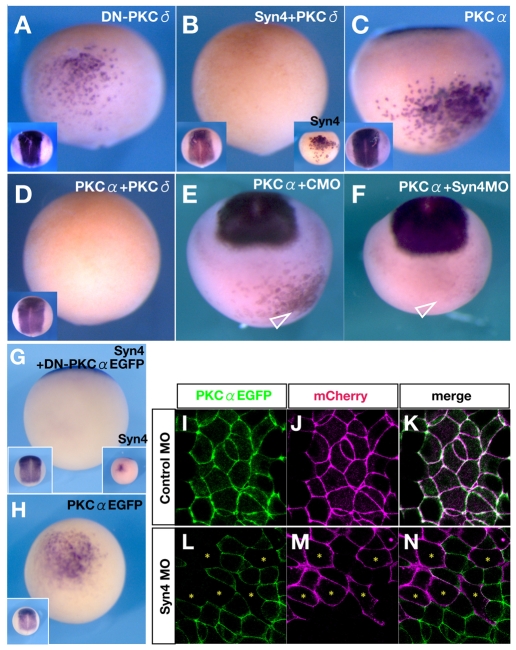
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of PKCδ or activation of PKCα is essential for neural induction by Syn4. (A-H) Sox2 expression in Xenopus embryos injected, as indicated, into A4 blastomeres at the 32-cell stage. (A-D) Ventral view, dorsal to the top. Insets on left show a dorsal view. (A) Dominant-negative Xenopus PKCδ (DN-PKCδ). Note the ectopic Sox2 induction (48%, n=71). (B) Co-injection of Syn4 and Xenopus full-length PKCδ mRNAs represses the ectopic expression of Sox2 (18%, n=91). Inset on the right shows the ventral ectopic Sox2 expression induced by Syn4 mRNA (95%, n=85). (C) Human (h) PKCα mRNA can induce ectopic Sox2 expression (68%, n=92). (D) Co-injection of hPKCα and PKCδ mRNAs shows inhibition of neural induction (20%, n=124). (E) Co-injection of hPKCα with control MO (CMO). Arrowhead indicates the ectopic expression of Sox2 (70%, n=68). (F) Co-injection of hPKCα mRNA with Syn4 MO. Sox2 induction is not observed in the injected cells (arrowhead) (23%, n=51). (G) Co-injection of Syn4 and a dominant-negative form of PKCα (DN-PKCα-EGFP) inhibits Sox2 expression (15%, n=51). (H) Injection of PKCα-EGFP mRNA. Ectopic induction of Sox2 is similar to that upon PKCα injection, showing that EGFP does not affect the activity of the fusion protein. (I-N) Confocal images of animal caps injected as indicated. PKCα-EGFP mRNA was injected into both blastomeres at the 2-cell stage. At the 16-cell stage, Syn4 or control MO and membrane Cherry mRNA were injected into one blastomere. (I-K) PKCα-EGFP spontaneously localises at the membrane, colocalising with membrane Cherry. (L-N) The distribution of Syn4 MO can be identified by the fluorescence of mCherry. Note that cells with a high level of Syn4 MO (asterisks) exhibit a low level of PKCα-EGFP in the membrane.