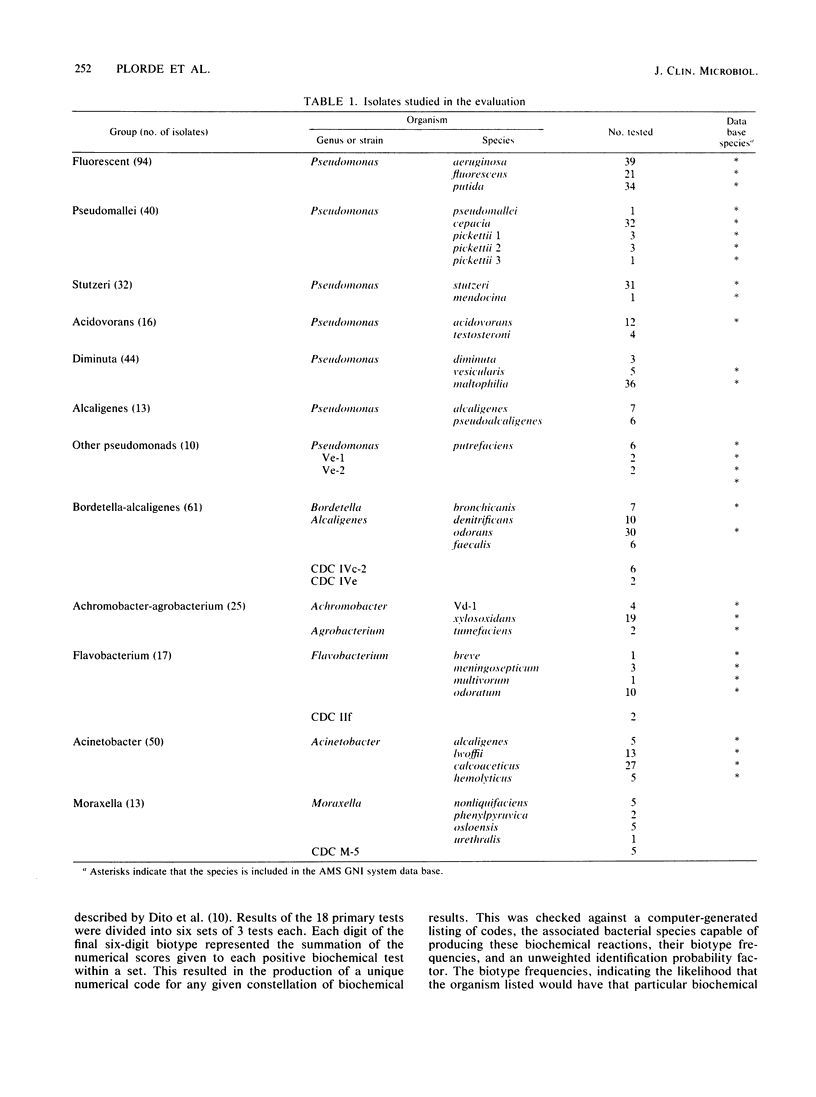
Abstract
During a 6-month study we critically evaluated the accuracy of the AutoMicrobic system Gram-Negative Identification Card (Vitek Systems, Inc., Hazelwood, Mo.) in identifying glucose-nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli by testing 419 selected isolates in parallel with a conventional reference method. Of 356 isolates included in the AutoMicrobic system profile, a total of 307 (86.2%) were correctly identified, 36 (10.1%) were not identified, and 13 (3.7%) were misidentified. Fifty-eight of 63 (92%) isolates not included in the profile were correctly reported as "unidentified organisms." Overall, if the first-choice identification was always accepted, only 18 (4.3%) isolates would have been incorrectly reported. When first-choice identifications appended with the special message "questionable biopattern" were rejected, and organisms were screened for characteristic odor and antimicrobial susceptibility before final acceptance of the AutoMicrobic system report, the number of misidentifications was reduced to 5 (1.2%). The average time to identification with the AutoMicrobic system Gram-Negative Identification Card was 15 h. This compares favorably with the 65 h required by the reference method.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum P. C., Stavitz J., Bentz M. S., von Kuster L. C. Four methods for identification of gram-negative nonfermenting rods: organisms more commonly encountered in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):271–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.271-278.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnishan J., Ayers L. W. Rapid identification of nonfermentative gram-negative rods by the Corning N/F system. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):239–243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.239-243.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Badal R. E. Identification of Enterobacteriaceae by the automicrobic system: Enterobacteriaceae biochemical cards versus Enterobacteriaceae-plus biochemical cards. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):575–581. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.575-581.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Gavan T. L., Badal R. E., Telenson M. J. Direct comparison of two mechanized systems for identification of gram-negative bacilli. Autobac ID system versus the auto microbic system (with EBC plus). Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Oct;78(4):462–470. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.4.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Gavan T. L., Badal R. E., Telenson M. J. Sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility of the automicrobic system (with the Enterobacteriaceae-plus biochemical card) for identifying clinical isolates of Gram- negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):582–588. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.582-588.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Gavan T. L., Smith P. B., Matsen J. M., Morello J. A., Sielaff B. H. Accuracy and precision of the autobac system for rapid identification of Gram-negative bacilli: a collaborative evaluation. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1111–1119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1111-1119.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester V., Cleary T. J. Evaluation of the Minitek system for identification of nonfermentative and nonenteric fermentative Gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.509-516.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costigan W. J., Hollick G. E. Use of the Autobac IDX system for rapid identification of Enterobacteriaceae and nonfermentative gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):301–302. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.301-302.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowda H. Evaluation of two rapid methods for identification of commonly encountered nonfermenting or oxidase-positive, Gram-negative rods. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):605–609. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.605-609.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Barnishan J. In vitro susceptibilities of nonfermentative gram-negative bacilli other than Pseudomonas aeruginosa to 32 antimicrobial agents. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Nov-Dec;2(6):841–853. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.6.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Infrequently encountered Pseudomonas species causing infection in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Aug;77(2):211–215. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Brinkley A. W. Comparison of the AutoMicrobic system and a conventional tube system for identification of nonfermentative and oxidase-positive gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):25–27. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.25-27.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Matsen J. M., Morello J. A., Smith P. B., Tilton R. C. Collaborative clinical evaluation of the Autobac IDX system for identification of gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):529–533. