Abstract
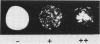
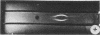
Haemophilus parasuis strains isolated from the noses of apparently healthy animals and from animals with pathological conditions were examined for the presence of a capsule, for their ability to agglutinate in acriflavine or after boiling, and for their peptide profile after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). The capsule was identified by precipitation against hexadecyl trimethylammonium bromide (Cetavlon), by demonstration of iridescence, and by means of a capsule-staining method. We found a group of capsulated strains showing a rather coccobacillary morphology compared with the morphology with polymorphism, varying from rod-like to filamentous, in strains without detectable capsules. The strains of the latter group were agglutinated by acriflavine or by boiling. Soluble antigens of capsulated strains reacting with Cetavlon were thermostable and resisted proteolytic enzymes, thus suggesting the presence of an acidic polysaccharide. A few of the capsulated strains did not precipitate with Cetavlon, which indicated that their chemical composition was different. Acriflavine-positive strains belonging to a definite PAGE pattern (type II) seemed to be associated with pathological conditions more frequently than were capsulated strains which were mostly isolated from nasal cavities of apparently healthy pigs. We put forward the hypothesis that the agglutinability in acriflavine, together with the PAGE profile type II, may be associated with particular structures responsible for virulence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R., Subronto P. Identification of type D strains of Pasteurella multocida with acriflavine. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Feb;34(2):293–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. A., Fothergill L. D., Dingle J. H. The Pattern of Dissociation in Hemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1939 Apr;37(4):415–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.37.4.415-427.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little T. W., Harding J. D. The comparative pathogenicity of two porcine haemophilus species. Vet Rec. 1971 May 22;88(21):540–545. doi: 10.1136/vr.88.21.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi T., Hiramune T., Kobayashi K. Glässer's disease in piglets produced by intraperitoneal inoculation with Haemophilus parasuis. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1981 Fall;21(3):121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil D. H., McKay K. A., L'Ecuyer C., Corner A. H. Glasser's disease of swine produced by the intracheal inoculation of haemophilus suis. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Jul;33(3):187–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J. Sur l'hémophilose du pore. 3. Différenciation sérologique de Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(4):487–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riising H. J. Prevention of Glässer's disease through immunity to Haemophilus parasuis. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1981;28(8):630–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1981.tb01784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON A. R., ZAMENHOF S. STUDIES ON THE TYPE-SPECIFIC SUBSTANCES OF HEMOPHILUS PARASUIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:963–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]