Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies that are broadly reactive with influenza A or influenza B viruses were produced as stable reagents for typing influenza viruses. Monoclonal antibodies to influenza A were specific for either matrix protein or nucleoprotein. The antibodies to influenza B were specific for nucleoprotein or hemagglutinin protein. In an enzyme immunoassay procedure, influenza A antibodies detected H1N1, H2N2, and H3N2 influenza A virus strains collected between 1934 and 1984. Each of the influenza B antibodies detected influenza B reference viruses collected between 1940 and 1984. Pools of either influenza A or influenza B monoclonal antibodies were used to detect influenza viruses reisolated from clinical specimens in tissue culture. At 48 h after inoculation, the influenza A monoclonal antibodies detected 64% of H1N1 and 94% of H3N2 influenza A specimens, and the influenza B monoclonal antibodies detected 79% of the influenza B specimens. The results of this study suggest that the monoclonal antibodies described should provide useful diagnostic reagents for workers in virology laboratories who wish to isolate and identify influenza virus but have been unable to obtain consistent supplies of animal sera specific for influenza A or B viruses.
Full text
PDF

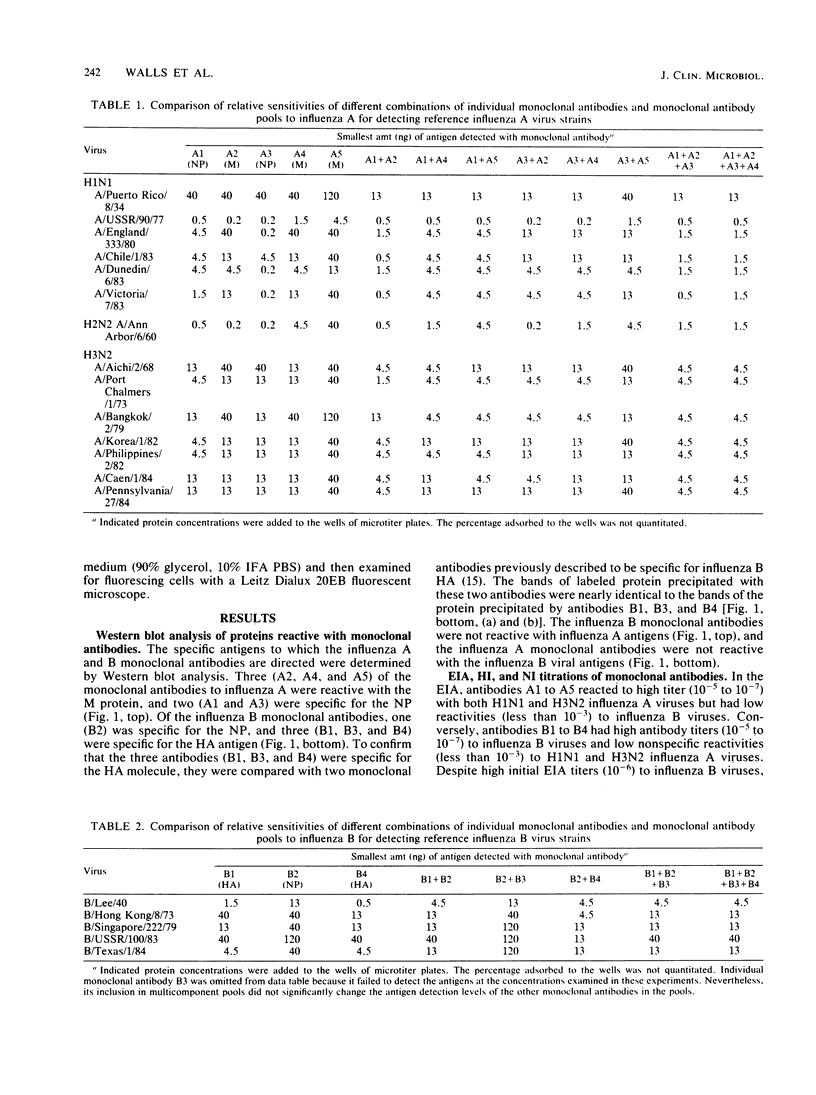
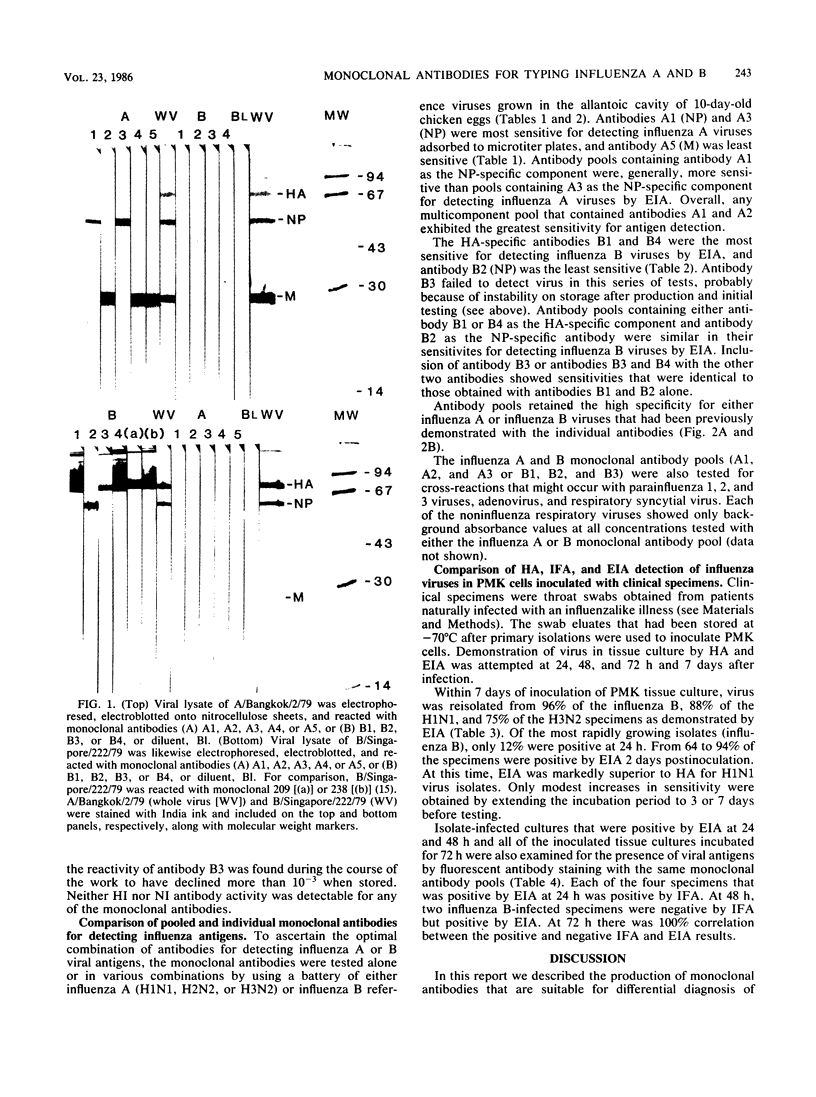
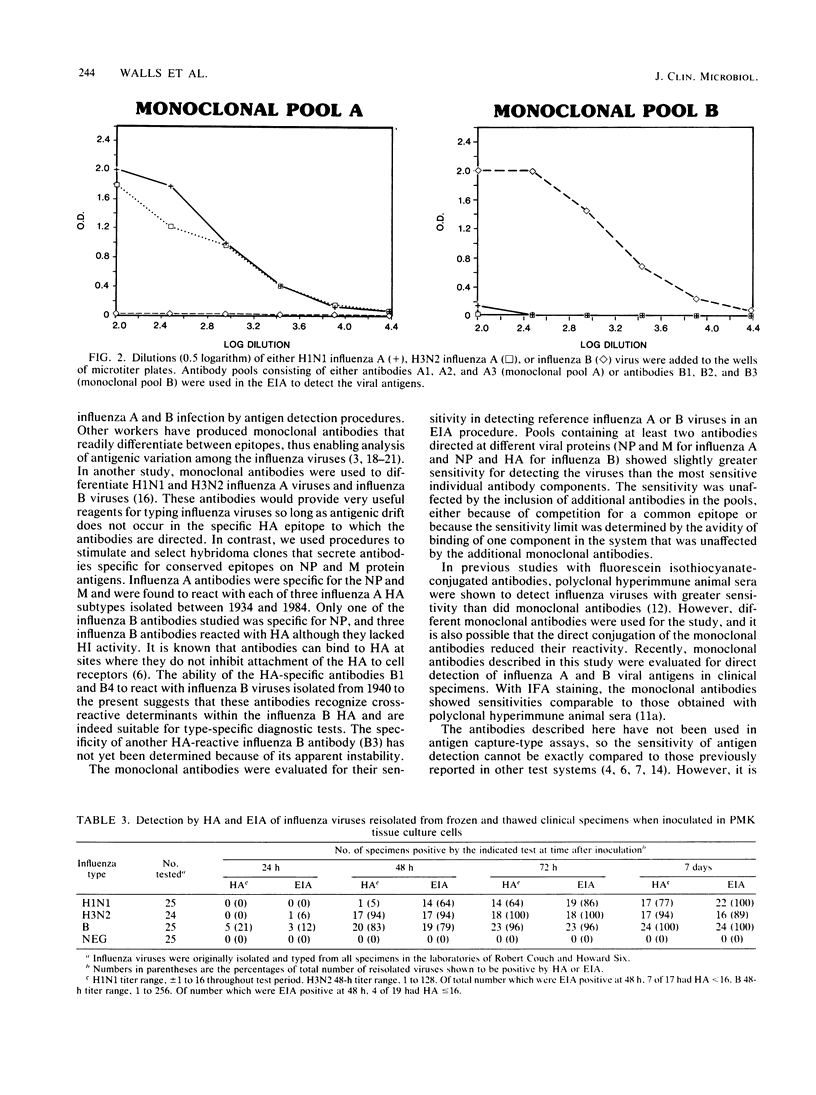
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aymard-Henry M., Coleman M. T., Dowdle W. R., Laver W. G., Schild G. C., Webster R. G. Influenzavirus neuraminidase and neuraminidase-inhibition test procedures. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(2):199–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao-Lan L., Webster R. G., Brown L. E., Nerome K. Heterogeneity of influenza B viruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(4):681–687. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. A., Yolken R. H., Rennard S. I., Dolin R., Murphy B. R., Straus S. E. New enzyme immunoassays for measurement of influenza A/Victoria/3/75 virus in nasal washes. Lancet. 