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.529-533.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koestenblatt E. K., Larone D. H., Pavletich K. J. Comparison of the Oxi/Ferm and N/F systems for identification of infrequently encountered nonfermentative and oxidase-positive fermentative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):384–390. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.384-390.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris M. J., Young V. M., Moody M. R. Evaluation of a multitest system for identification of saccharolytic pseudomonads. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jan;69(1):41–47. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. J., Jr, Wenzel R. P. Epidemiology of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6 (Suppl 3):S627–S642. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_3.s627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Gauthier A., Niles A. Evaluation of the Quantum II and Rapid E identification systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):509–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.509-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler H., George H., Barr J. Accuracy and reproducibility of the Oxi/Ferm system in identifying a select group of unusual gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):180–185. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.180-185.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhofer T. R. Comparison of the API 20E and Oxi/Ferm systems in identification of nonfermentative and oxidase-positive fermentative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):220–226. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.220-226.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhofer T. R., Rowen J. W., Cunningham G. F., Higbee J. W. Evaluation of the oxi/ferm tube system with selected Gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):559–566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.559-566.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto L. A., Blachman U. Nonfermentative bacilli: evaluation of three systems for identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):147–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.147-154.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S. L., Freundlich L. F., Washington W. Laboratory evaluation of a multitest system for identification of gram-negative organisms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Dec;70(6):914–917. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.6.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M., Lee A. M., McLynn D. M. Evaluation of the Oxi/Ferm tube system for identification of nonfermentative Gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):533–538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.533-538.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M., Maupin P. S., McGlynn D. M. Evaluation of the API 20E system for identification of nonfermentative Gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):539–545. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.539-545.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sielaff B. H., Matsen J. M., McKie J. E. Novel approach to bacterial identification that uses the autobac system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1103–1110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1103-1110.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Cundy K. R., Gilardi G. L., Wong W. Evaluation of the AutoMicrobic system for identification of glucose-nonfermenting gram-negative rods. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.302-307.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester M. K., Washington J. A., 2nd Evaluation of the Quantum II Microbiology System for bacterial identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1196–1197. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1196-1197.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warwood N. M., Blazevic D. J., Hofherr L. Comparison of the API 20E and Corning N/F systems for identification of nonfermentative gram-negative rods. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):175–179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.175-179.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfrey B. F., Lally R. T., Ederer M. N., Quall C. O. Evaluation of the AutoMicrobic system for identification and susceptibility testing of gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1053–1059. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1053-1059.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi E., Yamanaka K., Ohyama A. Evaluation of 36 Minitek tests and a new approach for identification of nonfermenters. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):572–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.572-587.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuravleff J. J., Yu V. L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas maltophilia with emphasis on bacteremia: case reports and a review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1236–1246. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



