Abstract
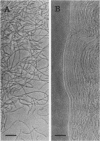
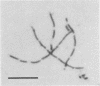
A strain of Salmonella choleraesuis subsp. choleraesuis serovar paratyphi-A isolated from the blood of a febrile patient grew into filaments on a nutrient agar containing various salts, such as NaCl, KCl, MgCl2, NH4Cl, (NH4)2SO4, or (NH4)2HPO4, at concentrations of 50 to 400 mM. The filamentous cells were nonseptate and multinucleate, and they had colony-forming ability. This mutant strain, however, did not show filamentous growth in liquid media which contained the same salts. On nutrient agar containing 20% sucrose but no salts, some of the cells formed large spheroplasts. Both ampicillin treatment and in vivo environment may in part be responsible for the induction of the mutant strain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Domingue G. J., Schlegel J. U. Novel bacterial structures in human blood: cultural isolation. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):621–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.621-627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., Waluschka A., Kim Y. Abnormal morphology of bacteria in the sputa of patients treated with antibiotics. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):382–386. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.382-386.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Kaminski T., Grieco M., Singer J. Aberrant forms of bacteria and fungi found in blood or cerebrospinal fluid. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Jul;124(1):39–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M., Schaechter M. Control of cell division in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):199–221. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.199-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIMAKOV V. D., RAGAN G. Ia. O metodike polucheniia i tsitomorfologicheskikh osobennostiakh L-form briushnotifoznykh bakterii. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1957 May;28(5):38–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]