1980 Apr 19;1(8173):851–853. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breschkin A. M., Ahern J., White D. O. Antigenic determinants of influenza virus hemagglutinin. VIII. Topography of the antigenic regions of influenza virus hemagglutinin determined by competitive radioimmunoassay with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):130–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P., Meurman O., Lövgren T., Hemmilä I., Soini E. Detection of viral antigens by time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;104:133–146. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68949-9_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendal A. P., Cox N. J., Galphin J. C., Maassab H. F. Comparative studies of wild-type and cold-mutant (temperature-sensitive) influenza viruses: independent segregation of temperature-sensitivity of virus replication from temperature-sensitivity of virion transcriptase activity during recombination of mutant A/Ann Arbor/6/60 with wild-type H3N2 strains. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):443–456. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillin J., Madeley C. R., Kendal A. P. Monoclonal antibodies for the rapid diagnosis of influenza A and B virus infections by immunofluorescence. Lancet. 1985 Oct 26;2(8461):911–914. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90849-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. J., Galland G. G., Reimer C. B., Kendal A. P. Evaluation of a solid-phase immunoassay with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated heterogeneous or monoclonal antibodies for identification of virus isolates, with influenza virus as a model. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):931–937. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.931-937.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. J., Kendal A. P., Webster R. G., Feorino P. M., Reimer C. B. Detection of monoclonal influenza antibodies synthesized in culture by hybridoma cells with a solid-phase indirect immunofluorometric assay. J Virol Methods. 1980;1(5):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(80)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkkinen H. K., Halonen P. E., Salmi A. A. Detection of influenza A virus by radioimmunoassay and enzyme-immunoassay from nasopharyngeal specimens. J Med Virol. 1981;7(3):213–220. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890070305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild G. C., Oxford J. S., de Jong J. C., Webster R. G. Evidence for host-cell selection of influenza virus antigenic variants. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):706–709. doi: 10.1038/303706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Ota M., Gallo D., Fox V. L. Monoclonal antibodies for rapid, strain-specific identification of influenza virus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):763–765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.763-765.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Berton M. T. Analysis of antigenic drift in the haemagglutinin molecule of influenza B virus with monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jun;54(Pt 2):243–251. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G. Determination of the number of nonoverlapping antigenic areas on Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus hemagglutinin with monoclonal antibodies and the selection of variants with potential epidemiological significance. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyke K. L., Hinshaw V. S., Bean W. J., Jr, Webster R. G. Antigenic variation of influenza A virus nucleoprotein detected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):24–30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.24-30.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyke K. L., Yewdell J. W., Reck L. J., Murphy B. R. Antigenic characterization of influenza A virus matrix protein with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.248-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]