Abstract
Exoantigens from 10-day-old cultures of 100 isolates of pathogenic and saprophytic dematiaceous fungi were analyzed by the exoantigen test. Antisera to Cladosporium bantianum ATCC 10958, Fonsecaea pedrosoi CDC AMO-B06, and Phialophora verrucosa CDC AMO-C12 were prepared in New Zealand rabbits immunized with soluble antigens from 1-month-old cultures. Absorbed and nonabsorbed antisera and exoantigens from the same organisms were used as reference reagents. Serologic reactions were analyzed in terms of the presence or absence of lines of identity or nonidentity. These reactions allowed presumptive differentiation of C. bantianum, F. pedrosoi, and Phialophora verrucosa from other dematiaceous fungi, including Cladosporium spp. (28 isolates), Exophiala spp. (18 isolates), Fonsecaea spp. (17 isolates). Lecythophora hoffmannii (4 isolates), Phaeoannellomyces werneckii (3 isolates), Phialophora spp. (17 isolates), Wangiella dermatitidis (9 isolates), and Rhinocladiella spp. (4 isolates).
Full text
PDF

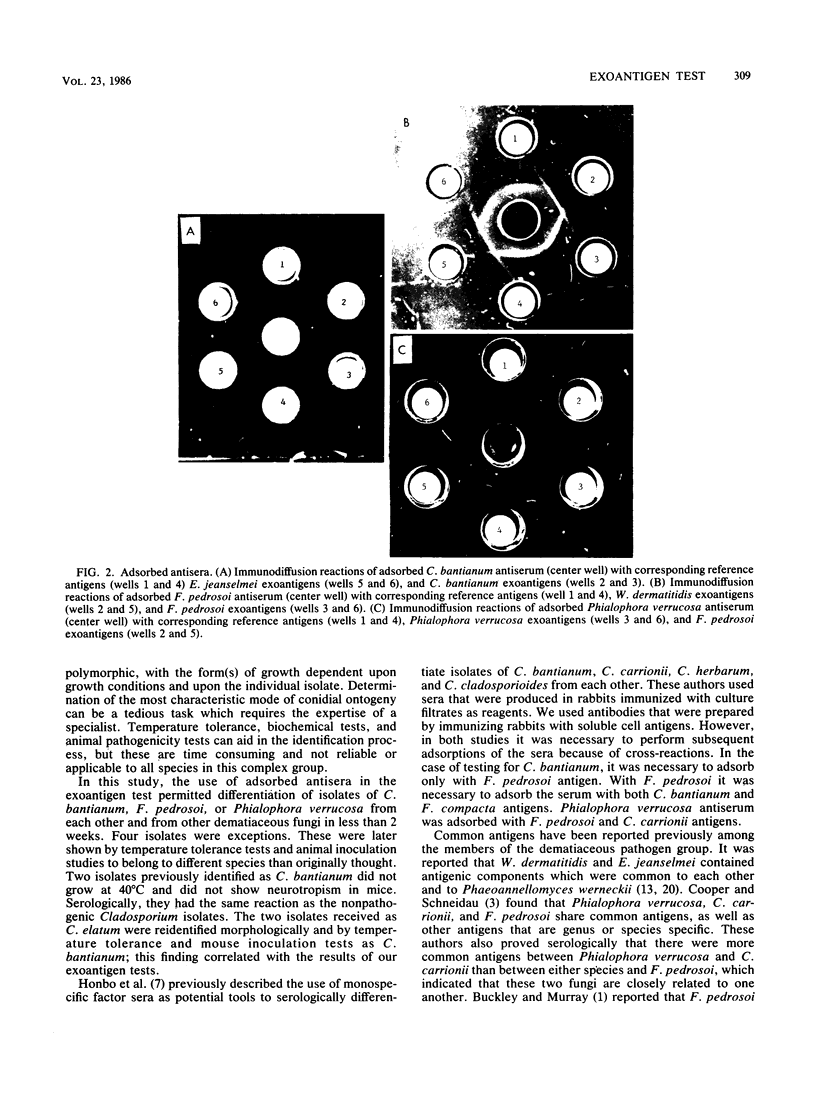

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckley H. R., Murray I. G. Precipitating antibodies in chromomycosis. Sabouraudia. 1966 Jun;5(1):78–80. doi: 10.1080/00362176785190121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper B. H., Schneidau J. D. A serological comparison of Phialophora verrucosa, Fonsecaea pedrosoi and Cladosporium carrionii using immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Sabouraudia. 1970 Nov;8(3):217–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinel-Ingroff A., Shadomy S., Kerkering T. M., Shadomy H. J. Exoantigen test for differentiation of Exophiala jeanselmei and Wangiella dermatitidis isolates from other dematiaceous fungi. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):23–27. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.23-27.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honbo S., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. The relationship of Cladosporium carrionii to Cladophialophora ajelloi. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(3):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honbo S., Standard P. G., Padhye A. A., Ajello L., Kaufman L. Antigenic relationships among Cladosporium species of medical importance. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(4):301–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Sun S. H., Rice E. H. Specificity of exoantigens for identifying cultures of Coccidioides immitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):346–348. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.346-348.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim-Granet O., de Bièvre C. Study of the conidial development and cleistothecium-like structure of some strains of Fonsecaea pedrosoi. Comparison with other close Dematiaeae. Mycopathologia. 1984 Feb 15;84(2-3):181–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00436530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. Improved version of the exoantigen test for identification of Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.42-45.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R. Chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: new concepts, diagnosis, and mycology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 Jan;8(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(83)70001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R. Recent taxonomic developments and changes in medical mycology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:109–135. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., Schell W. A., Carson J. Phaeoannellomyces and the Phaeococcomycetaceae, new dematiaceous blastomycete taxa. Sabouraudia. 1985 Jun;23(3):179–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morace G., Polonelli L. Exoantigen test for identification of Petriellidium boydii cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):237–240. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.237-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. S., Jr, Conant N. F. Practical evaluation of antigenic relationships of yeastlike dematiaceous fungi. Sabouraudia. 1967 Jun;5(4):283–294. doi: 10.1080/00362176785190541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Morace G. Exoantigen Studies of Sporothrix schenckii, Ceratocystis minor, and Graphium penicilliodes cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):362–365. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.362-365.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standard P. G., Kaufman L. Immunological procedure for the rapid and specific identification of Coccidioides immitis cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):149–153. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.149-153.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standard P. G., Kaufman L. Safety considerations in handling exoantigen extracts from pathogenic fungi. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):663–667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.663-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standard P. G., Kaufman L. Specific immunological test for the rapid identification of members of the genus Histoplasma. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):191–199. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.191-199.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]