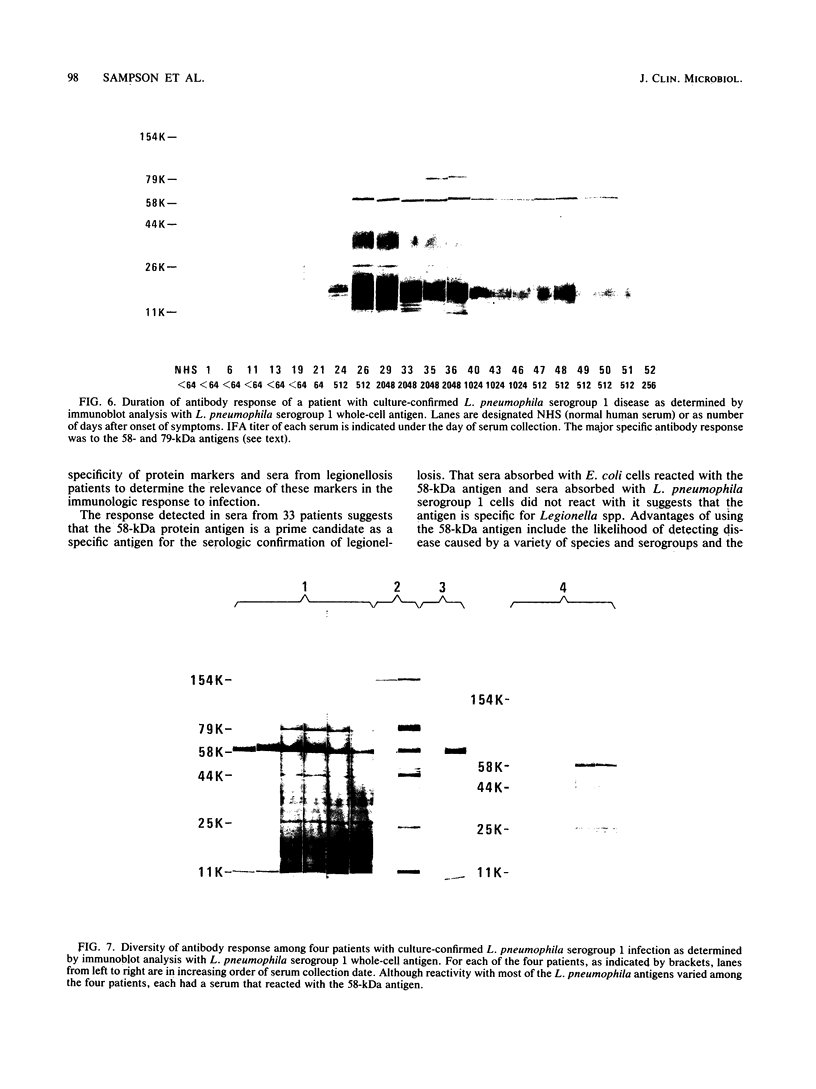
Major protein-containing antigens of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 were were identified by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analysis with rabbit antisera to 14 different Legionella species or serogroups. Fourteen bands were observed in immunoelectropherograms of whole-cell, sonicated cell, and heated cell preparations, seven of which appeared in the supernatant fluid from the heated cells and three of which were shown in an outer membrane fraction. Immunoblots of whole-cell antigen preparations of 14 Legionella species or serogroups revealed seven major Legionella proteins: antigens with molecular weights of 58,000, 79,000, and 154,000 were present in all Legionella sp. strains, antigens with molecular weights of 44,000 and 97,000 occurred in multiple species, and antigens with molecular weights of 14,000 and 25,000 were present only in L. pneumophila strains. All sera from 15 patients with culture-confirmed L. pneumophila serogroup 1 disease and 14 of 18 (78%) sera from serologically diagnosed patients reacted with the 58-kilodalton (kDa) common antigen. In contrast, less than one-half of the sera reacted with the L. pneumophila-specific proteins (14 and 25 kDa). Absorption of sera with Escherichia coli cells had no effect on their reactivity with the 58-kDa antigen, whereas absorption with L. pneumophila serogroup 1 cells removed reactivity. These data suggest that the 58-kDa antigen may prove useful in serodiagnostic tests for legionellosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Partial characterization of peptidoglycan-associated proteins of Legionella pneumophila. J Biochem. 1983 Aug;94(2):601–606. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. A., Street E. D., Hatch T. P., Hoffman P. S. Disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins in the genus Legionella. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.14-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Molecular cloning of the temperature-inducible outer membrane protein 1 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.72-78.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. T., Cho S. N., Høiby N., Espersen F., Baek L., Reif J. S. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic analysis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1428–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1428-1440.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehret W., Ruckdeschel G. Species specific membrane proteins of Legionellaceae. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;255(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Drutz D. J., Eisenstein B. I. Cloning and expression of Legionella pneumophila antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):222–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.222-227.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Pearlman E., Eisenstein B. I. Legionella pneumophila surface antigens cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli are translocated to the host cell surface and interact with specific anti-Legionella antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):199–203. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.199-203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesher A. R., Jennings H. J., Lugowski C., Kasper D. L. Isolation of a serogroup 1-specific antigen from Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):224–233. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Blake M., Niles W. D., Horwitz M. A. Purification of Legionella pneumophila major outer membrane protein and demonstration that it is a porin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.85-91.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosting L. H., Cabrian K., Sturge J. C., Goldstein L. C. Identification of a species-specific antigen in Legionella pneumophila by a monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1031–1035. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1031-1035.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of the Legionella pneumophila outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.107-113.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Elliott J. A., Helms C. M., Renner E. D. A high molecular weight antigen in Legionnaires' disease bacterium: isolation and partial characterization. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):638–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr, Glossmann H. Molecular weight determination of membrane protein and glycoprotein subunits by discontinuous gel electrophoresis in dodecyl sulfate. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:92–102. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman E., Engleberg N. C., Eisenstein B. I. Identification of protein antigens of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.74-79.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. S., Wilkinson H. W., Tsang V. C., Brake B. J. Kinetic-dependent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1340–1344. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1340-1344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker W. L., Plikaytis B. B., Wilkinson H. W. Identification of 22 Legionella species and 33 serogroups with the slide agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):779–782. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.779-782.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacker W. L., Wilkinson H. W., Benson R. F. Comparison of slide agglutination test and direct immunofluorescence assay for identification of Legionella isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1113–1118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1113-1118.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Farshy C. E., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D., Yealy L. P. Measure of immunoglobulin G-, M-, and A-specific titers against Legionella pneumophila and inhibition of titers against nonspecific, gram-negative bacterial antigens in the indirect immunofluorescence test for legionellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.685-689.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D. Indirect immunofluorescence test for serodiagnosis of Legionnaires disease: evidence for serogroup diversity of Legionnaires disease bacterial antigens and for multiple specificity of human antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):379–383. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.379-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Schalla W. O., Arko R. J., Bullard J. C., Feeley J. C. Immunochemical, serologic, and immunologic properties of major antigens isolated from the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Observations bearing on the feasibility of a vaccine. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):634–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]