Abstract
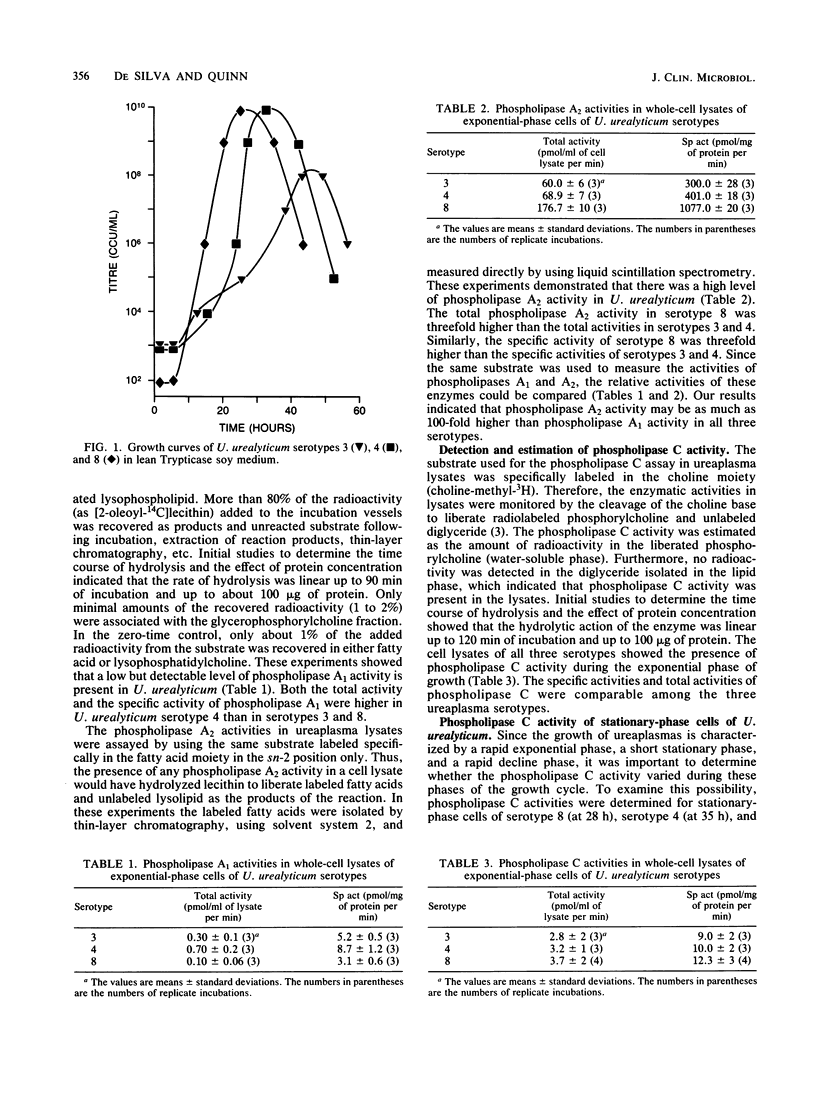
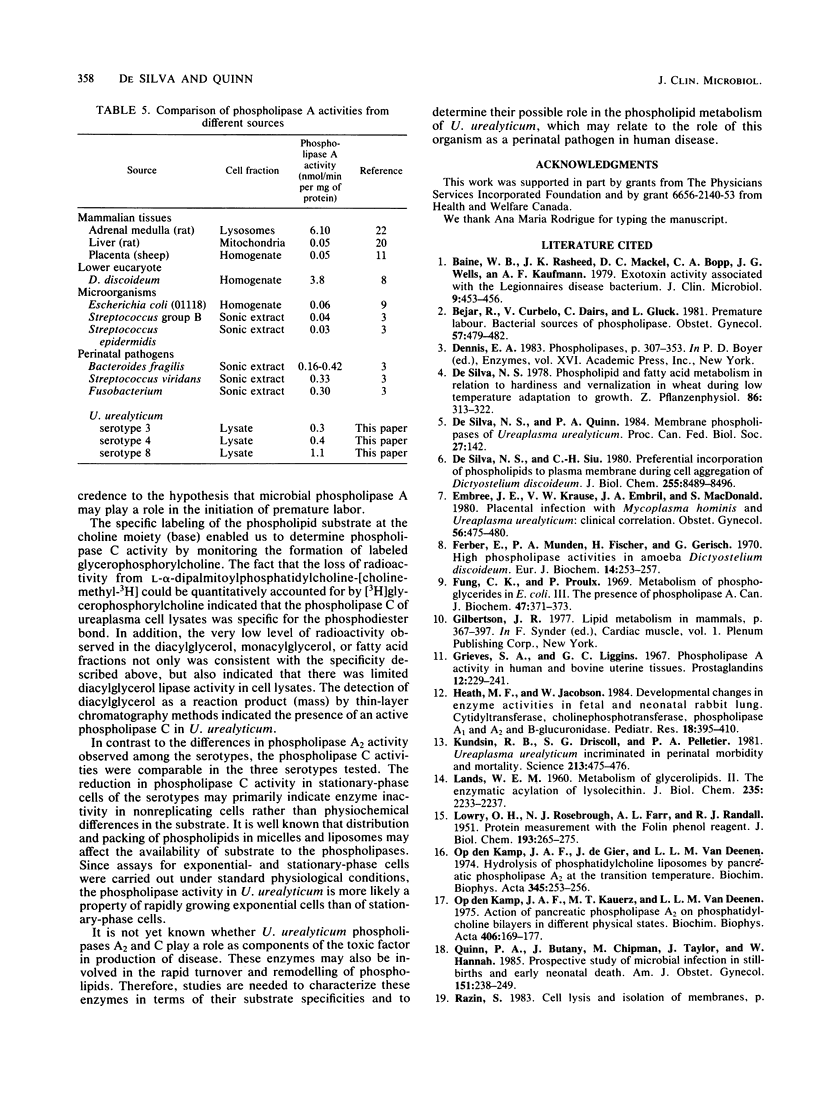
The results of recent studies support the concept that Ureaplasma urealyticum may be a major cause of perinatal infection in both term and preterm infants. It has been postulated that phospholipase degradation of placental phospholipids by microorganisms triggers the onset of premature labor. Since the presence of ureaplasmas in placentas is associated with pregnancy loss, prematurity, and neonatal morbidity, we assayed U. urealyticum for the presence of phospholipase A1, A2, and C activities. Phospholipase A1 activity was low in lysates of exponential-phase cells of U. urealyticum. Phospholipase A2 activity was present and was 100-fold higher than the activity of phospholipase A1 in serotypes 3,4, and 8. The total activity and specific activity of phospholipase A2 in serotype 8 were nearly threefold higher than the activities in serotypes 3 and 4. Cell lysates of all three serotypes showed the presence of phospholipase C activity during the exponential phase of growth, and no significant difference in activity was observed among the three serotypes. In stationary-phase cells the phospholipase C activity was 10-fold lower than the activity in exponential-phase cells. Our results demonstrate that phospholipase activities are present in U. urealyticum cells and that the specific activities of phospholipase A2 differed among the three serotypes tested, while the activities of phospholipases A1 and C were similar.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baine W. B., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Bopp C. A., Wells J. G., Kaufmann A. F. Exotoxin activity associated with the Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):453–456. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.453-456.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bejar R., Curbelo V., Davis C., Gluck L. Premature labor. II. Bacterial sources of phospholipase. Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Apr;57(4):479–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Silva N. S., Siu C. H. Preferential incorporation of phospholipids into plasma membranes during cell aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8489–8496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embree J. E., Krause V. W., Embil J. A., MacDonald S. Placental infection with Mycoplasma homonis and Ureaplasma urealyticum: clinical correlation. Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Oct;56(4):475–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber E., Munder P. G., Fischer H., Gerisch G. High phospholipase activities in amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):253–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grieves S. A., Liggins G. C. Phospholipase A activity in human and ovine uterine tissues. Prostaglandins. 1976 Aug;12(2):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath M. F., Jacobson W. Developmental changes in enzyme activities in fetal and neonatal rabbit lung. Cytidylyltransferase, cholinephosphotransferase, phospholipases A1 and A2, beta-galactosidase, and beta-glucuronidase. Pediatr Res. 1984 May;18(5):395–401. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198405000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundsin R. B., Driscoll S. G., Pelletier P. A. Ureaplasma urealyticum incriminated in perinatal morbidity and mortality. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.7244646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDS W. E. Metabolism of glycerolipids. 2. The enzymatic acylation of lysolecithin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2233–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A., Kauerz M. T., van Deenen L. L. Action of pancreatic phospholipase A2 on phosphatidylcholine bilayers in different physical states. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A., de Gier J., van Deenen L. L. Hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine liposomes by pancreatic phospholipase A2 at the transition temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;345(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90263-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. A., Butany J., Chipman M., Taylor J., Hannah W. A prospective study of microbial infection in stillbirths and early neonatal death. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Jan 15;151(2):238–249. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI C. R., SARTORELLI L., TATO L., BARETTA L., SILIPRANDI N. PHOSPHOLIPASE A ACTIVITY OF RAT-LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 1;98:207–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Hasin M., Razin S. Differences in susceptibility to phospholipase C of free and membrane-bound phospholipids of Mycoplasma hominis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 16;323(4):520–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. Lysosomal phospholipases A1 and A2 of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):867–874. doi: 10.1042/bj1080867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl W. L. Phospholipase C purification and specificity with respect to individual phospholipids and brain microsomal membrane phospholipids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M., van Deenen L. L. Hydrolysis of phospholipids and glycerides by rat-liver preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 6;137(3):498–517. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Quinn P. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of specific antibodies to Ureaplasma urealyticum serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):421–426. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.421-426.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Golde L. M., McElhaney R. N., van Deenen L. L. A membrane-bound lysophospholipase from Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;231(1):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 30;604(2):191–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90574-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



