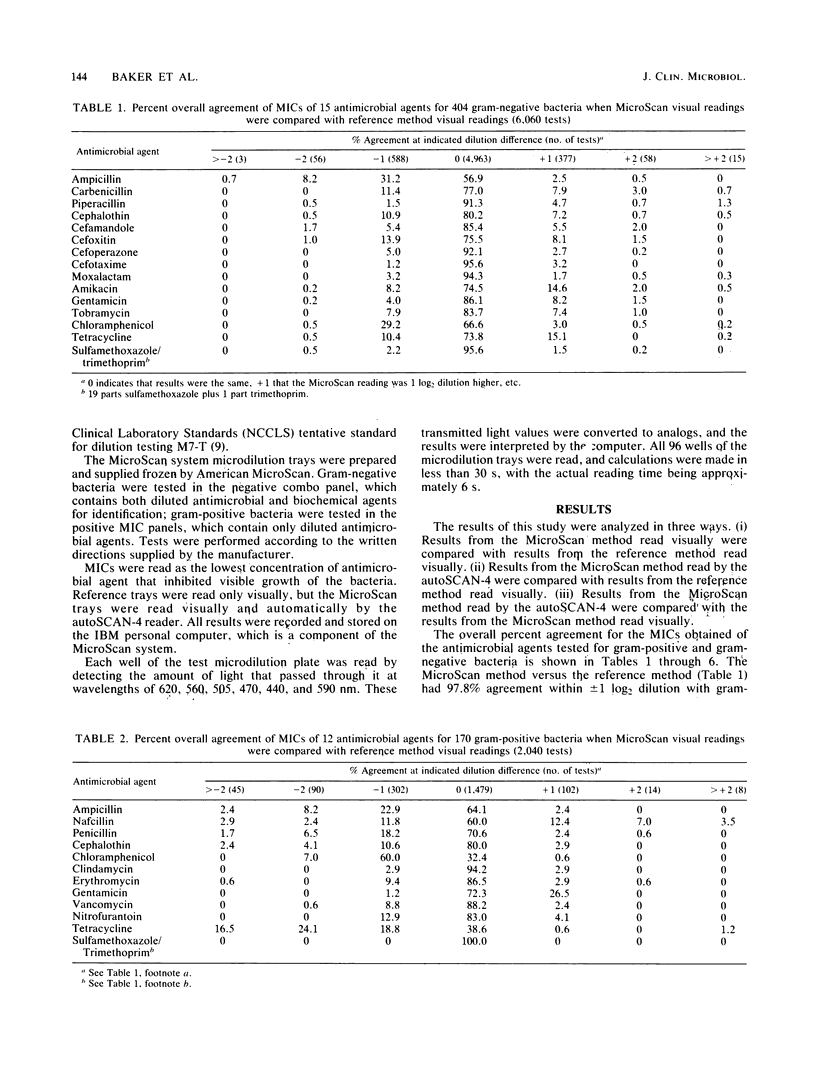
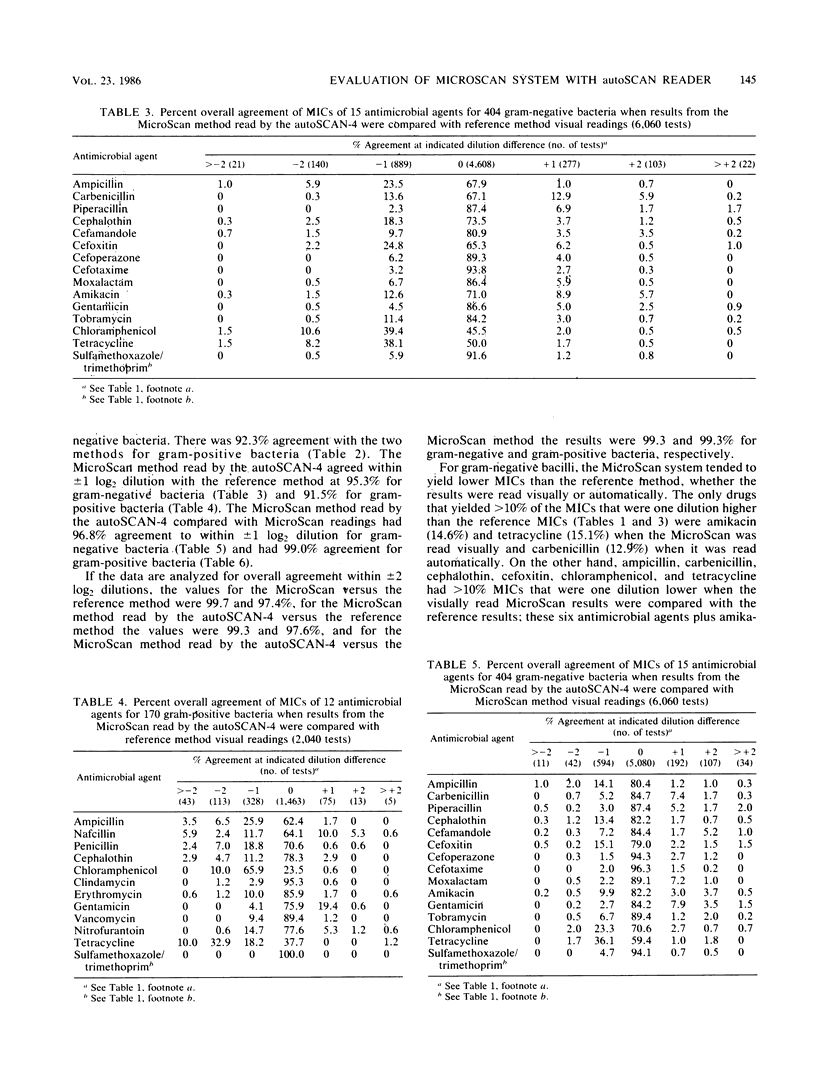
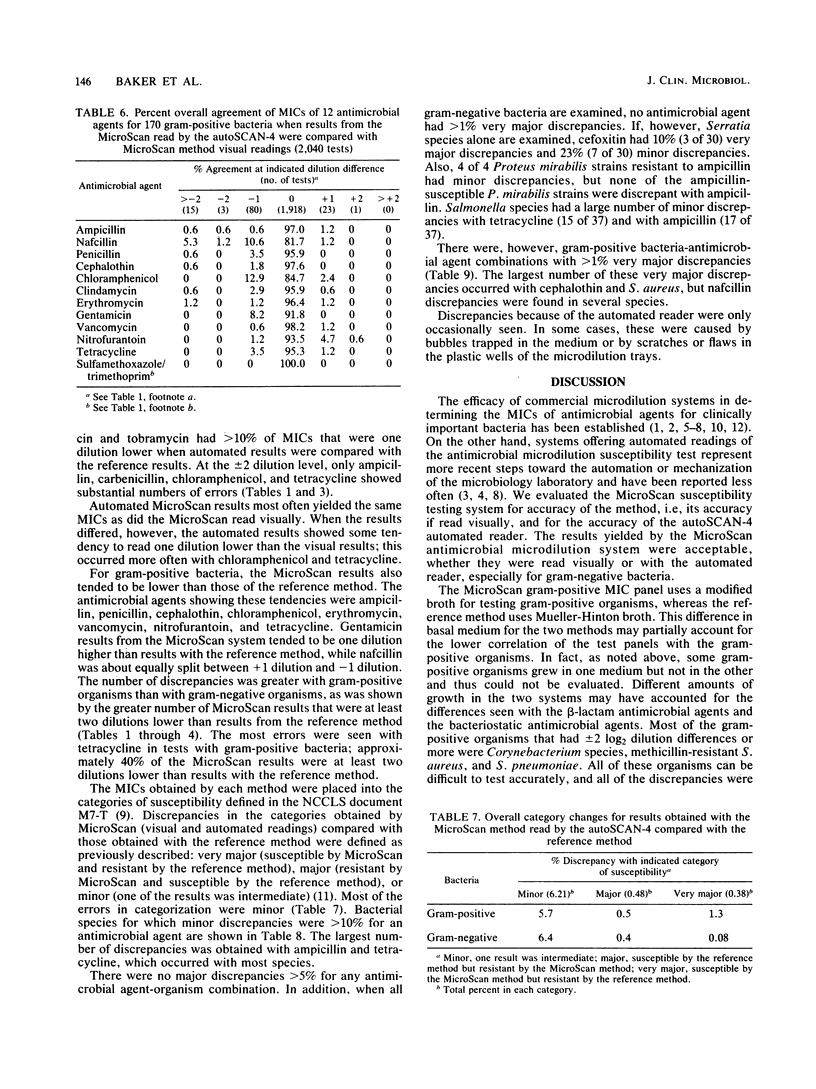
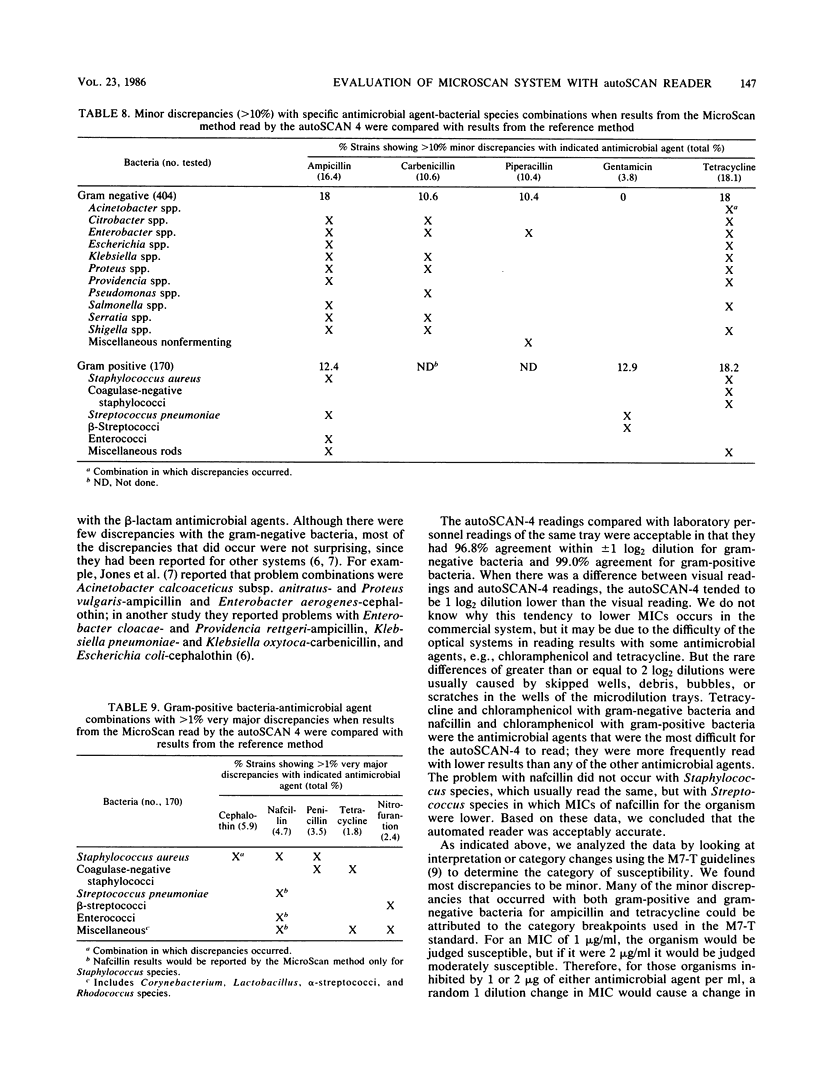
Abstract
The American MicroScan (American MicroScan, Mahwah, N.J.) identification and antimicrobial susceptibility system consists in part of an automated reading system (autoSCAN-4) with data management capabilities. We evaluated the system with 404 gram-negative and 170 gram-positive facultative anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. We compared MicroScan results read automatically and visually with each other and with the results obtained by the reference method (read visually). The overall agreement within +/- 1 log2 dilution was 94.3% when the MicroScan system (read automatically) was compared with the reference method (read visually), 96.4% when MicroScan panels (read visually) were compared with reference panels, and 97.4% when the autoSCAN-4 automated reading was compared with the visual reading of the MicroScan panels. Total discrepancies (susceptibility interpretation category changes) for the MicroScan system compared with the reference method were 7%, with 6.2% considered a minor discrepancy. The autoSCAN-4 and the complete MicroScan system yielded accurate results compared with the reference method.