Abstract
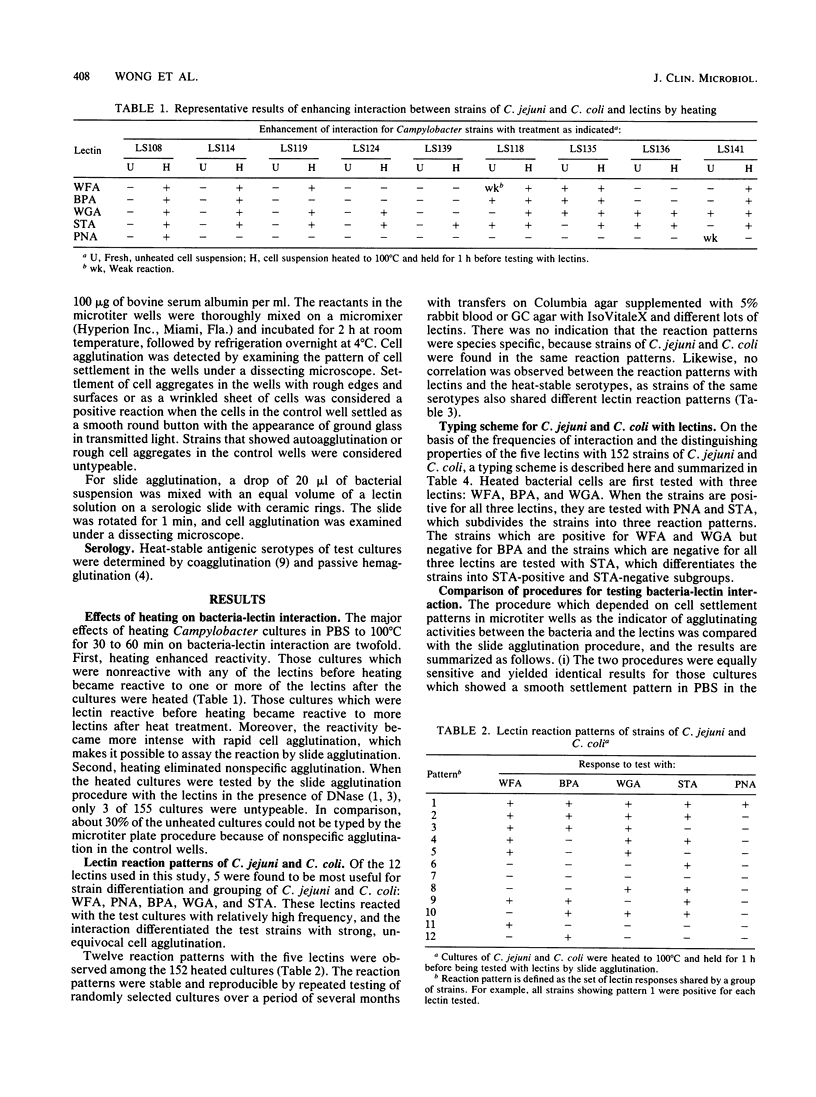
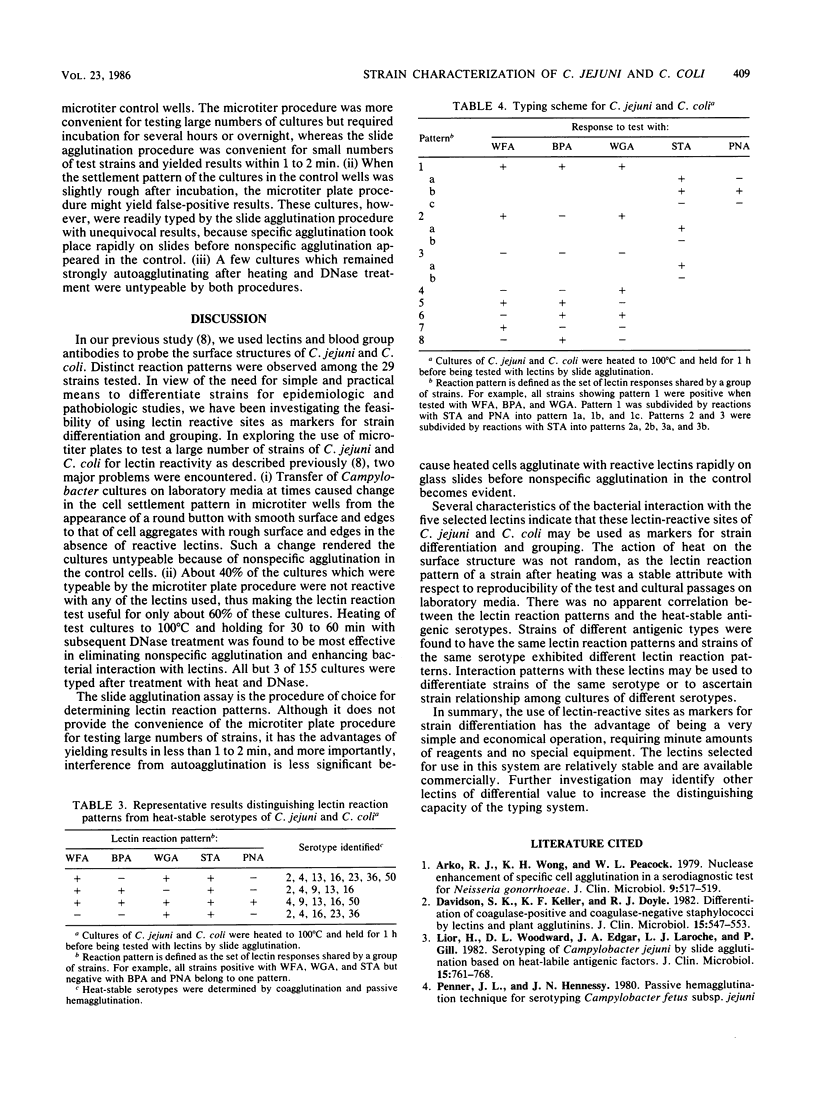
Strains of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli were characterized and grouped by their distinct reaction patterns with lectins. Heating of the Campylobacter cultures to 100 degrees C and holding for 30 to 60 min greatly enhanced their reactivity with lectins and permitted the grouping of all but 3 of 155 cultures tested in this study without interference of autoagglutination and other nonspecific activities. The lectin reaction patterns of the heated cultures were stable and reproducible. They were strain specific and independent of the heat-stable antigenic types. The lectin-reactive sites of C. jejuni and C. coli may be useful as additional markers for strain characterization. Based on these observations, a simple slide agglutination procedure is described for differentiating strains of C. jejuni and C. coli by their interaction with a selected group of commercially available lectins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arko R. J., Wong K. H., Peacock W. L. Nuclease enhancement of specific cell agglutination in a serodiagnostic test for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):517–519. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.517-519.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson S. K., Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Differentiation of coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative staphylococci by lectins and plant agglutinins. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):547–553. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.547-553.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N., Congi R. V. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli on the basis of thermostable antigens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;2(4):378–383. doi: 10.1007/BF02019474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistole T. G. Interaction of bacteria and fungi with lectins and lectin-like substances. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:85–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer R. L., Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Lectins in diagnostic microbiology: use of wheat germ agglutinin for laboratory identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):669–672. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.669-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Skelton S. K., Feeley J. C. Interaction of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli with lectins and blood group antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):134–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.134-135.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Skelton S. K., Patton C. M., Feeley J. C., Morris G. Typing of heat-stable and heat-labile antigens of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli by coagglutination. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):702–707. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.702-707.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