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Braun L. E. Reader error in determining minimal inhibitory concentrations with microdilution susceptibility test panels. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):228–230. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.228-230.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Gavan T. L. Evaluation of the micro-media system for quantitative antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courcol R. J., Deleersnyder H., Roussel-Delvallez M., Martin G. R. Automated reading of a microtitre plate: preliminary evaluation in antimicrobial susceptibility tests and Enterobacteriaceae identification. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;36(3):341–344. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGirolami P. C., Eichelberger K. A., Salfity L. C., Rizzo M. F. Evaluation of the AutoSCAN-3, a device for reading microdilution trays. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1292–1295. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1292-1295.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Bigelow J., Gavan T. L., Thornsberry C. Evaluation of the MICUR system for quantitative antimicrobial susceptibility testing: a multiphasic comparison with reference methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):153–163. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.153-163.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Gavan T. L., Barry A. L. Evaluation of the sensititre microdilution antibiotic susceptibility system against recent clinical isolates: three-laboratory collaborative study. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):426–429. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.426-429.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Barry A. L., Gavan T. L. Evaluation of the Sceptor microdilution antibiotic susceptibility testing system: a collaborative investigation. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):184–194. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.184-194.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy P. J., Miceika B. G., Ducate M. J. Automated methods in microbiology: II. Identification and susceptibility testing. Am J Med Technol. 1983 May;49(5):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Warren C., Waterworth P. M. Determination of antibiotic sensitivities by the Sensititre system. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):531–535. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C., Isenberg H. D. Evaluation of the performance parameters of a prediluted, quantitative antibiotic susceptibility test device. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):271–276. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



